9.2 Evaluation
138
780/781 pH/Ion Meter, Manual
9.2 Evaluation
9.2.1 pH calibration
pH calibration is used to assign the potentials measured at the pH
electrode to the corresponding pH values. This relationship is known
theoretically and is described by the Nernst equation. For pH meas-
urement it can be simplified to:
where
T: absolute temperature in K
R: ideal gas constant
F: Faraday constant
UpH=0 is the ordinate intercept at pH = 0. Its value depends on the
construction of the electrode. The theoretical Nernst constant UN is
temperature-dependent and is e.g. 59.16 mV at 25 °C.
This means that theoretically, i.e. with a standard pH glass electrode
(inner electrolyte c(KCl) = 3 mol/L: pH 7.0; Ag/AgCl reference system),
at pH 7.0 a potential of 0 mV should be measured. This represents the
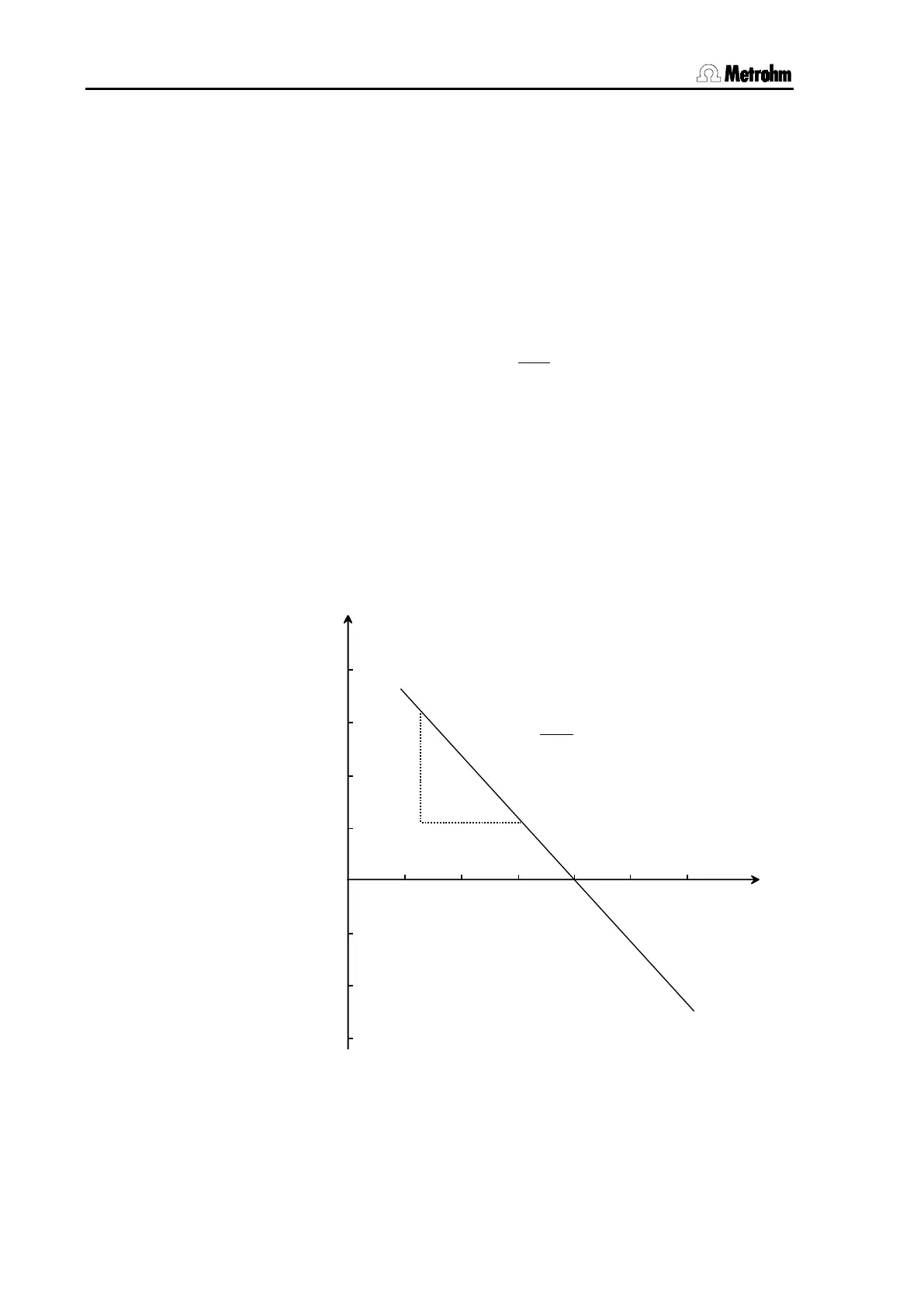
so-called zero point of the electrode. The graphical plot of further U/pH
pairs of values within the normal pH range then provides a linear rela-
tionship according to the above equation whose slope is -UN.
U/mV
4 7
9
pH
Slope = = - U
N
0
-100
100
200
∆
U
∆
pH
∆U
∆
pH
= - 59.16 mV (25°C)
pH(0) = 7.0
Fig. 15:
Theoretical U/pH relationship
In fact this U/pH curve is usually different. The offset potential of the
electrode (Uoff = U at pH 7.0) may not be zero as a result of the
asymmetry potential at the glass membrane, a contaminated inner elec-

 Loading...
Loading...