Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) | 885
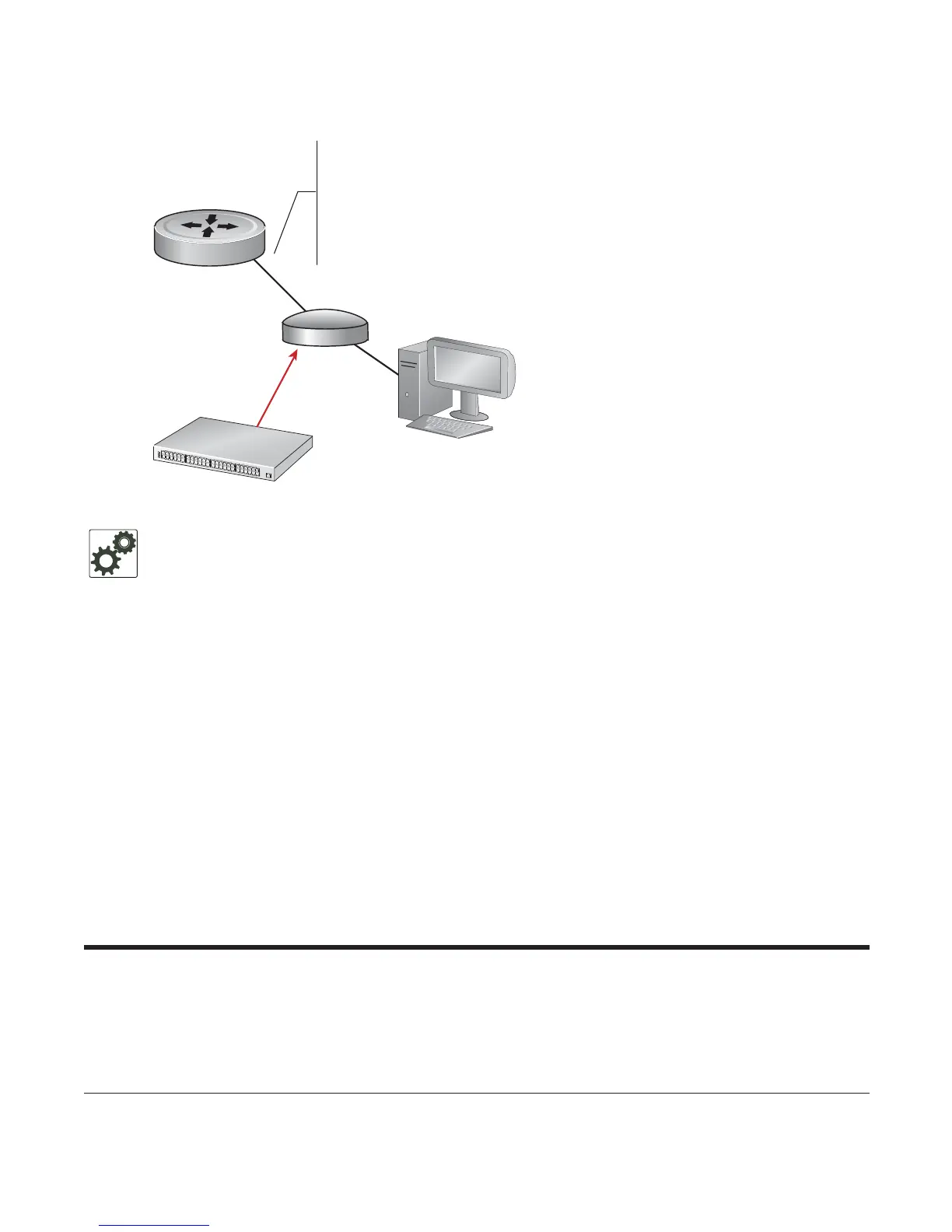
Figure 44-8. Enabling BPDU Guard
STP Root Selection
The Spanning Tree Protocol determines the root bridge, but you can assign one bridge a lower priority to
increase the likelihood that it will be selected as the root bridge. You can also specify that a bridge is the
root or the secondary root.
To change the bridge priority or specify that a bridge is the root or secondary root:
FTOS Behavior: BPDU Guard and BPDU filtering (see Removing an Interface from the Spanning
Tree Group on page 880) both block BPDUs, but are two separate features.
BPDU Guard:
• is used on edgeports and blocks all traffic on edgeport if it receives a BPDU
• drops the BPDU after it reaches the RPM and generates a console message
BPDU Filtering:
• disables Spanning Tree on an interface
• drops all BPDUs at the line card without generating a console message
Task Command Syntax Command Mode
Assign a number as the bridge priority or designate it as the
root or secondary root.
priority-value range: 0 to 65535. The lower the number
assigned, the more likely this bridge will become the root
bridge. The default is 32768.
• The primary option specifies a bridge priority of 8192.
• The secondary option specifies a bridge priority of 16384.
bridge-priority {priority-value |
primary | secondary}
PROTOCOL
SPANNING TREE
Hub
Switch with Spanning Tree Enabled
FTOS(conf-if-gi-3/41)# spanning-tree 0 portfast bpduguard shutdown-on-violati
FTOS(conf-if-gi-3/41)#show config
!
interface GigabitEthernet 3/41
no ip address
switchport
spanning-tree 0 portfast bpduguard shutdown-on-violation
no shutdown
3/41

 Loading...
Loading...











