272 Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
&
(append)
@ ¥ p key H 2 H key
string1
&
string2
⇒
string
Returns a text string that is
string2
appended to
string1
.
"Hello " & "Nick" ¸
"Hello Nick"
‰()
(integrate)
2<key
‰(
expression1
,
var
[,
lower
] [,
upper
]) ⇒
expression
‰(
list1,var
[,
order
]) ⇒
list
‰(
matrix1,var
[,
order
]) ⇒
matrix
Returns the integral of
expression1
with respect to
the variable
var
from
lower
to
upper
.
‰(x^2,x,a,b) ¸
bò
3
-
aò
3
Returns an anti-derivative if
lower
and
upper
are
omitted. A symbolic constant of integration such
as
C is omitted.
However,
lower
is added as a constant of
integration if only
upper
is omitted.
‰(x^2,x) ¸
xò
3
‰(aù x^2,x,c) ¸
aø xò
3
+ c
Equally valid anti-derivatives might differ by a
numeric constant. Such a constant might be
disguised—particularly when an anti-derivative
contains logarithms or inverse trigonometric
functions. Moreover, piecewise constant
expressions are sometimes added to make an
anti-derivative valid over a larger interval than
the usual formula.
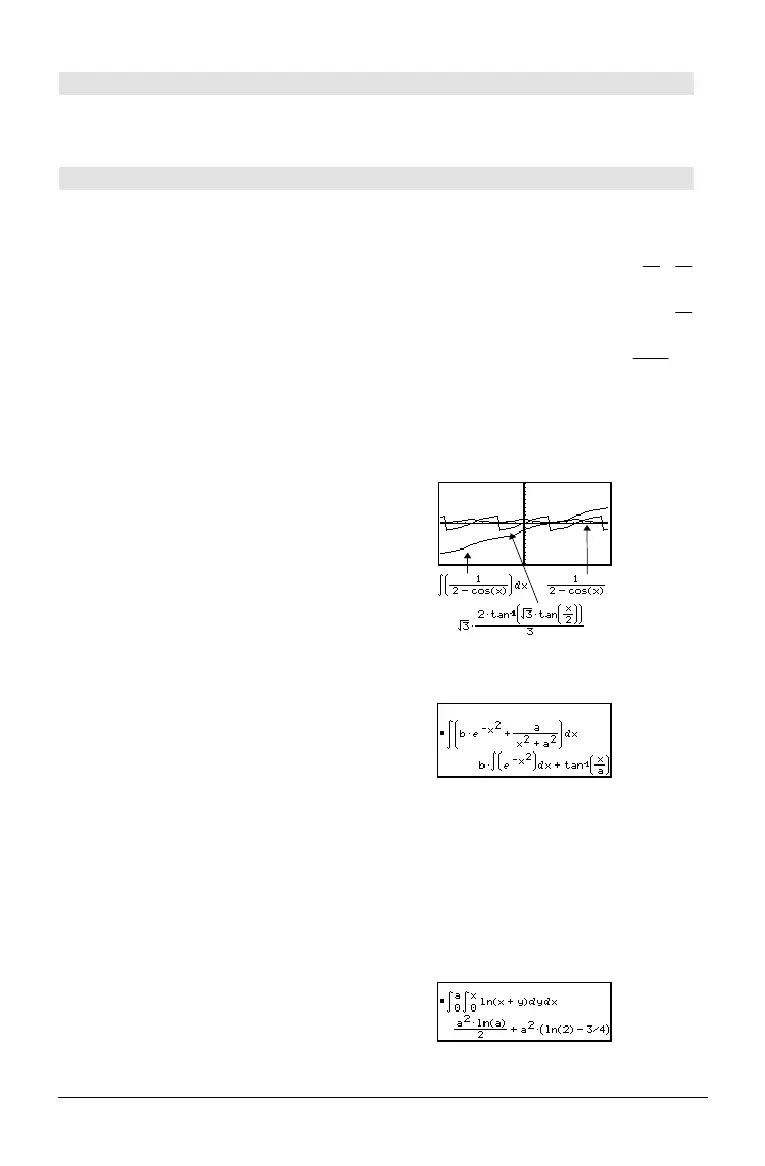
‰(1/(2ì cos(x)),x)! tmp(x) ¸
ClrGraph:Graph tmp(x):Graph
1/(2ì cos(x)):Graph ‡(3)
(2tanê (‡(3)(tan(x/2)))/3)
¸
‰() returns itself for pieces of
expression1
that it
cannot determine as an explicit finite
combination of its built-in functions and
operators.
When
lower
and
upper
are both present, an
attempt is made to locate any discontinuities or
discontinuous derivatives in the interval
lower <
var < upper
and to subdivide the interval at those
places.
‰(bù
e
^(ë x^2)+a/(x^2+a^2),x)
¸
For the AUTO setting of the Exact/Approx mode,
numerical integration is used where applicable
when an anti-derivative or a limit cannot be
determined.
For the
APPROX setting, numerical integration is
tried first, if applicable. Anti-derivatives are
sought only where such numerical integration is
inapplicable or fails.
‰(
e
^(ë x^2),x,ë 1,1)¥¸ 1.493...
‰
() can be nested to do multiple integrals.
Integration limits can depend on integration
variables outside them.
Note: See also
nInt().
‰(‰(ln(x+y),y,0,x),x,0,a) ¸
 Loading...
Loading...











