Chapter 13: Inferential Statistics and Distributions 242
Note: L1â99 and 1â99 specify infinity. If you want to view the area left of upperbound, for example,
specify
lowerbound= L1â99.
fx()
1
2πσ
--------------
e
x μ–()
2
2σ
2
-------------------–
–
σ 0>,=
normalpdf(
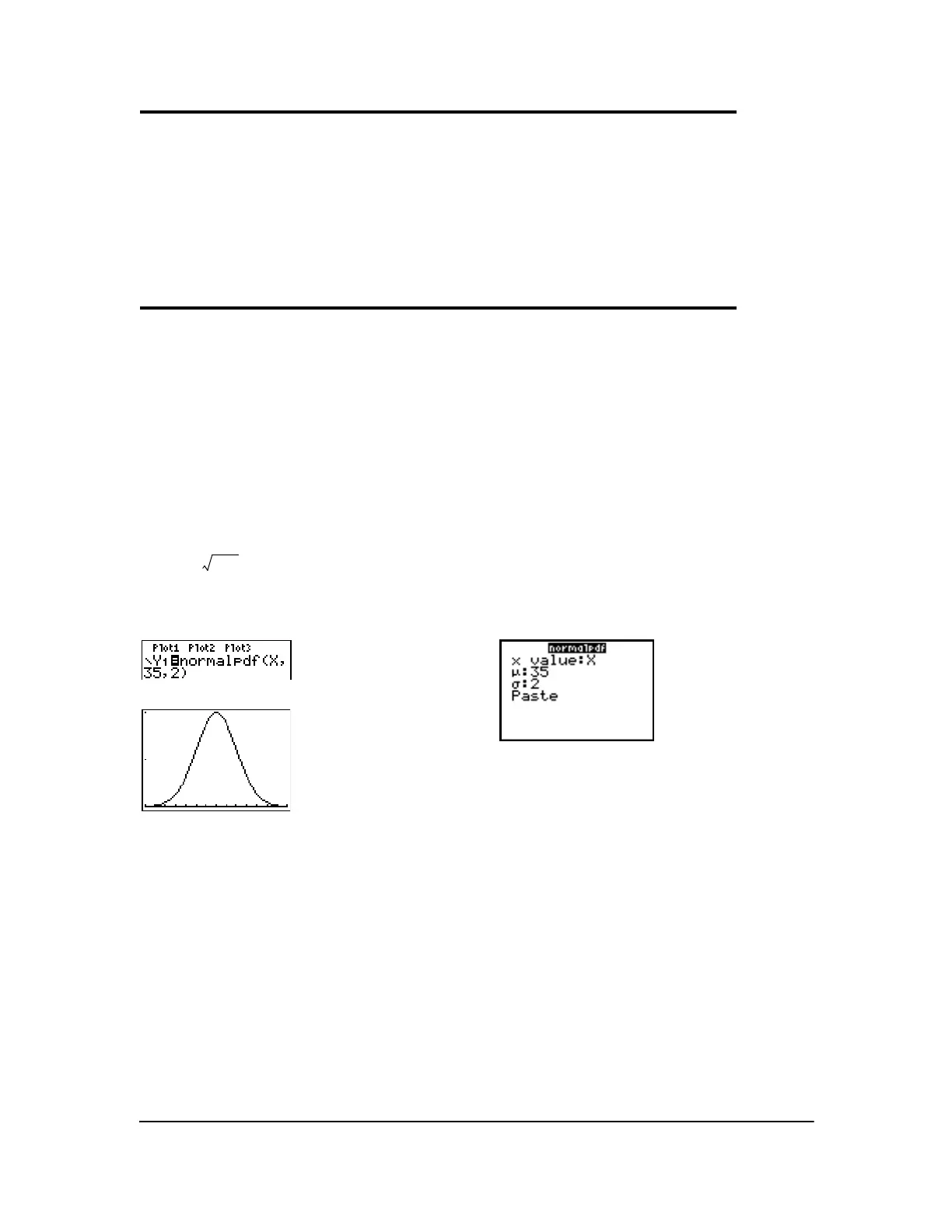
normalpdf( computes the probability density function (pdf) for the normal distribution at a specified
x value. The defaults are mean m=0 and standard deviation s=1. To plot the normal distribution,
paste
normalpdf( to the Y= editor. The probability density function (pdf) is:
normalpdf(x[,m,s])
Note: For plotting the normal distribution, you can set window variables Xmin and Xmax so that the
mean
m falls between them, and then select 0:ZoomFit from the ZOOM menu.
normalcdf(
normalcdf( computes the normal distribution probability between lowerbound and upperbound for the
specified mean m and standard deviation s. The defaults are m=0 and s=1.
A: binompdf(
Binomial probability
B: binomcdf(
Binomial cumulative density
C: poissonpdf(
Poisson probability
D: poissoncdf(
Poisson cumulative density
E: geometpdf(
Geometric probability
F: geometcdf(
Geometric cumulative density
Note: For this example,
Xmin = 28
Xmax = 42
Xscl = 1
Ymin = 0
Ymax = .2
Yscl = .1
DISTR DRAW

 Loading...
Loading...











