5-2
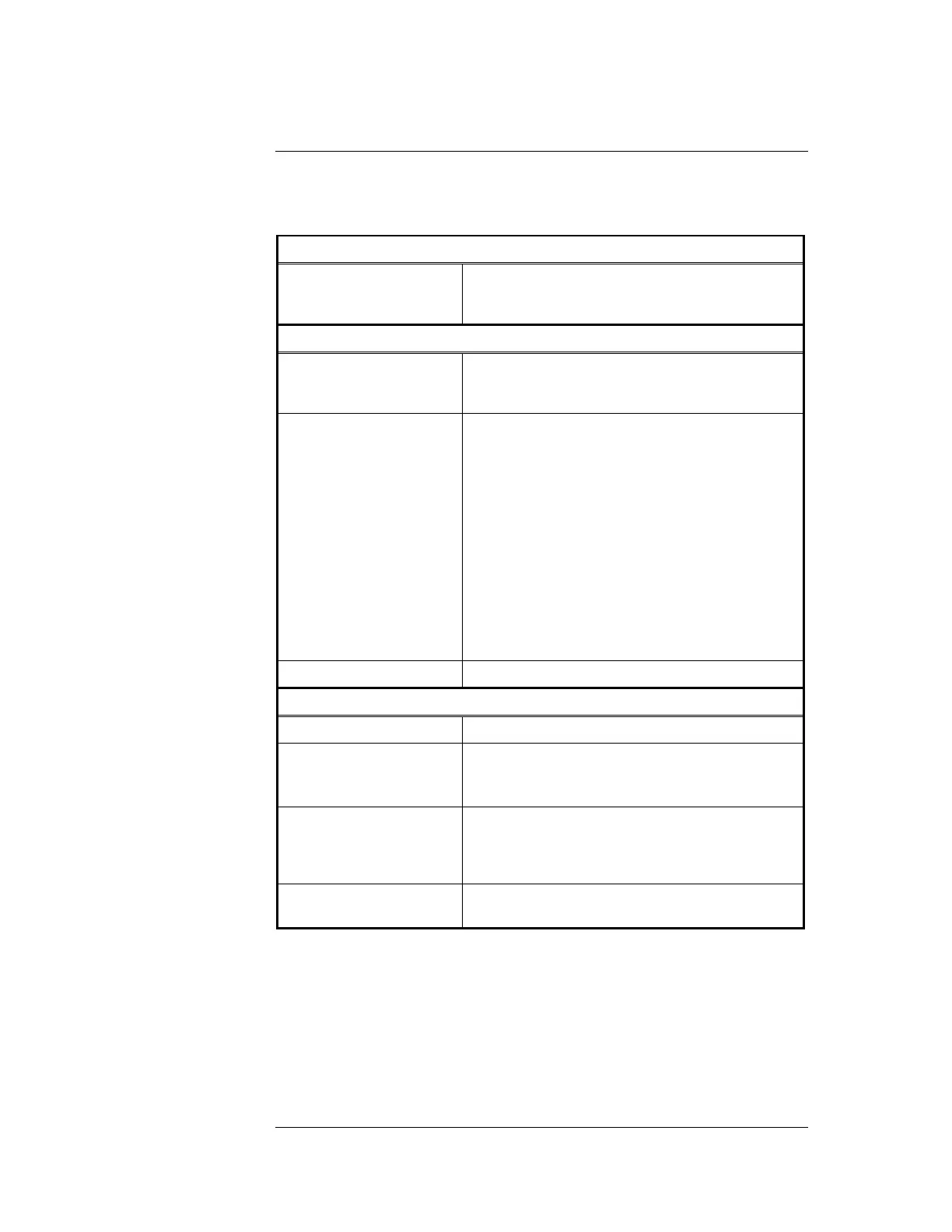
The following table summarizes the specifications for the SPS.{xe "system power supply
(SPS): specifications"}{xe "remote power supply (RPS): specifications"}
Table 5-1. SPS Input and Output Specifications
AC Input Specifications
SPS in Standard
Australian FIP
4100-9848AU
2 A Maximum
240 VAC + 6% -10% @ 50 Hz
DC Output Specifications
Voltage
Nominal 28VDC
Minimum: 19.5 VDC Maximum: 32 VDC
Ripple: 2 VDC p-p @ full load (9A)
Total Current (max)
24V Card
24V Aux
Each NAC (total A+B)
9A alarm load. Includes: NACs (+24V Sig);
+24V Card; +24V Aux; SPS card power
including on-board IDNet.
5A non-alarm load. Includes as per above,
allows for battery charging at high rate.
2A max. See note.
2A max
3A max alarm load
2A max non-alarm load (used as Aux 24V
power).
SPS IDNet Output 30 V or 35 V (see note below)
Battery Charger Specifications
Input Voltage Range 21-33 VDC
Output Float Voltage
27.3 VDC 200 mV @ 20C, temperature
compensated at approximately -36mV/C
(0 C to 50 C)
Supervision Voltages
(nominal at 20C)
Charger High 28.4Vdc
Charger Low 26.2Vdc
Battery Low 24.3Vdc
Battery Depleted 19.4Vdc
Output Current Limit
1.4 A (For 6.2 – 18 Ah battery)
3.3 A (Default; for 18-110 Ah battery)
Notes:
AC power must be provided to the 4100ES from a dedicated AC branch
circuit. The AC input is supervised.
A mains fail fault is generated when the DC voltage drops below 20.3V
(nominally 204Vac).
240 VAC: The service branch circuit breaker should be sized to handle at
least 150 percent of the total required by all of the power supplies in the
system.
Continued on next page
SPS Specifications
Input/Output/Battery
Specifications
 Loading...
Loading...


















