144
Remote I/O Communications Performance Section 5-3
■ Reference Example
The following table shows the calculation results for the maximum I/O
response time for a Word Slave Unit with the maximum number of nodes and
a CPU Unit cycle time of 1 ms.
(With message communications)
Bit Slave Units
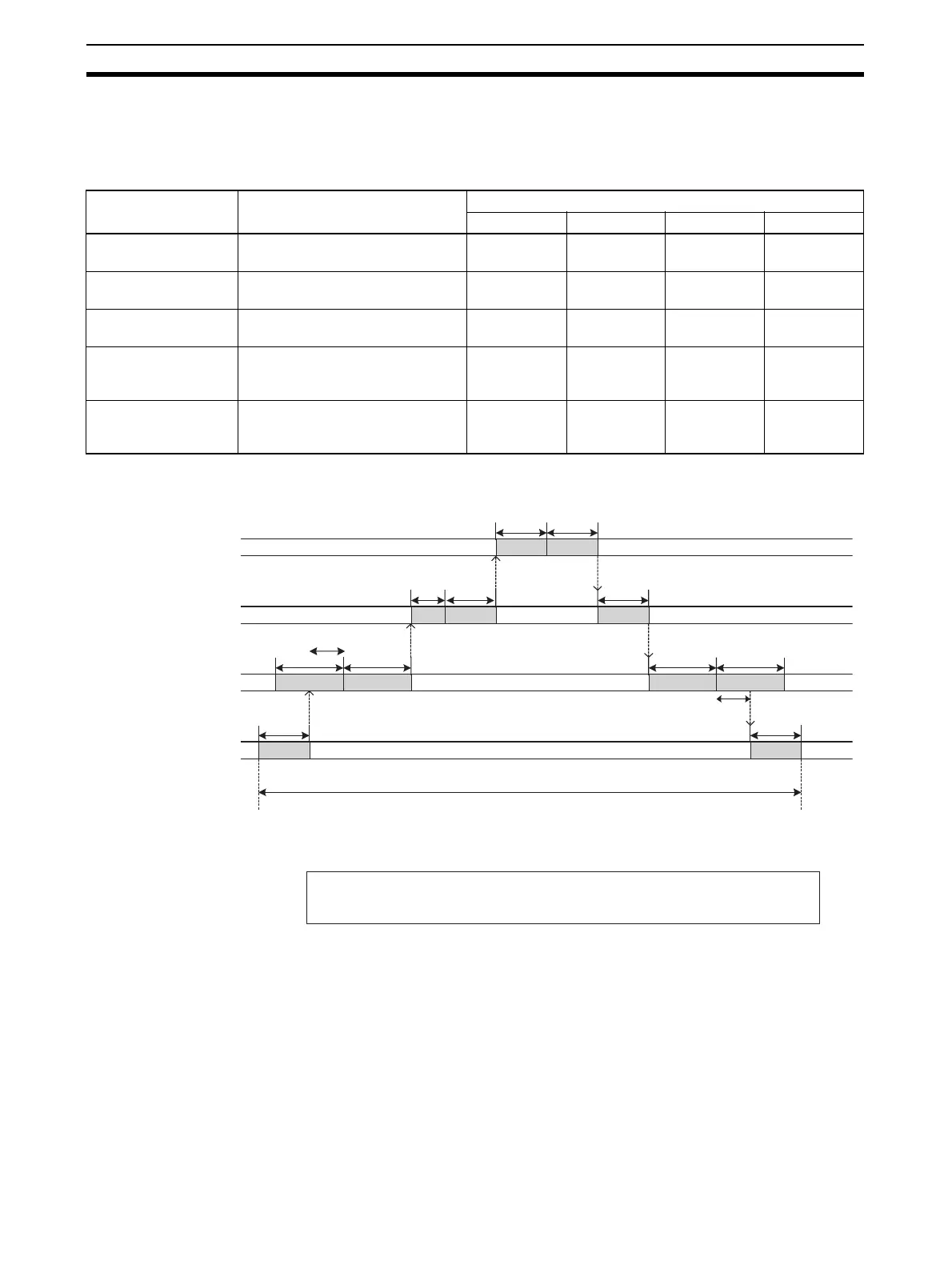
■ Formula for the Maximum I/O Response Time for a Bit Slave Unit
TIN: Input Slave Unit input delay time
TNetCyc: Communications cycle time
TNetBitIn: Time allotted for bit input frames in communications cycle time
TNetCycInt: Interrupt processing time
TCrmInMax: Maximum input processing time at Master Unit
Tcyc: CPU Unit cycle time
TCrmOutMax:Maximum output processing time at Master Unit
TNetOut: Time allotted for output frames in communications cycle time
TOUT: Output Slave Unit output delay time
Communications
mode
Number of nodes connected Word Slave Unit max. I/O response time (ms)
4.0 Mbit/s 3.0 Mbit/s 1.5 Mbit/s 93.75 kbit/s
Communications
mode 0
16 word nodes (8 input, 8 output) 7.7 7.8 9.2 53.8
Communications
mode 1
32 word nodes (16 input, 16 out-
put)
8.0 8.5 10.9 76.1
Communications
mode 2
64 word nodes (32 input, 32 out-
put)
8.8 9.6 14.8 121.3
Communications
mode 3
32 word nodes (16 input, 16 out-
put) 128 bit nodes (64 bit input, 64
bit output)
10.3 11.4 18.6 161.7
Communications
mode 8
128 word nodes (64 input, 64 out-
put) 256 bit nodes (128 bit input,
128 bit output)
16.7 19.3 35.8 374.9
Tcyc Tcyc
CPU Unit processing
Master Unit processing
Communications cycle
Maximum I/O response time
Slave Unit processing
TIN
TNetCyc
TNetCyc
TNetBitIn
TNetCycInt
TCrmInMax
TCrmOutMax
TNetCyc
TNetCyc
TNetOut
TOUT
TIN
+
TNetCyc
×
2
+
TNetBitIn
+
TNetCycInt
+
TCrmInMax
+
Tcyc
×
2
+
TCrmOutMax
+
TNetOut
+
TOUT
 Loading...
Loading...











