5050 CONTROL UNIT
Technical Manual & Cabling Instructions
19.10.2012
Epec Oy reserves all rights for improvements without prior notice
Epec Oy Postiosoite/Postal address Puhelin/Phone Fax Internet
Tiedekatu 6 PL/P.O.Box 194 +358-(0)20-7608 111 +358-(0)20-7608 110 www.epec.fi
FIN-60320 Seinäjoki FIN-60101 Seinäjoki, Finland
f
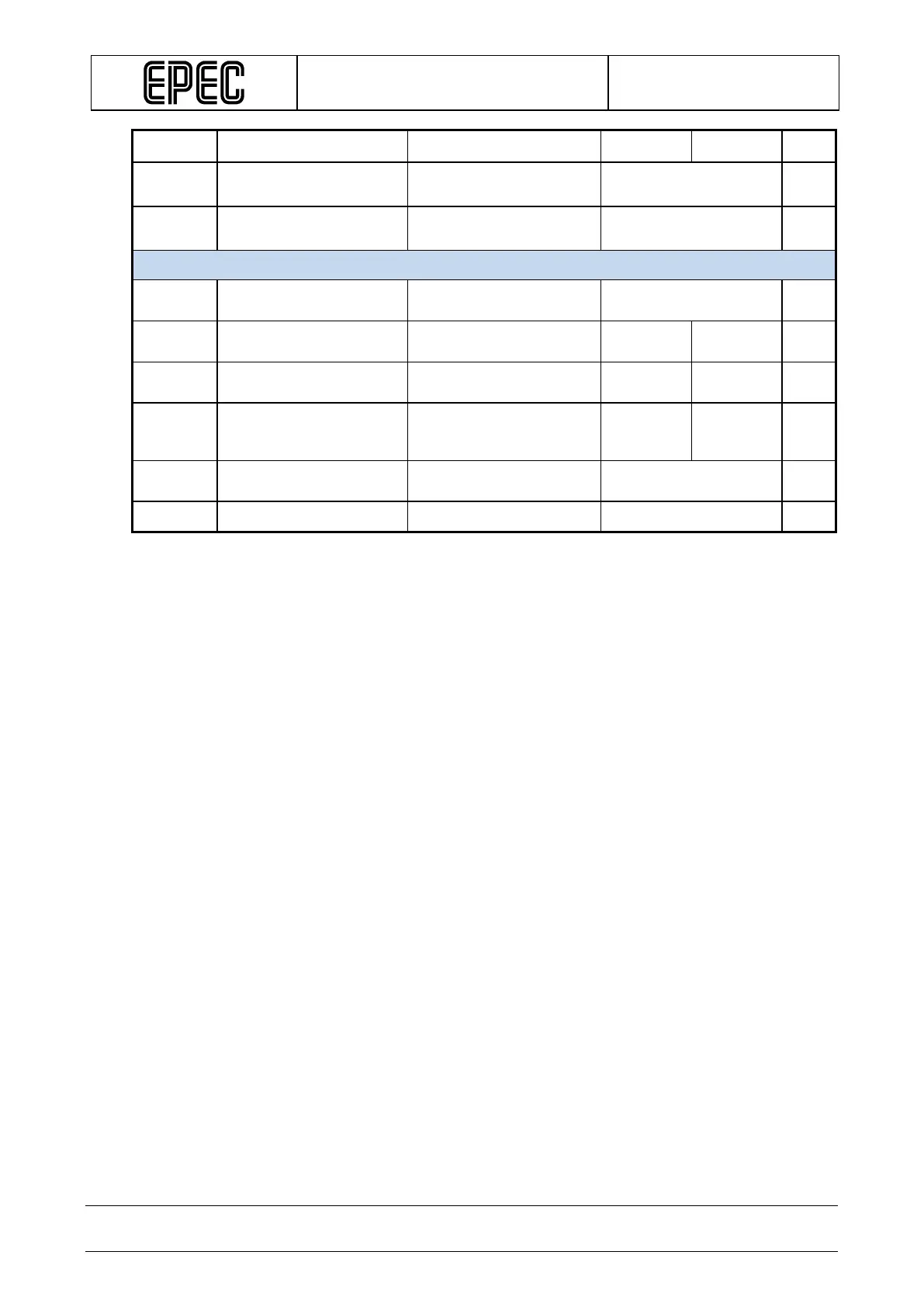
PWM
PWM Frequency (Note 1) 10 3000 Hz
Duty
PWM
PWM
Duty cycle
(Note 2, 10) 0 to 100 %
Res
PWM
PWM Resolution (Note 3) 0,1 %
Digital status input
R
I
Input Resistance
Output Off, Pull-up
typ. 12 kΩ
V
IH
Digital status input
High Voltage level
Output Off (Note6) 3,2 V
V
IL
Digital status input
Output Off
1,9 V
V
I-range
Input voltage range (Note 11) -0,5
VDCPOWERx
+ 0,2V
V
t
I
Digital Status Input
Pulse Width
(Note 2, 4, 8) tC + 25% ms
C
I
Input pin capacitance typ. 1
nF
Note 1: The frequency of a (PWM) Pulse Width Modulation is = 1 / Period
Note 2: The duty cycle is defined as the percentage of digital ‘high’ to digital ‘low’ signals present
during a PWM period.
Note 3: The PWM resolution is defined as the maximum number of pulses that you can pack into a
PWM period.
Note 4: tC denotes the software cycle time.
Note 5: Current limit for short circuit protection to protect cabling and to limit internal power
dissipation.
Note 6: Exceeding the max value might cause damage to input.
Note 7: The maximum output current depends on the load, PWM frequency and temperature.
Note 8: The pulse width must be greater that the software cycle time. For example with 50/50 pulse
ratio, the pulse frequency is 1 / (2*pulse width)
Note 9: When the limit is exceeded, the output voltage circuit starts to limit the current by switching the
output voltage. The switching does not effect the application software
Note 10: When the frequency increases, the actual duty cycle may be bigger than the value that has
been set.
Note 11: Overload conditions
 Loading...
Loading...