214 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
nPr(
list1
,
list2
) ⇒
list
Returns a list of permutations based on the
corresponding element pairs in the two lists. The
arguments must be the same size list.
nPr({5,4,3},{2,4,2}) ¸
{20 24 6}
nPr(
matrix1
,
matrix2
) ⇒
matrix
Returns a matrix of permutations based on the
corresponding element pairs in the two matrices.
The arguments must be the same size matrix.
nPr([6,5;4,3],[2,2;2,2]) ¸
[
30 20
12 6
]
nSolve() MATH/Algebra menu
nSolve(
equation
,
varOrGuess
) ⇒
number or error_string
Iteratively searches for one approximate real
numeric solution to
equation
for its one variable.
Specify
varOrGuess
as:
variable
– or –
variable
=
real number
For example, x is valid and so is x=3.
nSolve(x^2+5xì 25=9,x) ¸
3.844
...
nSolve(x^2=4,x=ë 1) ¸ ë 2.
nSolve(x^2=4,x=1)
¸ 2.
Note: If there are multiple solutions, you can
use a guess to help find a particular solution.
nSolve() is often much faster than solve() or
zeros(), particularly if the “|” operator is used to
constrain the search to a small interval containing
exactly one simple solution.
nSolve() attempts to determine either one point
where the residual is zero or two relatively close
points where the residual has opposite signs and
the magnitude of the residual is not excessive. If
it cannot achieve this using a modest number of
sample points, it returns the string “
no solution
found.”
If you use
nSolve() in a program, you can use
getType() to check for a numeric result before
using it in an algebraic expression.
Note: See also
cSolve(), cZeros(), solve(), and
zeros().
nSolve(x^2+5xì 25=9,x)|x<0 ¸
ë 8.844...
nSolve(((1+r)^24ì 1)/r=26,r)|r>
0 and r<.25
¸ .0068...
nSolve(x^2=ë 1,x) ¸
"no solution found"
OneVar MATH/Statistics menu
OneVar
list1
[[,
list2
] [,
list3
] [,
list4
]]
Calculates 1-variable statistics and updates all the
system statistics variables.
All the lists must have equal dimensions except
for
list4
.
list1
represents xlist.
list2
represents frequency.
list3
represents category codes.
list4
represents category include list.
Note:
list1
through
list3
must be a variable name
or c1–c99 (columns in the last data variable
shown in the Data/Matrix Editor).
list4
does not
have to be a variable name and cannot be c1–
c99.
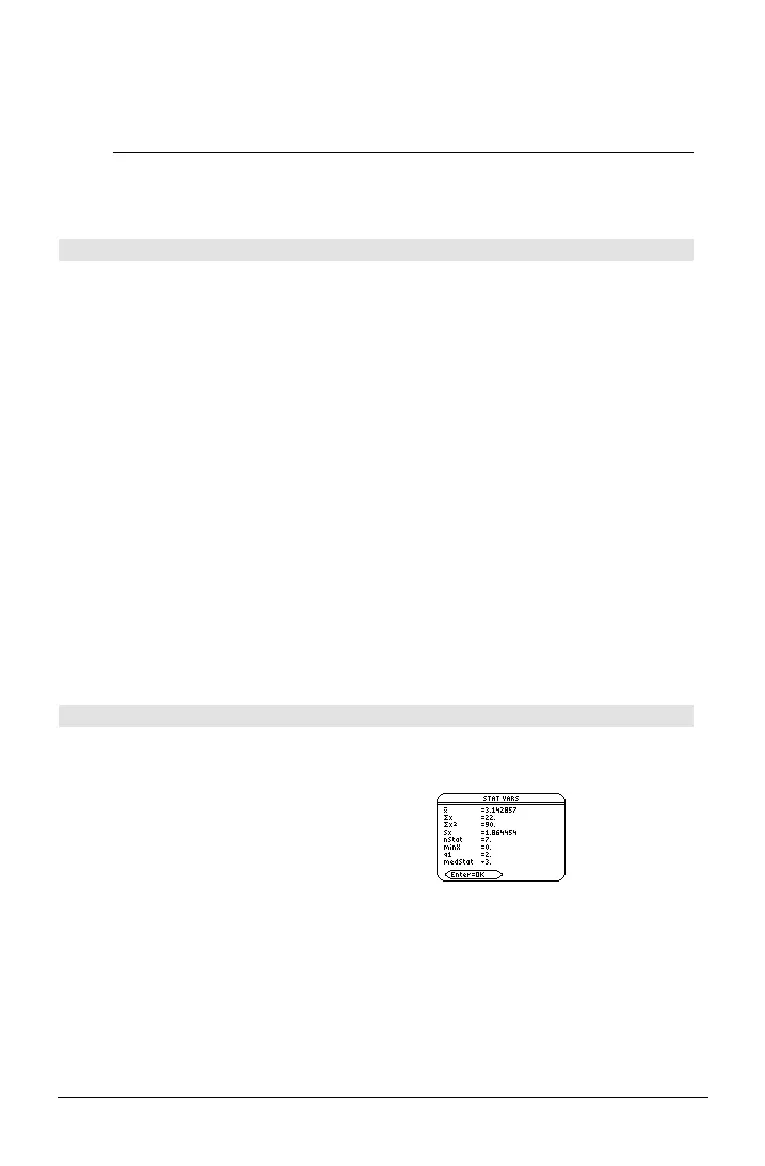
{0,2,3,4,3,4,6}! L1 ¸
OneVar L1
¸ Done
ShowStat
¸

 Loading...
Loading...











