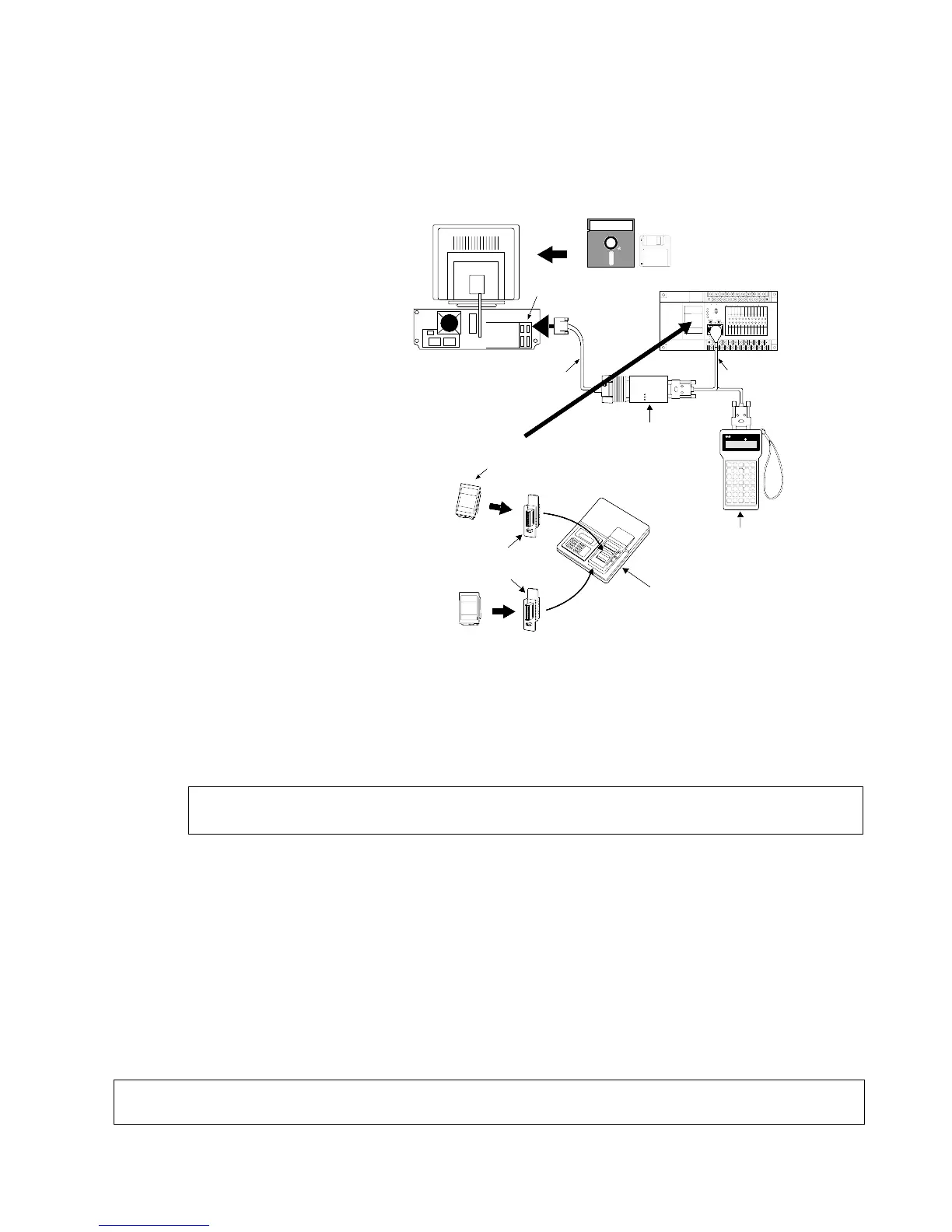
■ Writing a program to the memory (EPROM) via the master memory (EEPROM) with a
commercially available ROM programmer
[Program in FP1’s internal RAM → Master memory (EEPROM) → commercially available ROM programmer’s
internal memory → memory (EPROM)]
Procedure:
1 Attach master memory (EEPROM)
to FP1 Control Unit. Transfer to
master memory (EEPROM) using
FP Programmer in FP1’s internal
RAM.
Remove master memory
(EEPROM) from FP1, and attach
to commercially available ROM
programmer.
2 Transfer contents of that master
memory (EEPROM) to the internal
memory of the ROM programmer.
Replace the ROM programmer’s
master memory (EEPROM) with
the memory (EPROM).
3 Write the contents of the ROM
programmer’s internal memory to
the memory (EPROM).
Necessary tools
• Computer: Commercially available
personal computer (IBM PC-AT or
100% compatible machine)
Main memory: 550 KB or more free
EMS: 800 KB or more free
Hard disk space: 2 MB or more required
Operating System: MS-DOS Ver. 3.30 or later
Video mode (Display mode): EGA or VGA
• NPST-GR Software Ver. 3: AFP266538
Note:
• RS232C cable (3 m / 9.843 ft.): AFB85833/AFB85853
• RS422/232C Adapter: AFP8550
• FP1 Peripheral Cable:
0.5 m / 1.640 ft.: AFP15205
3 m / 9.843 ft.: AFP1523
• FP Programmer II: AFP1114
• Socket adapter for FP ROM Writer: AFP1810
• Master Memory (EEPROM): AFP1202 (for C24 and C40 series)
AFP1203 (for C56 and C72 series)
• Memory (EPROM): AFP1201
• Commercially available ROM programmer: We recommend Aval Data Corporation’s PECKER 11.
Note:
• When using NPST-GR Software Ver. 2, refer to page 241, “1. Differences Between NPST-GR Ver. 2.4
and 3.1.”
• The .EXE files are compressed in the system disks. When installing the NPST-GR, you will
have to expand them.
18
1-4. Programming Tools
 Loading...
Loading...