SEBU8603-01 67
Maintenance Section
Refill Capacities
i04156282
Fluid Recommendations
General Lubricant Information
Because of go
vernment regulations regarding the
certification of exhaust emissions from the engine,
the lubricant recommendations must be f ollowed.
•
API_______ ______________ American Petroleum Institute
•
SAE_______
____________________________________
Society Of
Automotive Engineers Inc.
•
ACEA_____
_____________________________
Association d es
Constructers European Automobiles.
•
ECF-3___
____________________
Engine Crankcase Fluid
Licensing
The Engine Oil Licensing and Certification System
by the American Petroleum Institute (API) and
the Asso
ciation des Constructers European
Automobilesand (ACRA) is recognized by Perkins.
For detailed information about this system, see the
latest e
dition of the “API publication No. 1509”.
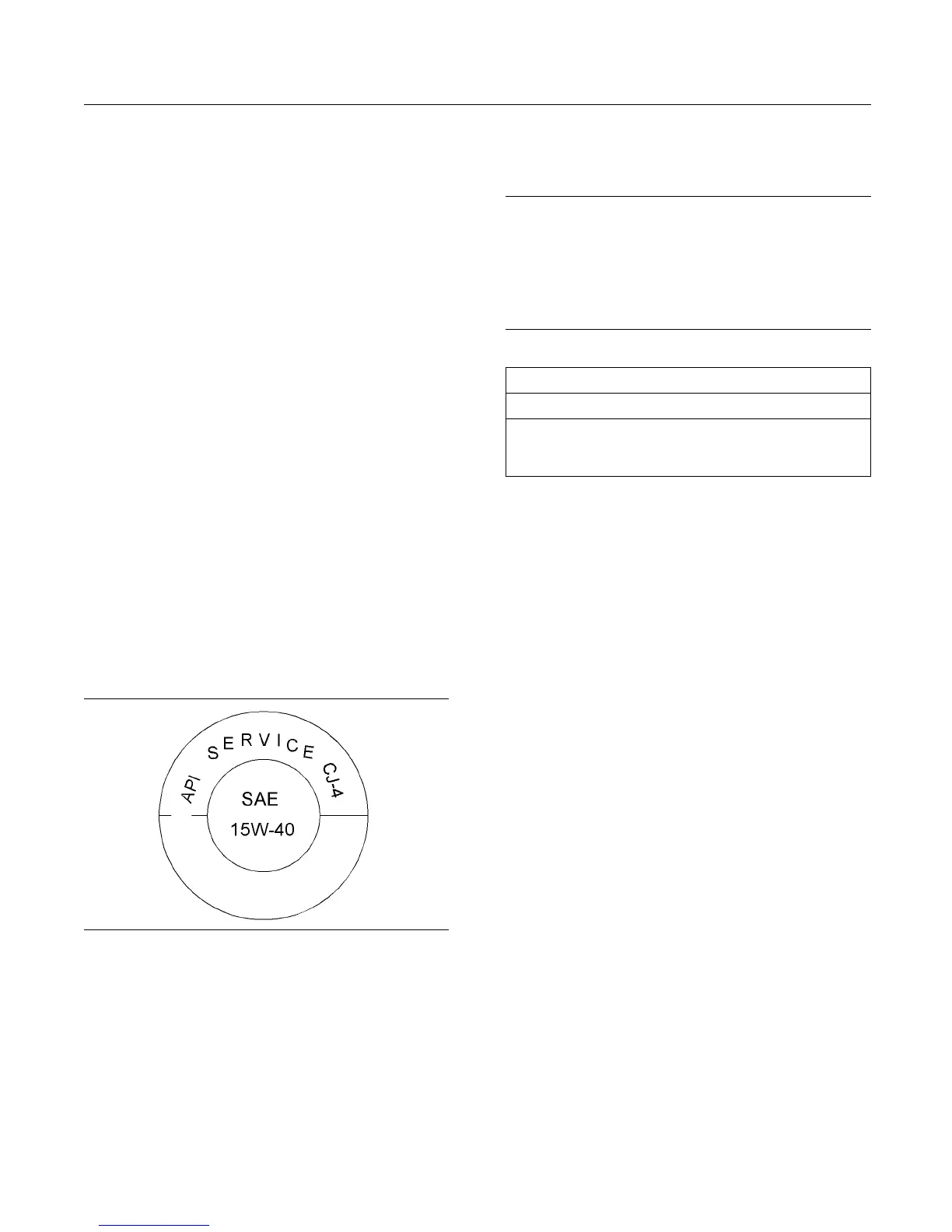
Engine oils that bear the API symbol are authorized
by API.
g01987816
Illustration 36
Typical A PI s ym bol
Terminology
Certain abbreviations follow the nomenclature of
“SAE J754”. Some classifications follow “SAE J183”
abbreviations, and some classifications follow the
“EMA Recommended Guideline on Diesel Engine
Oil”. In addition to Perkins definitions, there are other
definitions that will be of assistance in purchasing
lubricants. Recommended oil viscosities can be found
in this publication, “Fluid Recommendations/Engine
Oil” topic (Maintenance Section).
Engine Oil
Commercial Oils
NOTICE
Perkins requ
ire the use of the following specifica-
tion of engine oil. Failure to use the appropriate
specification o f engine oil will reduce the life of
your engine
. Failure to use the appropriate spec-
ification of engine oil w ill also reduce the life of
your aftertreatment system.
Table 16
Classifications for the 1200 Series Industrial Engine
Oil Specification
API CJ-4
ACEA E9
ECF-3
API CJ-4 and ACEA E9 oil categories have the
following chemical limits:
•
1 percent maximum sulfated ash
•
0.12 percent maximum phosphorous
•
0. 4 percent maximum sulfur
The chemical limits were developed in order
to maintain the expected life of the engine
aftertreatment system. The performance of the
engine aftertreatment system can be adversely
affected if oil that is not specified in table 16 is used.
The life of your Aftertreatment system is defined by
the accumulation of ash on the surface of the filter.
Ash is the inert part of the particulate matter. The
system is designed in order to collect this particulate
matter. There is a very small percentage of particulate
matter that is left behind as the soot is burnt. This
matter will eventually block the filter, causing loss
of performance and increased fuel consumption.
Most of the ash comes from the engine oil which is
gradually consumed during normal operation. This
ash is passes through the exhaust. To meet the
designed life of the product, the use of the appropriate
engine oil is essential. The oil specification that is
listed in table 16 has low ash content.
Maintenance intervals for engines that use
biodiesel – The oil change interval can be adversely
affected by the use of biodiesel. Use oil analysis in
order to monitor the condition of the engine oil. Use
oil analysis also in order to determine the oil change
interval that is optimum.
Note: These engine oils are not approved by
Perkins and these engine oils mus t not be
used:CC, CD, CD-2, CF-4, CG-4, CH-4, and CI-4.
 Loading...
Loading...