unicast via the right p
ort, MAC address duplication is used to expand the VLANs the MAC
address is in. Normally, the egress ports for forwarding these packets are identified through
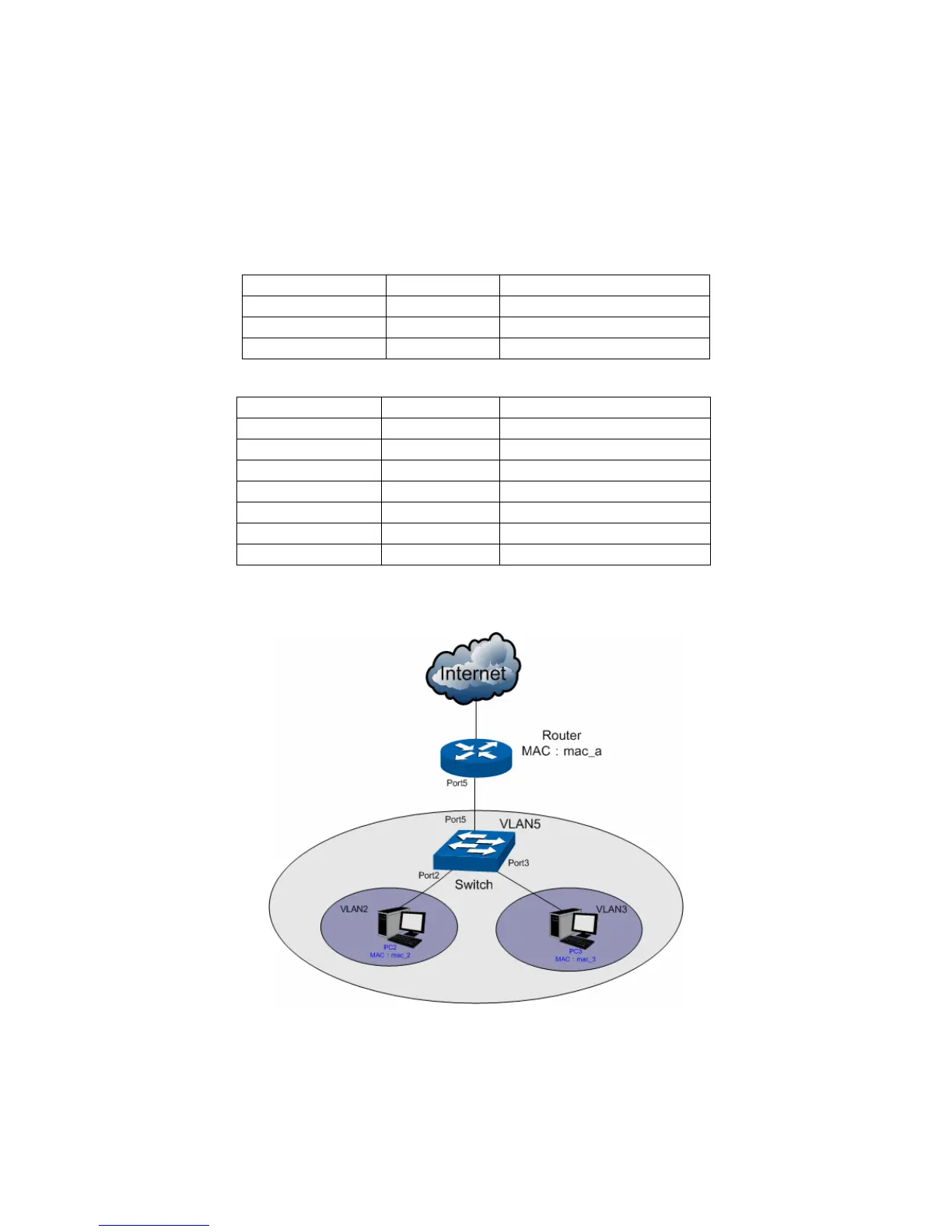
MAC address learning. For example the switch in Figure 6-13 maintains a MAC address
t
able shown in Table 6-6. The MAC address duplication process has two aspects, that is,
duplicating the dynamic MAC addresses learned by the host ports in the secondary VLANs
to the Primary VLAN and copying the dynamic MAC addresses learned by the promiscuous
ports in the Primary VLAN to the secondary VLANs. As shown in Figure 6-13, supposing
the Router s
ends a packet with the source MAC as mac_2 and the destination Mac as
mac_a. The MAC address table on the Switch is changed to the one shown in Table 6-7.
Destination MAC VLAN Egress Port
mac_a 5 port 5
mac_2 2 port 2
mac_3 3 port 3
Table 6-6 MAC address table before duplication
Destination MAC VLAN Egress Port
mac_a 5 port 5
mac_a 2 port 5
mac_a 3 port 5
mac_2 2 port 2
mac_2 5 port 2
mac_3 3 port 3
mac_3 5 port 3
Table 6-7 MAC address table after duplication
Packet forwarding in Private VLAN
The Private VLAN packet forwarding process (here we take traffic transmission for PC2) based on
the figure above is illustrated as follows:
1) PC2 sends out its first upstream packet with the source MAC as mac_2 and the
destination MAC as mac_a. This packet is untagged.
72

 Loading...
Loading...











