Chapter 19 - Configuring Traffic Prioritization
Reorder the queues and filters by clicking on the arrows in the Move field. Some
restrictions apply with queues. You are not allowed to reorder queues in a way that
violates the priority implicit in their name.
The Transmit Queue Length Selector allows you to make a tradeoff between latency
and performance.
Remove prioritization by selecting the Delete and Apply button.
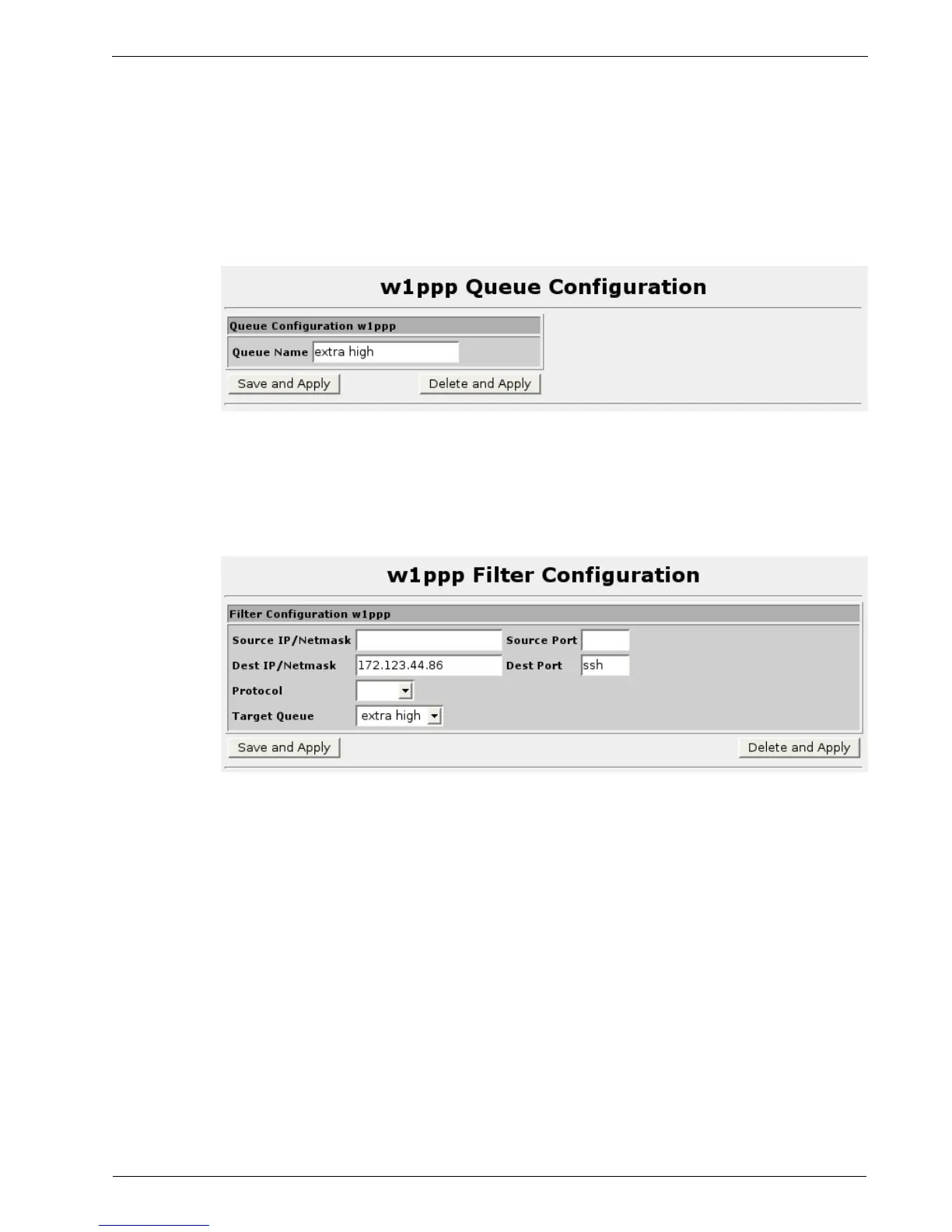
Prioritization Queues
Figure 160: Prioritization Queue Configuration
This menu allows you to edit the name of of a priority queue and to delete the queue.
If you delete a queue referenced by filters, the filters will be adjusted to use the next
lowest queue.
Prioritization Filters
Figure 161: Prioritization Filter Configuration
This menu allows you to edit and delete traffic filters.
The Source IP/Netmask and Dest IP/Netmask fields specify the IP addresses and
masks used to match an outgoing packet. Use 0.0.0.0/0 to generate an “all packets”
match.
The Source Port and Dest Port fields specify the port numbers used to match an
outgoing packet. You may specify either a raw number or a mnemonic as specified in
the /etc/services file. This setting matches both udp and tcp ports, unless the
Protocol field specifies udp or tcp.
The Protocol field specifies a protocol to match against, currently either tcp, udp,
icmp, ospf, vrrp or ipsec.
The Target Queue field selects one of the available priority queues.
RuggedCom 187

 Loading...
Loading...