33
3 Specific Usage Applications
No. 99MAF029B
4
Measure the height of a3.
»
The difference with a2 is displayed in the bottom row.
3.1.2 Continuously Measuring the Distance from One Specific
Point to Multiple Other Points
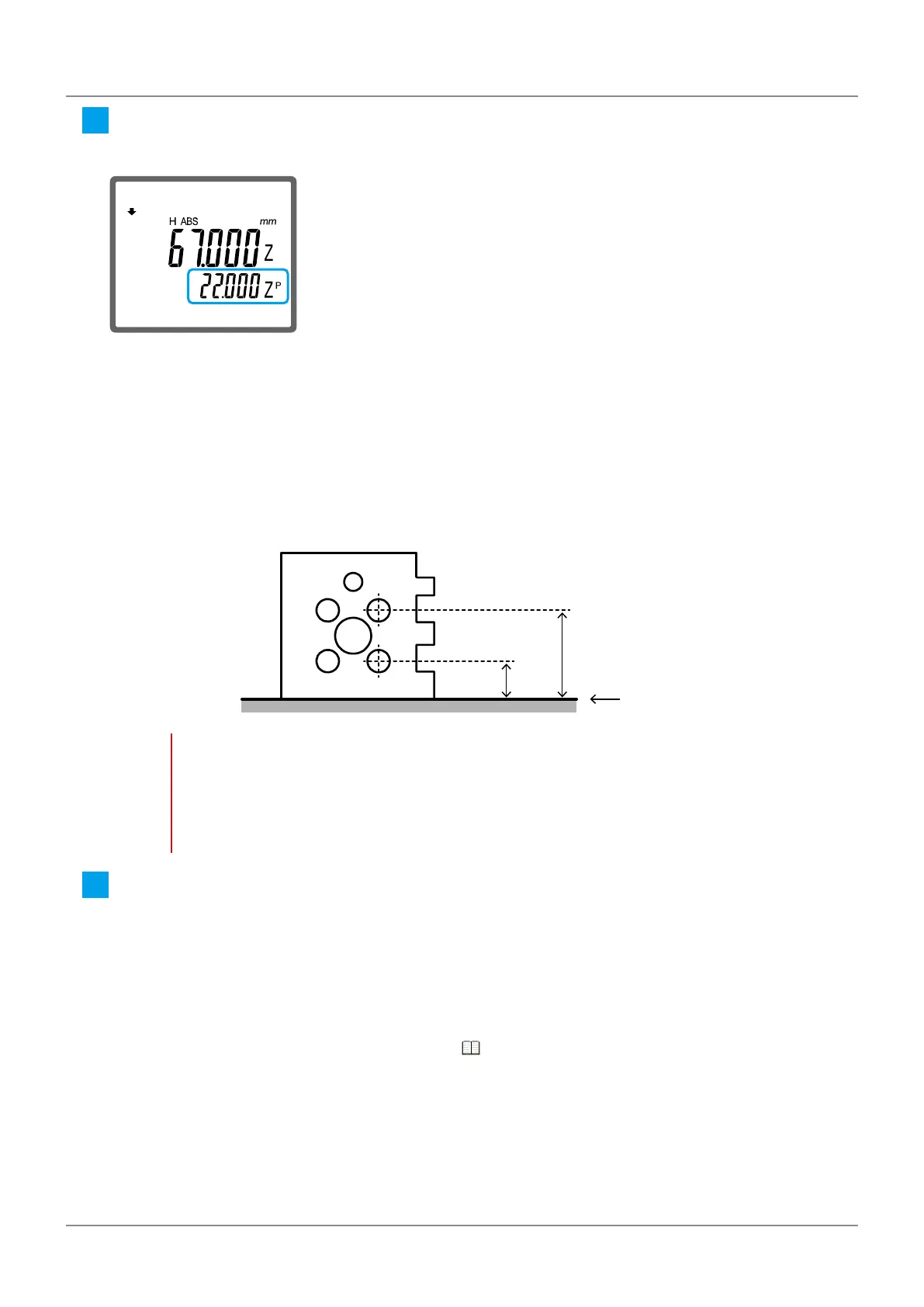
Set an arbitrary point as the origin, and proceed to measure the distance continuously from that point.
As an example, the procedure for continuously obtaining the distance between a1 (center height of
circle s1) and a2 (center height of circle s2) shown below with the surface plate set as the origin is
explained.
a2
a1
10 mm
30 mm
s2
s1
ABS origin
NOTE
The following values can be set as the origin point.
• Height measurement
• Median value of an inner or outer diameter measurement
• Median, minimum, or maximum value of a plane scanning measurement
1
Set the origin point.
1
Slowly bring the probe into contact with the surface plate until a beep sound is made.
Maintain contact with the probe.
Tips
• Perform the same operation even if a point other than the height of the surface plate is set as the
origin point. (Bring the probe into contact with the point to set as the origin.)
• To set an inner diameter, outer diameter, or plane scanning measurement as the origin point, make
the appropriate measurement. For details,
"2.3 Measuring the Inner Diameter" (page 21),
"2.4 Measuring the Outer Diameter" (page 25), "2.5 Measuring the Plane Displacement (Plane
Scanning Measurement)" (page 29)

 Loading...
Loading...











