246 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
Each solution variable starts at its guessed value
if there is one; otherwise, it starts at 0.0.
Use guesses to seek additional solutions one by
one. For convergence, a guess may have to be
rather close to a solution.
solve(
e
^(z)ù y=1 and
ë y=sin(z),{y,z=2p}) ¸
y=.001… and z=6.281…
SortA MATH/List menu
SortA
listName1
[,
listName2
] [,
listName3
] ...
SortA
vectorName1
[,
vectorName2
] [,
vectorName3
] ...
Sorts the elements of the first argument in
ascending order.
If you include additional arguments, sorts the
elements of each so that their new positions
match the new positions of the elements in the
first argument.
All arguments must be names of lists or vectors.
All arguments must have equal dimensions.
{2,1,4,3}! list1 ¸ {2,1,4,3}
SortA list1
¸ Done
list1
¸ {1 2 3 4}
{4,3,2,1}! list2
¸ {4 3 2 1}
SortA list2,list1
¸ Done
list2
¸ {1 2 3 4}
list1
¸ {4 3 2 1}
SortD MATH/List menu
SortD
listName1
[,
listName2
] [,
listName3
] ...
SortD
vectorName1
[,
vectorName 2
] [,
vectorName 3
] ...
Identical to SortA, except SortD sorts the
elements in descending order.
{2,1,4,3}! list1 ¸ {2 1 4 3}
{1,2,3,4}! list2
¸ {1 2 3 4}
SortD list1,list2
¸ Done
list1
¸ {4 3 2 1}
list2
¸ {3 4 1 2}
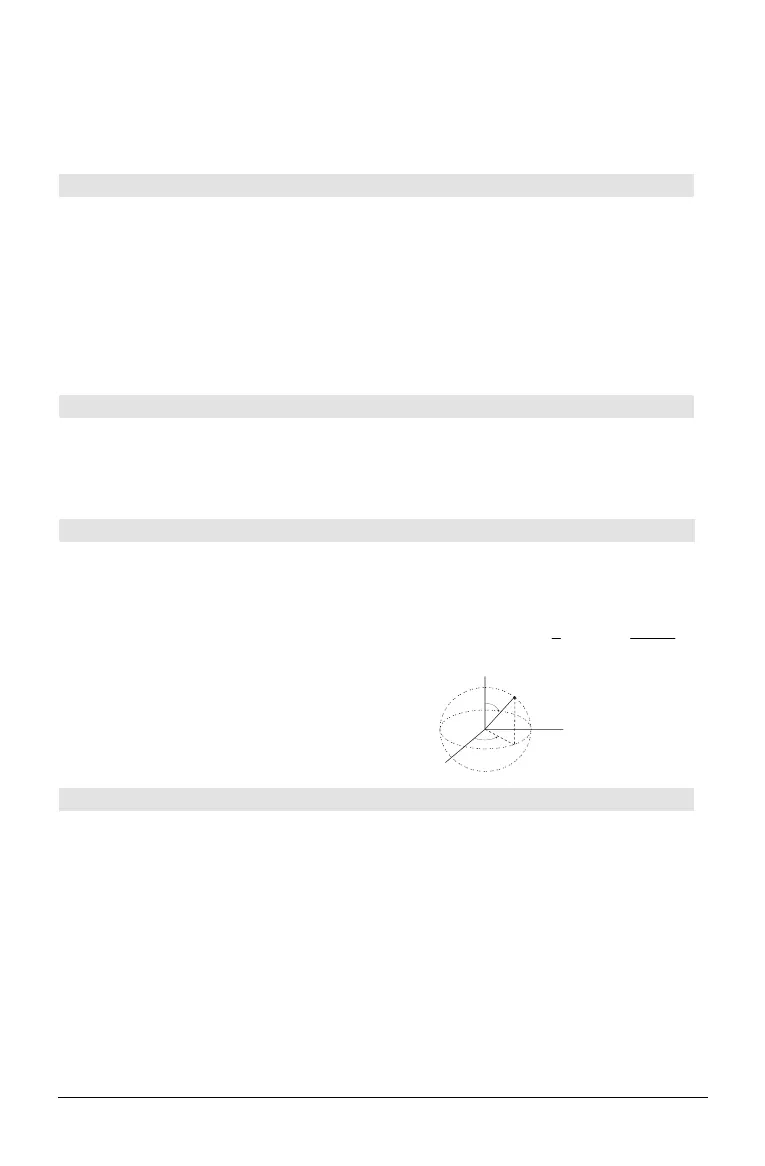
4Sphere MATH/Matrix/Vector ops menu
vector
4Sphere
Displays the row or column vector in spherical
form [r oq of].
vector
must be of dimension 3 and can be either a
row or a column vector.
Note:
4Sphere is a display-format instruction,
not a conversion function. You can use it only at
the end of an entry line.
[1,2,3]4Sphere
¥ ¸ [3.741... o1.107... o.640...]
[2,opà4,3]4Sphere
¥ ¸ [3.605... o.785... o.588...]
¸ [‡13 o
p
4
ocosê (
3ø ‡13
13
)]
X
Y
Z
(ρ,θ,φ)
θ
φ
ρ
startTmr() CATALOG
startTmr() ⇒
integer
Returns the current value of the clock in its
integer representation, giving the
starttime
for a
timer. You can enter the
starttime
as an argument
in
checkTmr() to determine how many seconds
have elapsed.
You can run multiple timers simultaneously.
Note: See also
checkTmr() and timeCnv().
startTmr() ¸ 148083315
checkTmr(148083315) 34
startTmr()!Timer1
©
startTmr()!Timer2
©
checkTmr(Timer1)!Timer1Value
©
checkTmr(Timer2)!Timer2Value

 Loading...
Loading...











