DMC-1000 Chapter 4 Communication • 35
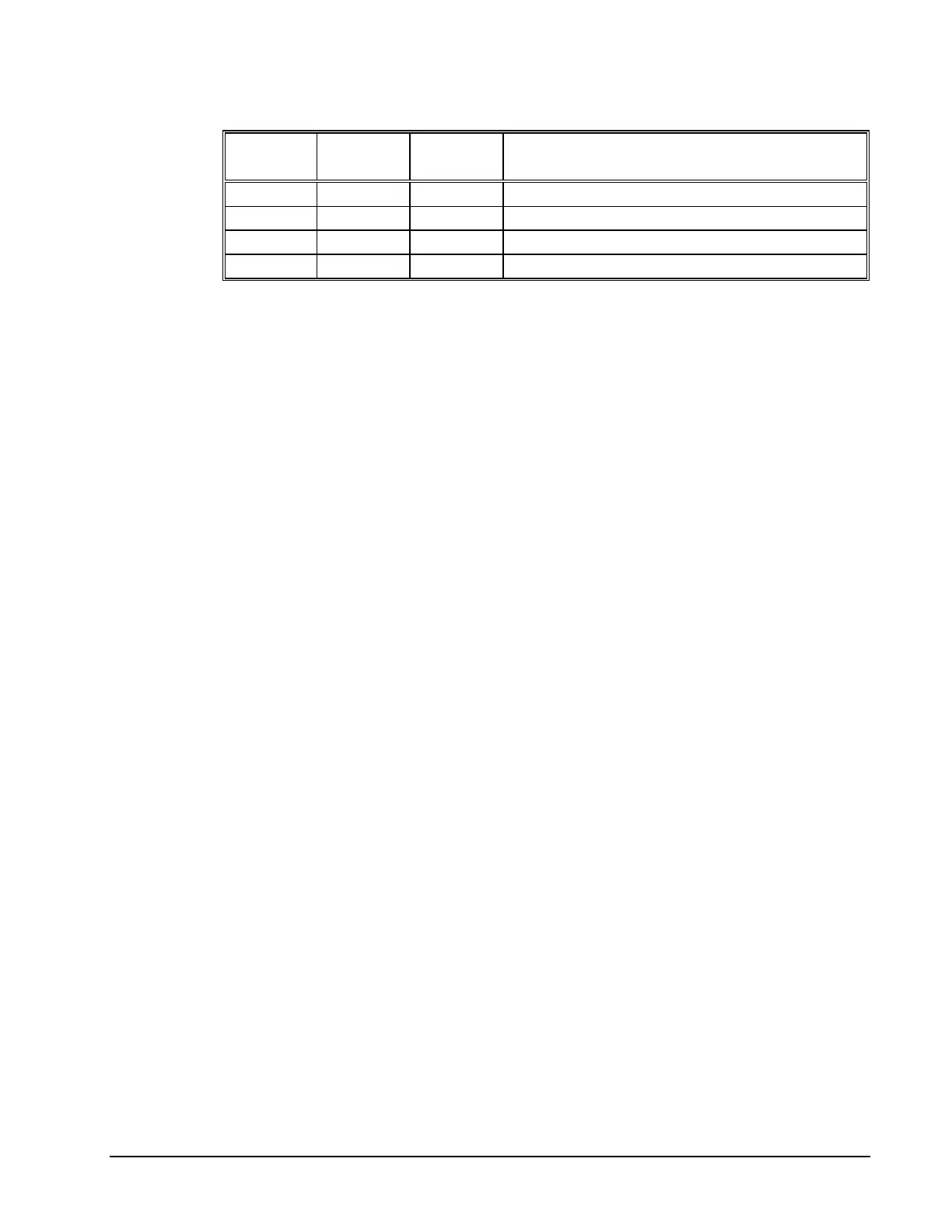
Status Bit Name Logic
State
Meaning
5 READ 0 Data to be read
5 READ 1 No data to be read
4 WRITE 0 Buffer not full, OK to write up to 16 characters
4 WRITE 1 Buffer almost full. Do not send data
Read Procedure
To receive data from the DMC-1000, read the control register at address N+1 and check bit 5. If bit 5
is zero, the DMC-1000 has data to be read in the READ register at address N. Bit 5 must be checked
for every character read and should be read until it signifies empty. Reading data from the READ
register when the register is empty will result in reading an FF hex.
Write Procedure
To send data to the DMC-1000, read the control register at address N+1 and check bit 4. If bit 4 is
zero, the DMC-1000 FIFO buffer is not almost full and up to 16 characters may be written to the
WRITE register at address N. If bit 4 is one, the buffer is almost full and no additional data should be
sent. The size of the buffer may be changed (see "
Changing Almost Full Flags" on pg. 35).
Any high-level computer language such as C, Basic, Pascal or Assembly may be used to communicate
with the DMC-1000 as long as the READ/WRITE procedure is followed as described above.
Example software drivers are contained on the COM-DISK from Galil.
Advanced Communication Techniques
Changing Almost Full Flags
The Almost Full flag (Bit 4 of the control register) can be configured to change states at a different
level from the default level of 16 characters.
The level, m, can be changed from 16 up to 256 in multiples of 16 as follows:
1. Write a 5 to the control register at address N+1.
2. Write the number m-16 to the control register where m is the desired
Almost Full level between 16 and 256.
For example, to extend the Almost Full level to 256 bytes, write a 5 to address N+1. Then write a 240
to address N+1.
Clearing FIFO Buffer
The FIFO buffer may be cleared by writing the following sequence:
Read N+1 address
Send 01H to N+1 address
Send 80H to N+1 address
Send 01H to N+1 address
Send 80H to N+1 address
Read N+1 address (Bit 7 will be 1)
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...