°
Group 1: cables very sensitive to interference, such as analog measuring
cables
°
Group 2: cables sensitive to interference, such as device cables, communica‐
tion signals, bus signals
°
Group 3: cables that are a source of interference, such as control cables for
inductive loads and motor brakes
°
Group 4: cables that are a powerful source of interference, such as out‐
put cables from frequency inverters, welding system power supplies, power
cables
b
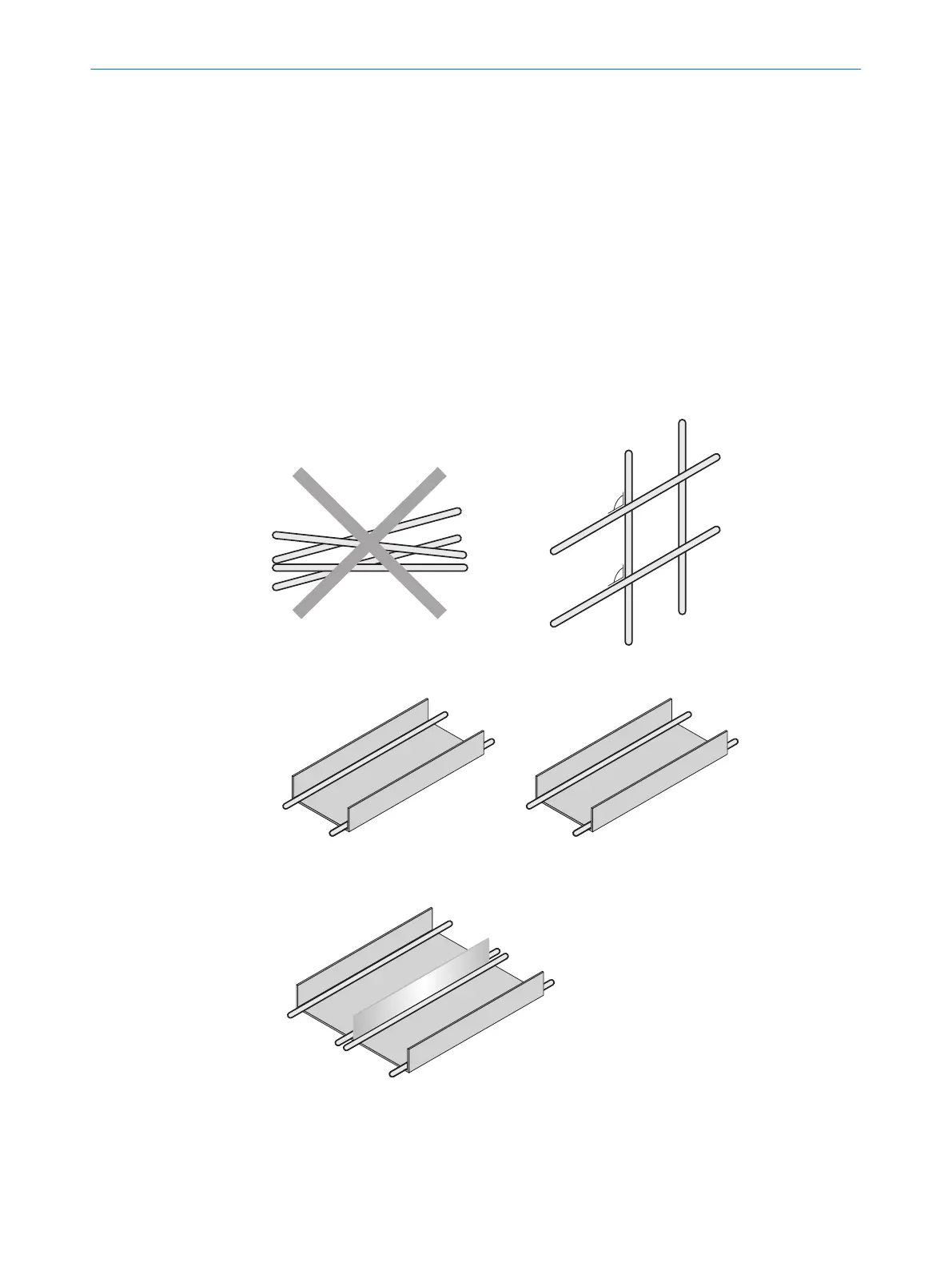
Cables in groups 1, 2 and 3, 4 must be crossed at right angles (see
figure 16).
b
Route the cables in groups 1, 2 and 3, 4 in different cable channels or
use metallic separators (see figure 17 and see figure 18). This applies partic‐
ularly if cables of devices with a high level of radiated emission, such as
frequency converters, are laid parallel to device cables.
Figure 16: Cross cables at right angles
Figure 17: Ideal laying – Place cables in different cable channels
Figure 18: Alternative laying – Separate cables with metallic separators
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
6
8015069/19H9/2021-10-15 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | DL100 Pro PROFINET
31
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...











