DMC-1000 Chapter 6 Programming Motion • 57
WT50 Wait 50 msec for the knife to engage
BGS Do the circular cut
AMS After the coordinated move is complete
CB0 Disengage knife
MG "ALL DONE"
EN End program
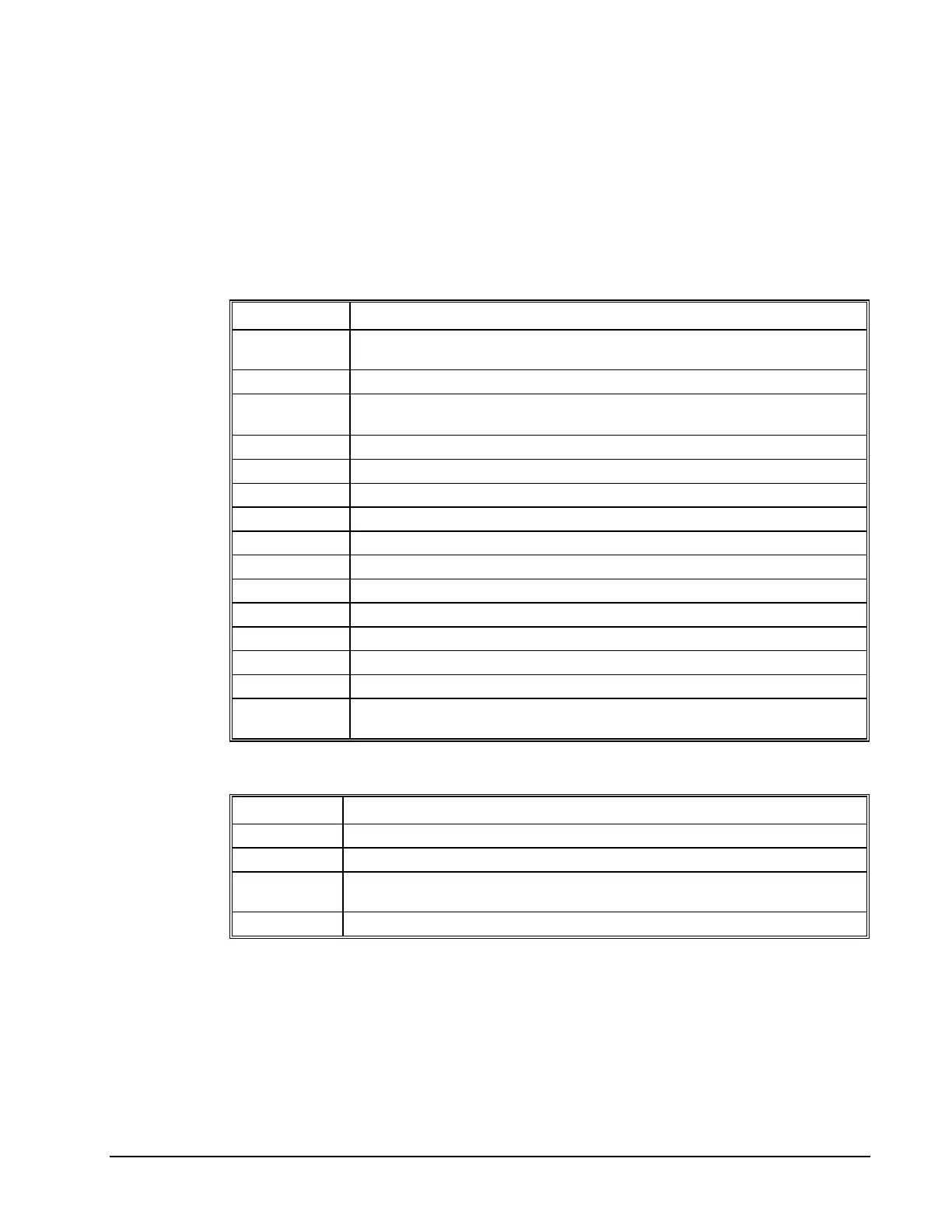
Command Summary - Vector Mode Motion
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
VM m,n Specifies the axes for the planar motion where m and n represent the planar axes and p is
the tangent axis.
VP m,n Return coordinate of last point, where m=X,Y,Z or W.
CR r,Θ, ±ΔΘ Specifies arc segment where r is the radius, Θ is the starting angle and ΔΘ is the travel
angle. Positive direction is CCW.
VS n Specify vector speed or feedrate of sequence.
VA n Specify vector acceleration along the sequence.
VD n Specify vector deceleration along the sequence.
VR n Specify vector speed ratio
BGS Begin motion sequence.
CS Clear sequence.
AV n Trippoint for After Relative Vector distance, n.
AMS Holds execution of next command until Motion Sequence is complete.
TN m,n Tangent scale and offset.
ES m,n Ellipse scale factor.
VT S curve smoothing constant for coordinated moves
LM? Return number of available spaces for linear and circular segments in DMC-1000
sequence buffer. Zero means buffer is full. 512 means buffer is empty.
Operand Summary - Vector Mode Motion
OPERAND DESCRIPTION
_VPM The absolute coordinate of the axes at the last intersection along the sequence.
_AV Distance traveled.
_LM Number of available spaces for linear and circular segments in DMC-1000 sequence
buffer. Zero means buffer is full. 512 means buffer is empty.
_CS Segment counter - Number of the segment in the sequence, starting at zero.
When AV is used as an operand, _AV returns the distance traveled along the sequence.
The operands _VPX and _VPY can be used to return the coordinates of the last point specified along
the path.
Example:
Traverse the path shown in Fig. 6.3. Feedrate is 20000 counts/sec. Plane of motion is XY
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...