4.3.5
Comparison of
COLD RESTART and
RETENTIVE COLD
RESTART
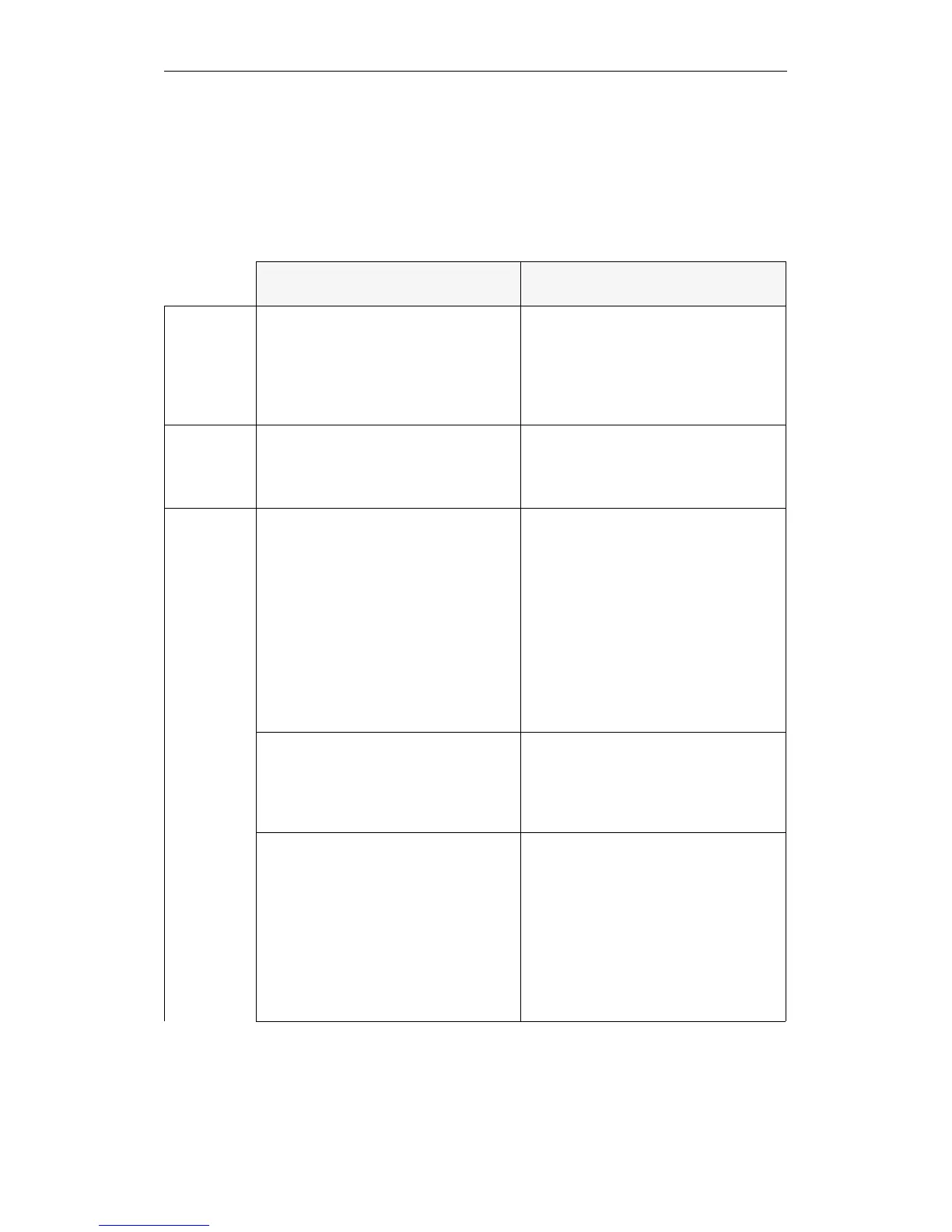
The following table shows the differences between a COLD
RESTART and RETENTIVE COLD RESTART.
COLD RESTART RETENTIVE COLD RESTART
Manual
triggering:
Mode selector from position STOP to
position RUN and reset switch set to
RESET
or
PG function PLC START (COLD
RESTART)
Mode selector from position STOP to
position RUN
or
PG function PLC START (WARM
RESTART)
Automatic
triggering:
Switching on the power supply, when
AUTOMATIC COLD RESTART after
POWER UP is entered in DX 0
Switching on the power supply when
AUTOMATIC WARM RESTART after
POWER UP and COLD RESTART WITH
MEMORY is entered in DX 0
System
program
activities:
Set up block address in DB 0
Delete process image of the inputs
Delete process image of the outputs
Delete delayed interrupts and timed jobs
Delete flags, timers and counters
Delete digital/analog I/Os
(each 2 x 128 bytes)
Block address list retained in DB 0
Process image of the inputs retained
Process image of the outputs retained
Delete delayed interrupts and timer jobs
Flags, timers and counters retained
Delete digital I/O (128 bytes)
Analog I/Os retained (128 bytes)
Delete IPC flags (256 bytes)
Delete ISTACK/BSTACK
Delete semaphore
IPC flags retained
Delete ISTACK/BSTACK
Semaphore retained
If DB 1 exists:
enter the digital I/Os and IPC flags it
contains in the PI lists
If DB 1 does not exist:
enter the existing modules (only digital
I/Os) in the PI lists
IPC flags are ignored
No entries from DB 1
Table 4-3 Differences between a cold restart and a RETENTIVE COLD RESTART
START-UP Mode
CPU 948 Programming Guide
C79000-G8576-C848-04
4 - 23
 Loading...
Loading...











