Preamble
UM-23100B-U User manual ATEQ F CLASS Page 6/90
3. THE MAIN TYPES OF MEASUREMENTS
There are three measurement methods:
Direct measurement, indirect measurement and sealed component measurement.
These three methods apply to measurements taken both under pressure and in vacuum
conditions.
The configuration is determined by the application and must be carried out prior to the
use of the instrument.
3.1. DIRECT/PRESSURE DROP MEASUREMENT
After filling the test and reference parts to the required pressure level, the ATEQ F
CLASS measures the differential pressure between the two volumes which are
separated by the equalisation valve.
At the end of a cycle, the ATEQ empties the components via the dump valve.
3.2. INDIRECT/ PRESSURE RISE MEASUREMENT
The test part is placed in a sealed bell and the ATEQ F CLASS is pneumatically
connected to the bell. The part is externally pressurised (with up to 20 MPa or 200 bar),
and the bell is lightly pressurised. In the event of a part leakage, the pressure in the bell
will rise. This method allows certain parts to be tested at high pressure levels whilst
avoiding the associated constraints. The ATEQ F CLASS only tests and measures the
pressure in the bell. In the event of a large leak, electronic monitoring of the pressure in
the bell will switch the instrument to safety.
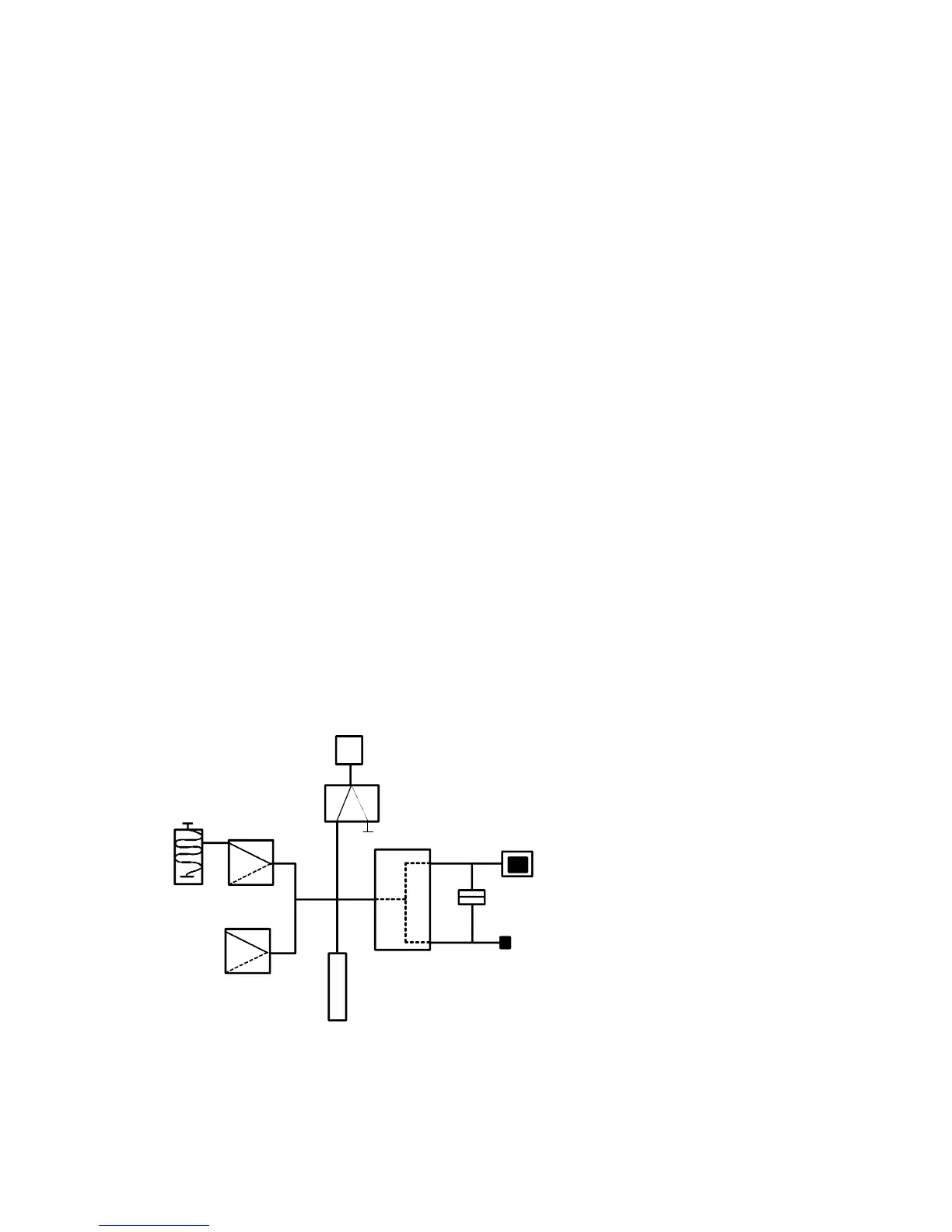
3.3. SEALED COMPONENT MEASUREMENT
INTERNAL VOLUME
FILL
VALVE
REGULATOR
DUMP VALVE
ELECTRONIC
PRESSURE SWITCH
REFERENCE PART
SEALING CONNECTOR
BELL
PART
SENSOR
This test is for hermetically
sealed parts, which can not be
filled. They are placed inside a
bell which is pressurised.
The first and the third measurements may be carried out in comparison with a
reference, without reference or in central zero.

 Loading...
Loading...