44 Rockwell Automation Publication 7000-UM202D-EN-P - May 2018
Chapter 2 Power Component Definition and Maintenance
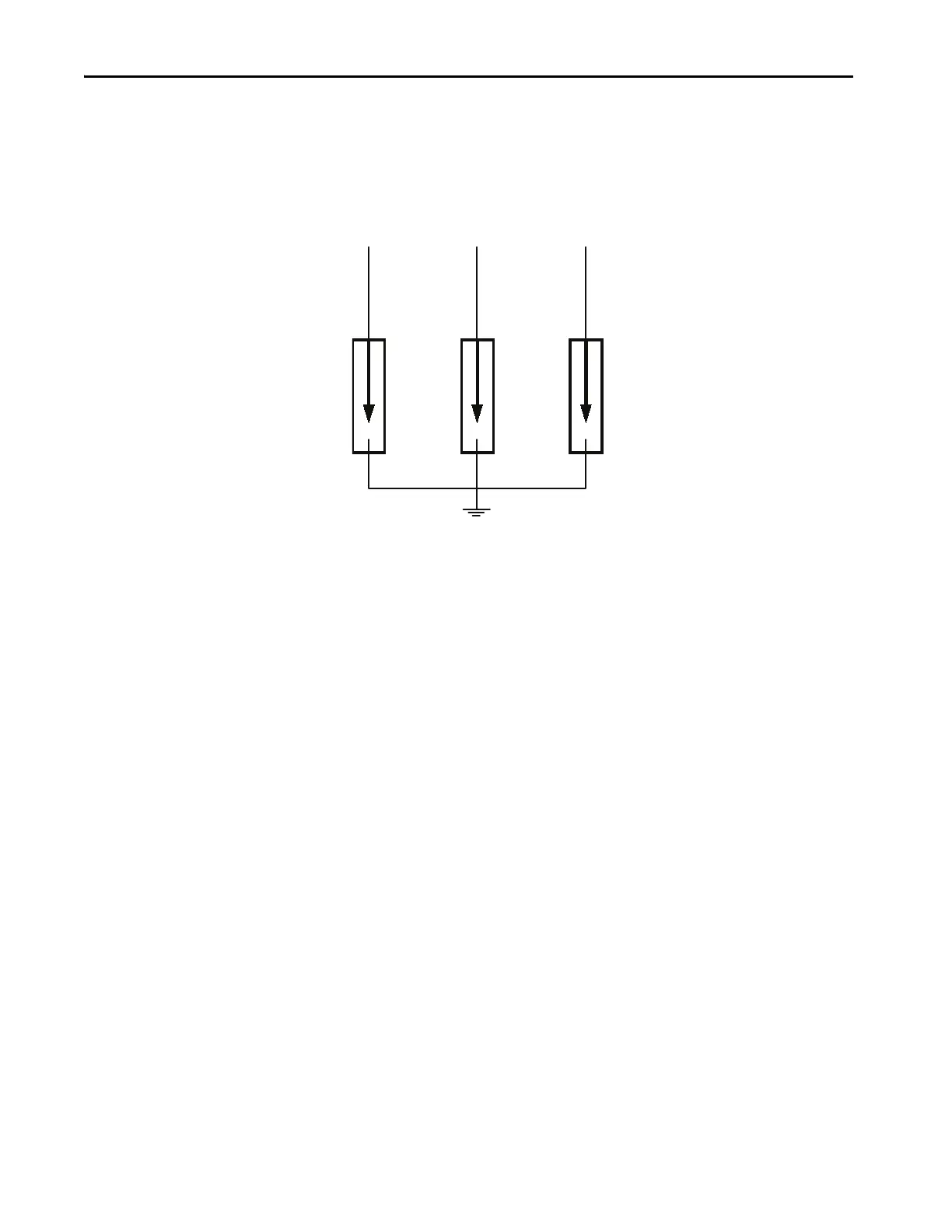
Three Y-connected surge arresters attach to the incoming MV lines. The
neutral point of the arresters connects to the ground bus.
Figure 31 - Surge Arresters on Incoming MV Lines
Operation
Arrester operation without a gap is the same as that of MOVs in the TSN.
Depending on design, the arrester may also have a gap. Both gapped and un-
gapped arresters provide adequate overvoltage protection.
The arresters can withstand most commonly-seen bus transients within their
capability. If there is a harmonic filter on the MV bus connected to the drive,
the filter must satisfy relevant international or local standards, such as IEEE Std
1531— Clause 6.4, to avoid high inrush currents.
The surge arrester is certified as per ANSI/IEEE Std C62.11-1993.
Certification tests include high current short duration tests, low current long
duration tests, and fault current withstand tests. The fault current withstand
tests consist of different combinations of kA and number of cycles, including a
20kA 10-cycle test, under which the arresters are non-fragmenting without
expelling any internal components.
When the incoming energy exceeds the handling capability of the arrester and
causes arrester failure, the housing splits open to vent without causing damage
to any adjacent components.
U
Drive Input from Line Terminals
Heavy-duty
Distribution Class
Surge Arrestor

 Loading...
Loading...











