9.2 Memory Access via Address in ACCU 1
Application
The operations listed in this section are suitable primarily for access to
data blocks and other operand areas. You should, however, not access
blocks containing STEP 5 programs (OBs, FBs, PBs and SBs) with
these operations.
To access these areas, you can use various 16 or 32-bit wide registers.
These registers include the accumulators ACCU 1 to ACCU 4 and
other special registers used as resources by the CPU.
Operations
Operation Operand Function
LIR Register
no.
0 to 15
Load the 16-bit register with the content
of a memory word addressed by ACCU 1
(20-bit address).
TIR Register
no.
0 to 15
Load the content of the 16-bit register in
the memory word addressed by ACCU 1
(20-bit address).
LDI Register
name
Load the 32-bit register with the contents
of the memory words ’n’ and ’n+1’
addressed by ACCU 1 (20-bit address).
TDI Register
name
Load the contents of the 32-bit register in
the memory words ’n’ and ’n+1’ addressed
by ACCU 1 (20-bit address).
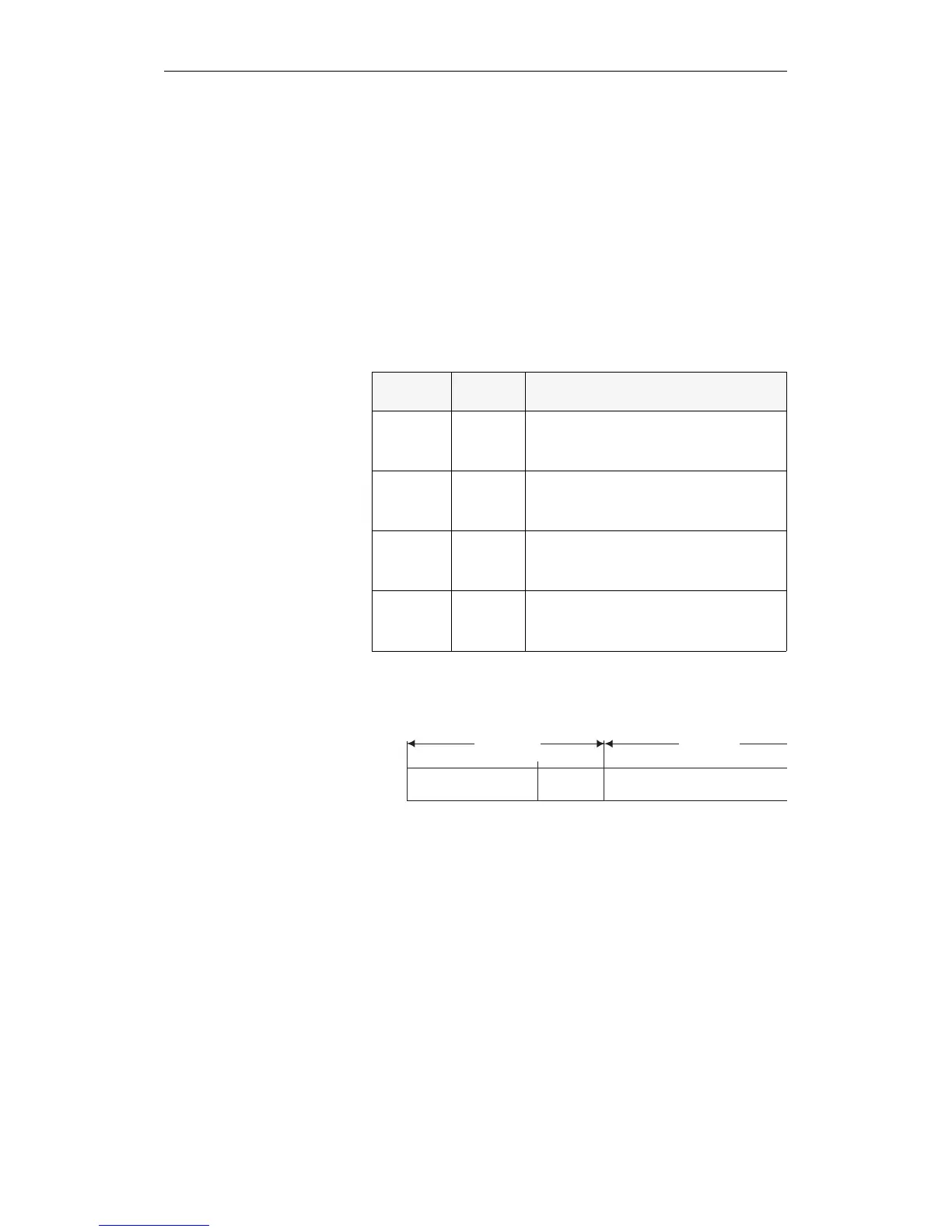
The absolute address of the memory word or the first of the two
memory words is located in ACCU 1 in the following representation:
The following pages explain which registers you can use with the
operations.
Examples explain how to use the operations.
Table 9-1 Operations for indirect memory access using registers
Bit no.
ACCU-1-H
ACCU-1-L
31
20 19
16
15
0
Address bits
Address bits 0 to 15
16 to 19
Memory Access via Address in ACCU 1
CPU 948 Programming Guide
9 - 8 C79000-G8576-C848-04
 Loading...
Loading...











