5.3 UL Standards
200 YASKAWA SIEPC71061753C GA500 Technical Manual
■ L1-01: Motor Overload (oL1) Protection
No.
(Hex.)
Name Description
Default
(Range)
L1-01
(0480)
Motor Overload (oL1)
Protection
Sets the motor overload protection with electronic thermal protectors.
Determined by A1-02
(0 - 6)
This parameter enables and disables the motor overload protection with electronic thermal protectors.
The cooling capability of the motor changes when the speed control range of the motor changes. Use an electronic
thermal protector that aligns with the permitted load characteristics of the motor to select motor protection.
The electronic thermal protector of the drive uses these items to calculate motor overload tolerance and supply
overload protection for the motor:
• Output current
• Output frequency
• Motor thermal characteristics
• Time characteristics
If the drive detects motor overload, the drive will trigger an oL1 [Motor Overload] and stop drive output.
Set H2-01 = 1F [Term MA/MB-MC Function Selection = Motor Overload Alarm (oL1)] to set a motor overload
alarm. If the motor overload level is more than 90% of the oL1 detection level, the output terminal activates and
triggers an overload alarm.
0 : Disabled
Disable motor protection when motor overload protection is not necessary or when the drive is operating more
than one motor.
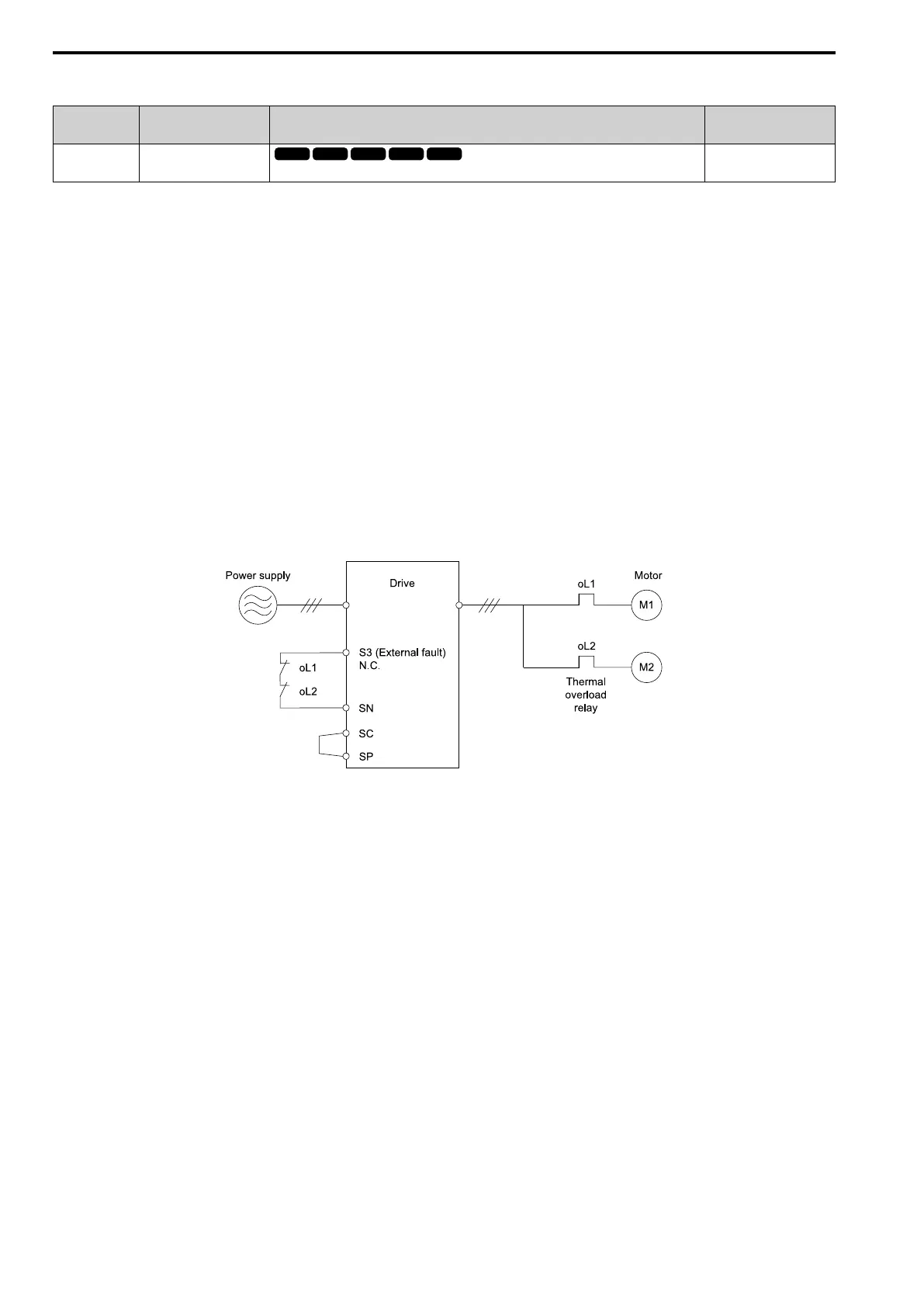
Refer to Figure 5.18 for an example of the circuit configuration to connect more than one motor to one drive.
Figure 5.18 Protection Circuit Configuration to Connect More than One Motor to One Drive
NOTICE: When you connect more than one motor to one drive or when the motor amp rating is higher than the drive amp
rating, set L1-01 =0 [Motor Overload (oL1) Protection = Disabled] and install thermal overload relays for each motor. The
electronic thermal protection of the drive will not function and it can cause damage to the motor.
1 : Variable Torque
Use this setting for general-purpose motors with a 60 Hz base frequency.
The overload tolerance decreases as motor speed decreases because the cooling fan speed decreases and the ability
of the motor to cool decreases in the low speed range.
The overload tolerance characteristics of the motor change the trigger point for the electronic thermal protector.
This provides motor overheat protection from low speed to high speed across the full speed range.

 Loading...
Loading...