5.5 Error Handling Using Organization Blocks
When the system program detects an error, it calls the appropriate
organization block to handle it. You can determine further operation of
the CPU by programming the appropriate organization block.
Therefore, the CPU can do one of the following:
•• continue normal program processing
•• go into the STOP mode
and/or
•• process a special "error handling program"
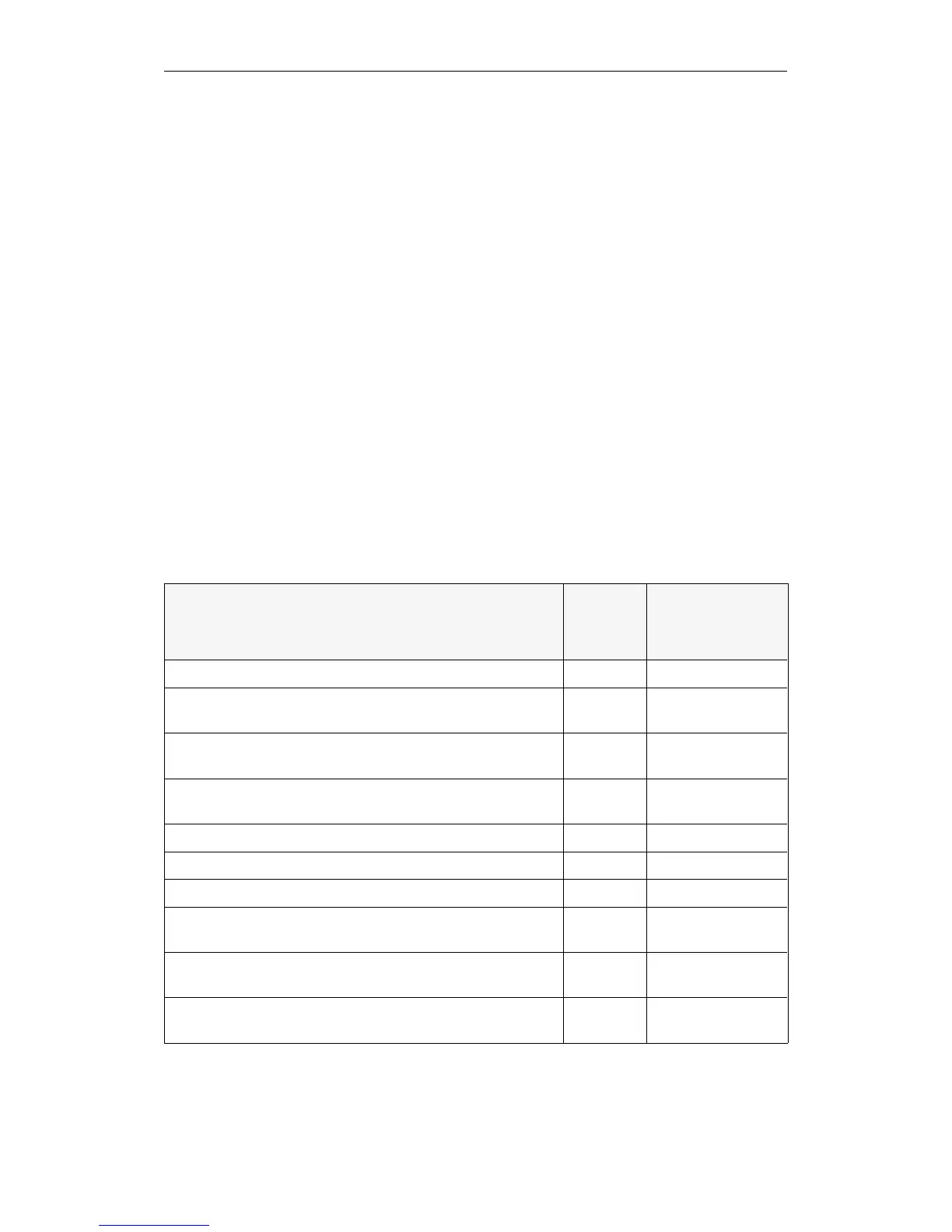
For the following causes of error, OBs are available:
Cause of error Organization
block called
Reaction of CPU
if OB is not
programmed
Call of a block that is not loaded (KB) OB 19 none
Attempt to open a data block DB/DX that is not loaded
(KDB)
OB 19 STOP
Timeout in the user program during access to I/O peripherals
(QVZ)
OB 23 none
Timeout during update of the process image table and during
interprocessor communication flag transfer (QVZ)
OB 24 none
Addressing error (ADF) OB 25 STOP
1)
Cycle time exceeded (ZYK) OB 26 STOP
Substitution error (SUF) OB 27 STOP
Timeout by reading input byte IB 0
(process interrupts – QVZ)
OB 28 STOP
Timeout during access to the distributed I/O peripherals (extended
address area — QVZ)
OB 29 none
Parity error and timeout in the user memory (PARE) OB 30 STOP
Table 5-7 The organization blocks called in case of errors
Error Handling Using Organization Blocks
CPU 948 Programming Guide
5 - 20 C79000-G8576-C848-04
 Loading...
Loading...











