MI 3290 Earth Analyser Tests and Measurements
77
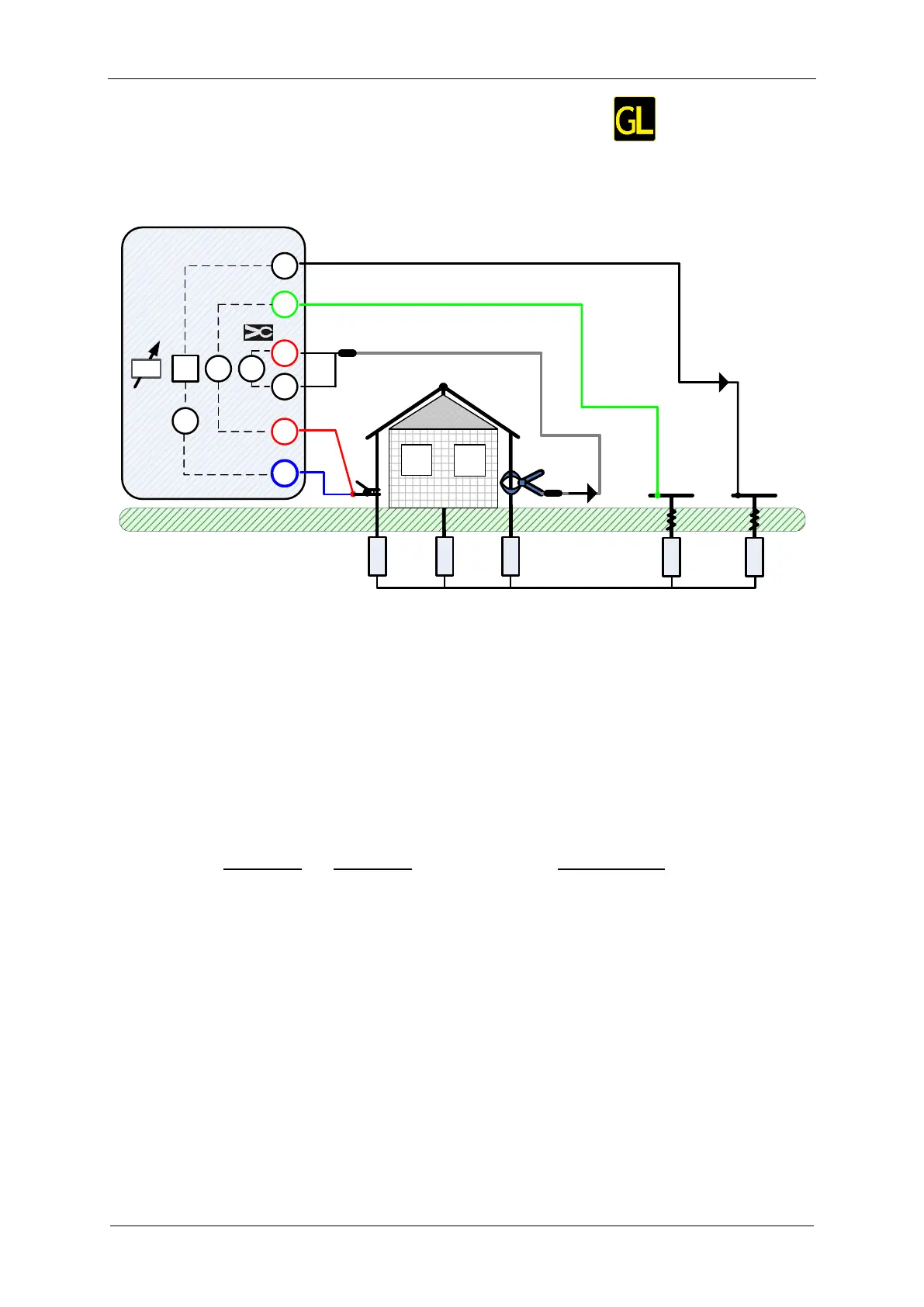
11.2.4 Selective (Iron Clamp) Measurement
This measurement is applicable for measuring selective earth resistances of individual
earthing points in an earthing system. The earthing rods do not need to be disconnected
during measurement. 4-pole wiring is used for this measurement.
E a r t h
S
ES
E
MI 3290 Earth Analyser
Rp
G
V
A
S - probe
H - auxiliary
current probe
Rc
A
C
C
Ze2
Ze1
Ze3
fset
H
Ie
Ic
Figure 11.20: Selective (Iron Clamp) example
During the measurement a sinusoidal current I
e
is injected into the earth through an auxiliary
current probe (H). The impedance of the auxiliary probe (H) should be as low as possible in
order to inject a high test current. The impedance R
c
can be decreased by using more probes
in parallel. A higher injected current improves the immunity against spurious earth currents.
The voltage drop is measured by auxiliary potential probe (S) and (ES) terminal. The
selective current I
c
is measured through the earthing electrode (Z
e1
) selected by the user.
The selected earth impedance Z
sel
is determined from the voltage/current (external current
clamp – I
c
) ratio.
According to the example selective (individual) earth impedance is measured:
where:
Z
sel
.................................... Selected Earth impedance
Z
e1-3
................................... Earth impedance
R
c
...................................... Impedance of auxiliary current probe (H)
R
p
..................................... Impedance of auxiliary potential probe (S)
I
e
........................................ Injected test current
I
c
........................................ Measured current with Iron clamp
U
S-ES
.................................. Test voltage between S and ES terminal
N ....................................... Turn ratio of current clamps (depending on the model)
f
set
..................................... Test frequency
Refer to Appendix C – Functionality and placing of test probes for more information
how to place the earth auxiliary current (H) and potential probe (S).

 Loading...
Loading...











