163
Sending Explicit Messages Section 6-4
Command Format
Example
■ In this example, the code to clear an error is written to the CPU Unit.
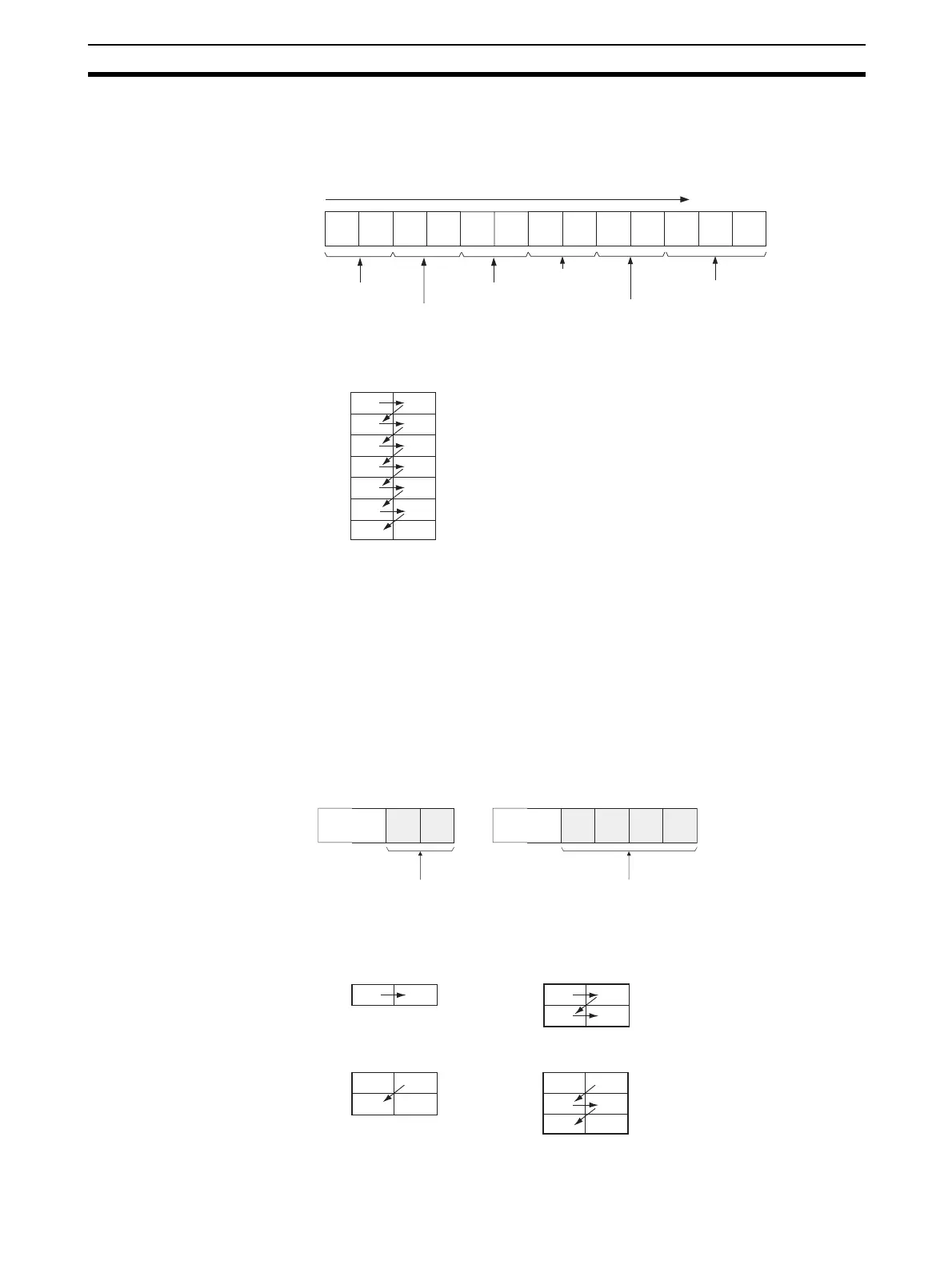
Setting Data from CMND(490) Operand S Onwards
Similarly, from the CMND(490) operand D (first response word) onwards,
response data is stored from the upper word to the lower word in the I/O
memory in the order of the response format.
Note (1) When the data in the Service Data is in word (2-byte) or double word (4-
byte) units, such as for word data or error clearing codes, it is specified
from the lower byte to the higher byte as the command format.
For example, to specify word data 1234 hex, specify 34 hex and 12 hex
in that order. To specify double word data 12345678 hex, specify 78 hex,
56 hex, 34 hex, and 12 hex in that order. The command formats are as
follows:
Command Formats
The data from CMND(490) operand S onwards will thus be as follows:
00
00 00001028 02 2f FE FF65
Class ID
Instance ID
Destination
node address
Service Code
Command code
Service Data
The command data is written from the upper word to the lower
word in the I/O memory from operand S onwards, in this order.
1000
S + 0
S + 1
S + 2
S + 3
S + 4
S + 5
28
10
00
00
65
FF
01
00
2F
00
FE
00
FINS command code
Node address
Service Code
Class ID
Instance ID
Service Data
Service Data
15 08 07 00
Bit
00
10
S + 6
34 12
Service Data
Example for 1234 Hex
78 56 34 12
Service Data
Example for 12345678 Hex
S + nn34 12
08 07 00
Bit 15
S + nn
12
34
08 07 00
Bit 15
Example for 1234 Hex
From high byte
Example for 1234 Hex
From high byte
From low byte
S + n
56
12
78
34
Bit 15 08 07 00
From low byte
S + nn78
34
56
12
08 07 00
Bit 15
 Loading...
Loading...











