66 Netra T2000 Server Administration Guide • September 2006
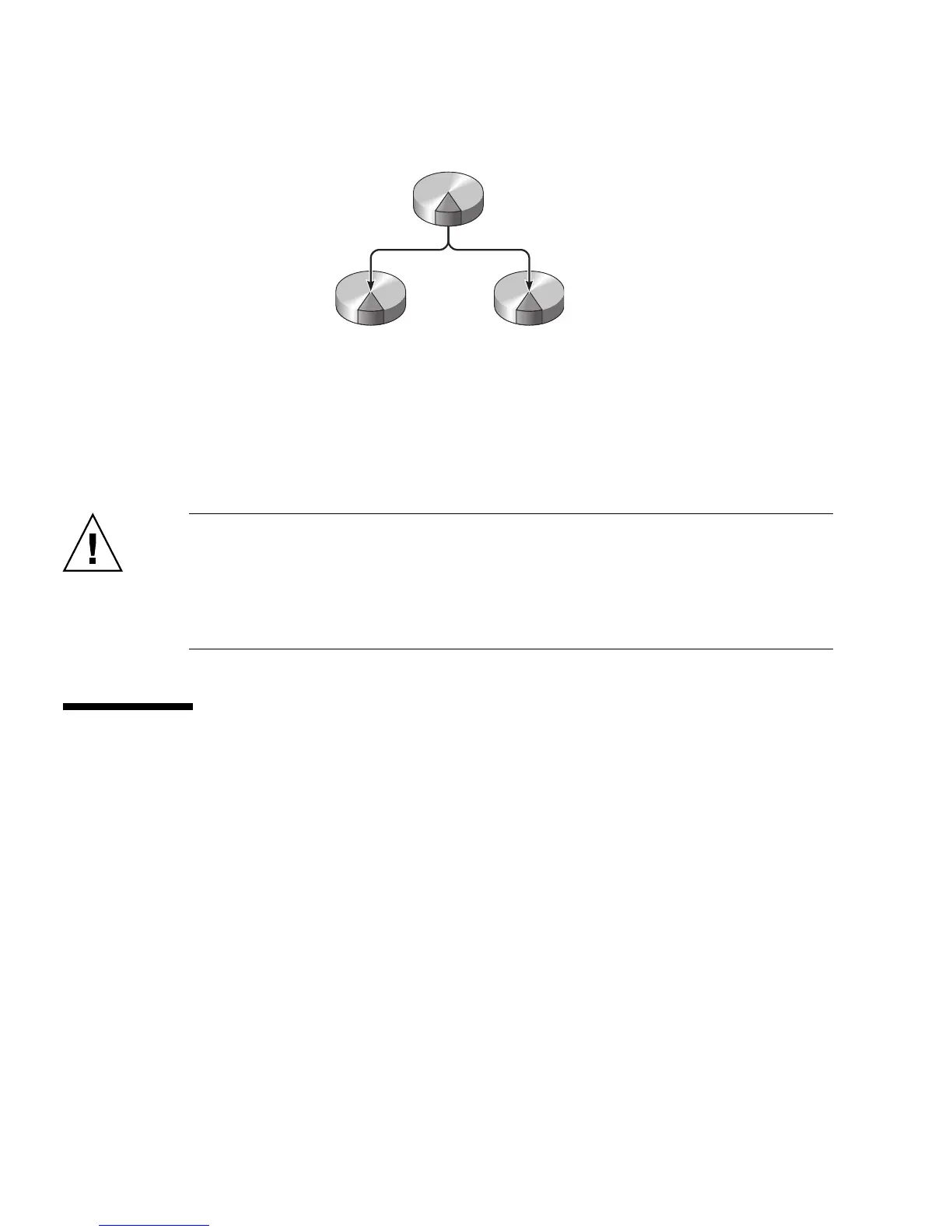
FIGURE 6-2 Graphical Representation of Disk Mirroring
Whenever the operating system needs to write to a mirrored volume, both disks are
updated. The disks are maintained at all times with exactly the same information.
When the operating system needs to read data, it reads from whichever disk is more
readily accessible at the moment, which can result in enhanced performance for read
operations.
Caution – Creating RAID volumes using the on-board disk controller destroys all
data on the member disks. The disk controller’s volume initialization procedure
reserves a portion of each physical disk for metadata and other internal information
used by the controller. Once the volume initialization is complete, you can configure
the volume and label it using format(1M). You can then use the volume in the
Solaris Operating System.
Hardware RAID Operations
On the server, the SAS controller supports mirroring and striping using the Solaris
OS raidctl utility.
A hardware RAID volume created under the raidctl utility behaves slightly
differently than one created using volume management software. Under a software
volume, each device has its own entry in the virtual device tree, and read/write
operations are performed to both virtual devices. Under hardware RAID volumes,
only one device appears in the device tree. Member disk devices are invisible to the
operating system, and are accessed only by the SAS controller.
 Loading...
Loading...











