Advanced DVB-S2 Receiver Operational Manual
SR1 Specifications
9
4
44
4 SR1 Functionality
4.1
SR1 Integration in Satellite over IP Networks
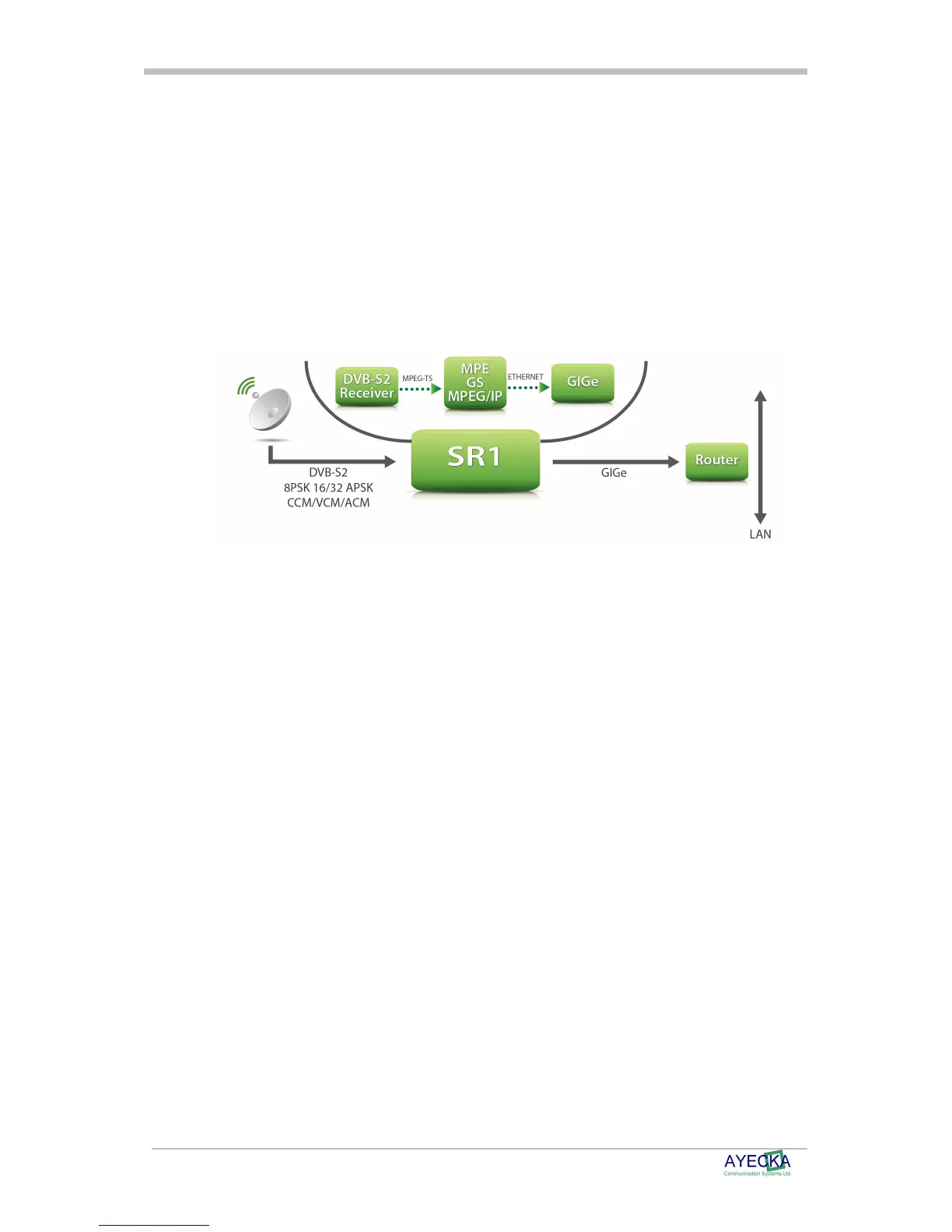
The SR1 is designed to be integrated into IP over satellite network topologies as described in
Figure 1. The Satellite dish (with LNB to receive the signal), and the IP router (which enables
the SR1 to forward the IP packets) are common to all the systems. Figure 1 demonstrates a
general installation scenario of the SR1.
Figure 1 Typical SR1 Installation
The SR1 integration process is described as follows:
The SR1 RF input is connected to the LNB on the satellite dish. SR1 provides the LNB with the
appropriate power and control and receives the DVB-S/S2 signal in L-Band.
The only parameter the operator requires to configure is the RF L-band frequency. The SR1
automatically detects all other parameters.
For a symbol rate below 1 Msps or for modulations higher then 8PSK, a manual configuration
of the symbol rate may be required.
The automatic channel parameters detection enables the operator to change the MODCOD of
the link without the requiring to re-configure the receiver.
The SR1 supports two RF inputs and can be operated either as single demodulator with two RF
inputs or dual demodulators.
The selection between the two Rx channels and the Rx configuration profiles can be performed
manually or automatically.
All the Unicast IP packets that the SR1 extracts from the satellite signal are forwarded to the
router. The SR1 does not support routing functionality what’s so ever.
The IP address of the default router is configured manually. The SR1 uses ARP to find the
MAC address of the router.
The IP address of the default router is not required to be on same subnet as the Traffic
interface of the SR1. The Default router must replies to the ARP request of the SR1.
SR1 supports internal ARP table of 16 entries, making it capable of serving a LAN without a
router. When an MPE section has a destination IP address different to the default router, the
SR1 will initiate an ARP request to learn the MAC address. If a reply is received the SR1 will
keep the match in its internal ARP table. If the table reaches the 17
th
, address, the oldest
entry will be overridden.
In SR1 uses the ARP table IP address and the ARP table IP mask to determine if an incoming
packet is in its subnet and implement the ARP mechanism. If the packet is not in the SR1
 Loading...
Loading...