Basic Cabling Testing
Noise
7
7-9
Noise
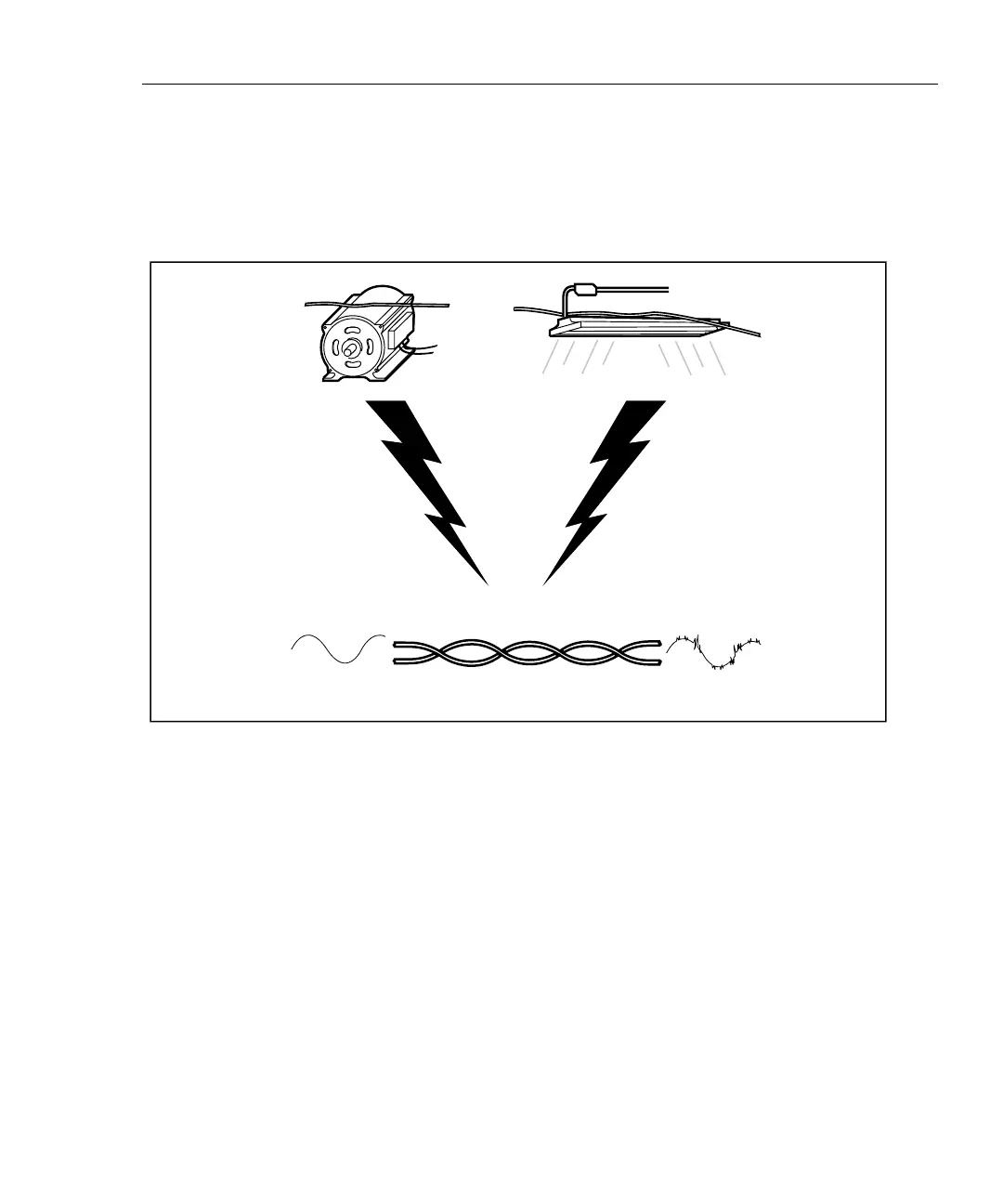
Electrical noise is unwanted electrical signals that alter the shape of the signals
transmitted on a LAN cabling. Figure 7-8 shows an example of how noise affects
the shape of an electrical signal known as a sine wave. Signals that are severely
distorted by noise can cause communication errors in a LAN.
OUT
IN
oy31f.eps
Figure 7-8. Sources of Electrical Noise
Electrical noise is generated by any device that uses or generates voltages that vary
over time. Varying voltage generates a varying electromagnetic field, which
transmits noise to nearby devices in the same way that a radio transmitter transmits
signals to your radio. For example, fluorescent lights, which use 50 Hz or 60 Hz ac
(alternating current) power, continuously radiate a 50 Hz or 60 Hz signal that can
be received by nearby devices as electrical noise.
 Loading...
Loading...










