S5-115F Manual Error Diagnostics
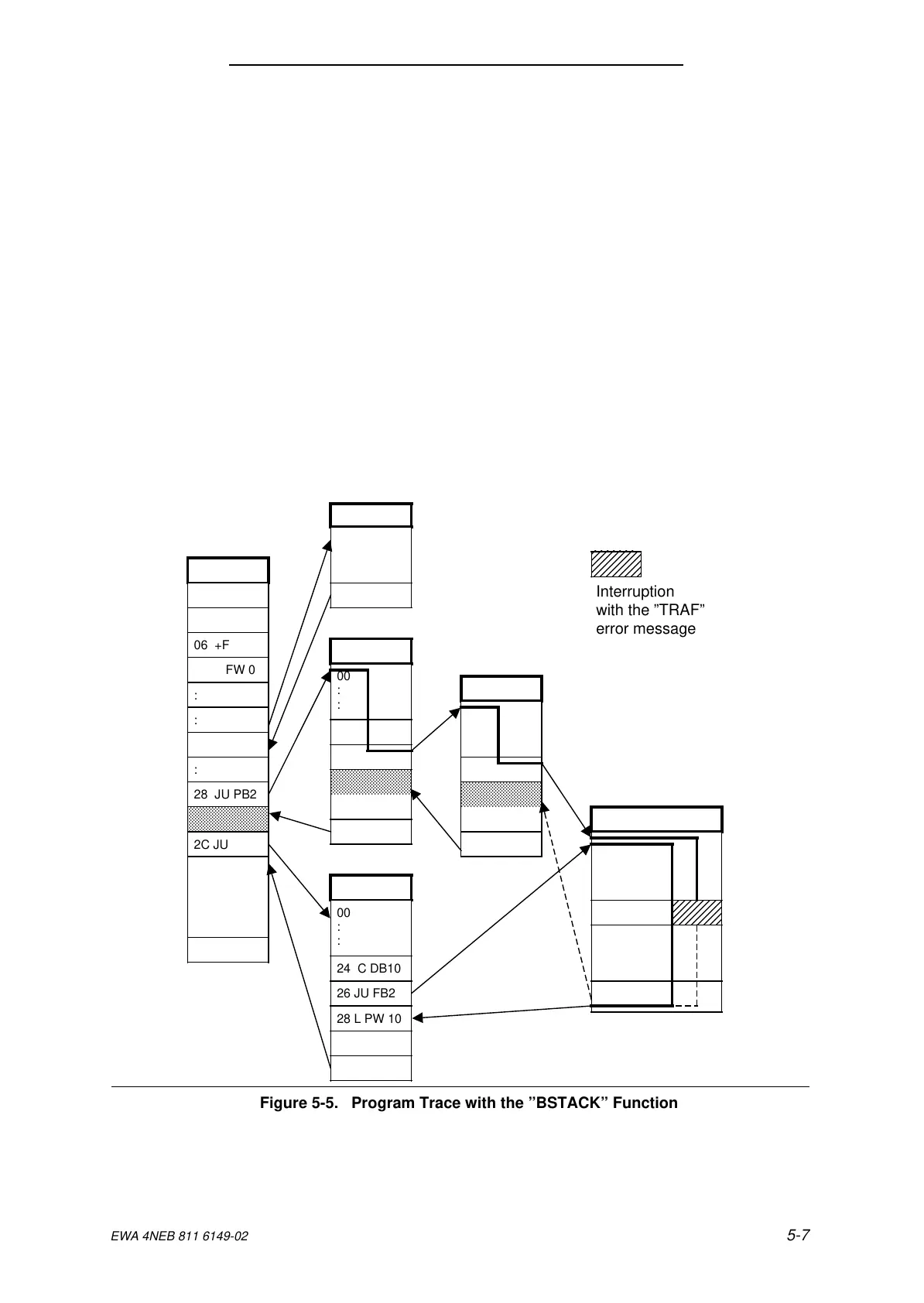
5.2.2 Program Trace with the Block Stack (”BSTACK”) Function
During program scanning, jump operations enter the following information in the block stack:
• The data block that was valid before program scanning exited a block
• The relative return address. This address indicates the location at which program scanning
continues after it returns from the block that was called.
• The absolute return address. This address indicates the location in the program memory at
which program scanning continues after it returns from the block that was called.
You can call the information listed above using the ”BSTACK” programmer function in the ”STOP”
mode if the CPU has entered this mode as the result of a malfunction. The ”BSTACK” reports the
status of the block stack at the time the interruption occurred.
Example: Program scanning was interrupted at function block FB 2. The CPU went into the
”STOP” mode with the error message ”TRAF” because of incorrect access. (DB 5 is
two words long. DB 10 is twelve words long.)
You can use the ”BSTACK” function to determine the path used to reach FB 2 and to
determine which block has passed the wrong parameter. The ”BSTACK” contains the
three return addresses.
2A
OB 1
:
PB 1
xx BE
00
:
:
PB 2
14
12 JU PB4
10 A DB5
xx BE
xx BE
PB 3
:
PB 4
18 JC FB2
00
:
:
1A
xx BE
FB 2
00
:
:
26 L DW4
:
:
:
xx BE
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
Interruption
with the ”TRAF”
error message
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
2C JU PB3
xx BE
:
:
:
:
:
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
a
02 L KF+1
00 L FW 0
08 T FW 0
06 +F
:
:
:
28 JU PB2
00
:
:
26 JU FB2
00
:
:
28 L PW 10
24 C DB10
Figure 5-5. Program Trace with the ”BSTACK” Function
EWA 4NEB 811 6149-02
5-7
 Loading...
Loading...











