Appendix A: Functions and Instructions 203
ln() @ 2x key H x key
ln(
expression1
) ⇒
expression
ln(
list1
) ⇒
list
Returns the natural logarithm of the argument.
For a list, returns the natural logarithms of the
elements.
ln(2.0) ¸ .693...
If complex format mode is
REAL:
ln({ë 3,1.2,5}) ¸
Error: Non-real result
If complex format mode is RECTANGULAR:
ln({ë 3,1.2,5}) ¸
{ln(3) + pø
i
.182... ln(5)}
ln(
squareMatrix1
) ⇒
squareMatrix
Returns the matrix natural logarithm of
squareMatrix1
. This is
not
the same as calculating
the natural logarithm of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer
to
cos() on.
squareMatrix1
must be diagonalizable. The result
always contains floating-point numbers.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular
complex format mode:
ln([1,5,3;4,2,1;6,ë 2,1]) ¸
1.831…+1.734…øi .009…ì 1.490…øi …
.448…ì.725…øi 1.064…+.623øi …
ë.266…ì 2.083…øi 1.124…+1.790…øi …
LnReg MATH/Statistics/Regressions menu
LnReg
list1
,
list2
[, [
list3
] [,
list4
,
list5
]]
Calculates the logarithmic regression and updates
all the system statistics variables.
All the lists must have equal dimensions except
for
list5
.
list1
represents xlist.
list2
represents ylist.
list3
represents frequency.
list4
represents category codes.
list5
represents category include list.
Note:
list1
through
list4
must be a variable name
or c1–c99 (columns in the last data variable
shown in the Data/Matrix Editor).
list5
does not
have to be a variable name and cannot be c1–
c99.
In function graphing mode:
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}! L1 ¸
{1 2 3
...}
{1,2,2,3,3,3,4,4}! L2
¸
{1 2 2 ...}
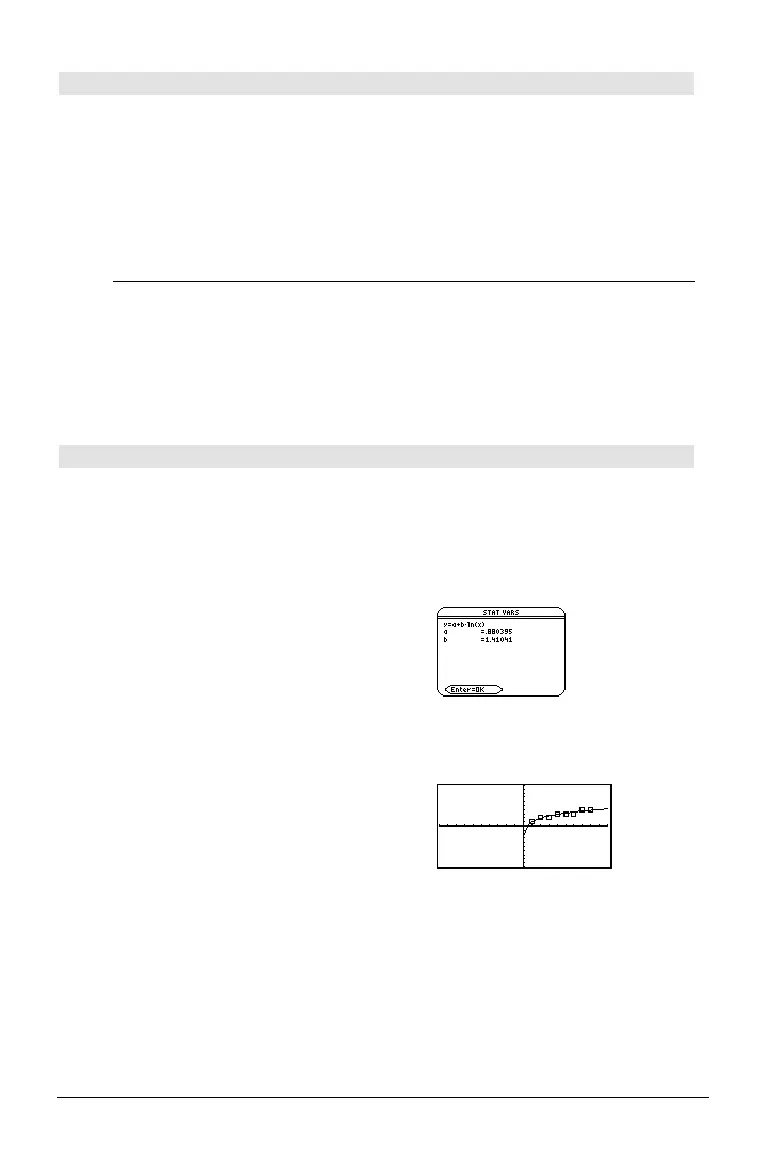
LnReg L1,L2
¸ Done
ShowStat
¸
¸
Regeq(x)"y1(x)
¸ Done
NewPlot 1,1,L1,L2
¸ Done
¥%

 Loading...
Loading...











