70 6LE005550A
Function of the Energy trip unit
3.4 Managing alarms and logs
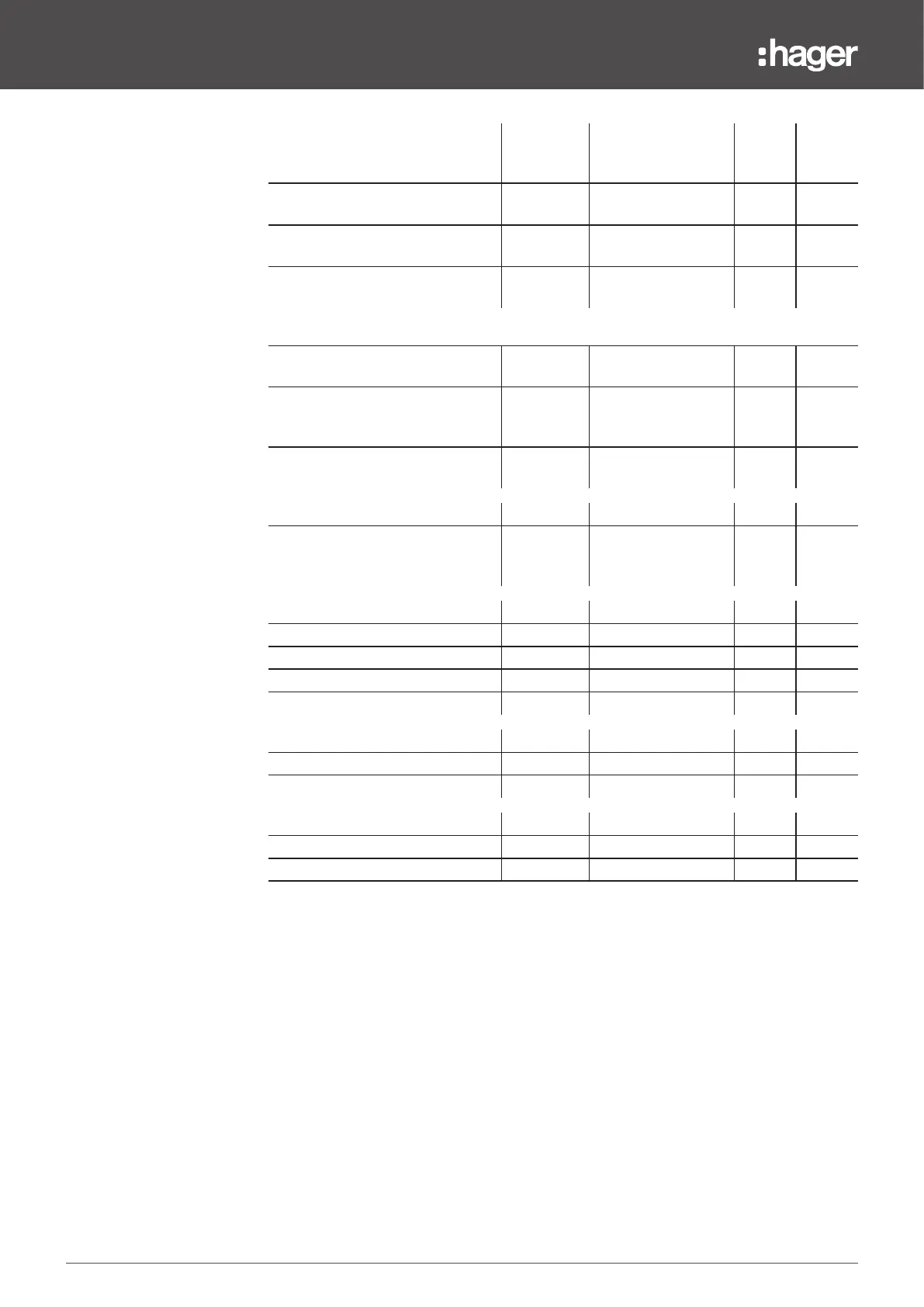
Measurement monitored
Possible
activation
conditions
Activation/
deactivation
threshold ranges
Version
3P
Version
4P
Average currents over interval
(Demand currents)
I1_dmd, I2_dmd, I3_dmd,
Iavg_dmd
>
<
0.2xIn to 10xIn
(increments of 0.1 A)
X X
Current request IN_dmd
>
<
0.2xIn to 10xIn
(increments of 0.1 A)
– X
Averaged power over interval (Demand power)
Total active power Pdmd
>
<
1 kW to 3000 kW
(increments of 0.1 kW)
X X
Total reactive power Qdmd
>
<
1 kvar to 3000 kvar
(increments of 0.1
kvar)
X X
Total apparent power Sdmd
>
<
1 kVA to 3000 kVA
(increments of 0.1 kVA)
X X
Frequency
Frequency
>
<
45 Hz to 65 Hz
(increments of 0.01
Hz)
X X
Quadrant
Operating quadrant 1 =
– X X
Operating quadrant 2 =
– X X
Operating quadrant 3 =
– X X
Operating quadrant 4 =
– X X
Field
Direct rotating field =
– X X
Indirect rotating field =
– X X
Lead or lag circuit
Capacitive circuit (lead) =
– X X
Inductive circuit (lag) =
– X X
3.4.7
Alarm log
The Energy trip unit has an internal memory to enable the following logs to be stored:
- Trip alarm log (up to 10 events)
- Custom alarm log (up to 40 events)
- Log of modifications to trip unit protection settings (up to 5 events per protection
parameter)
These logs are updated after each event.
Trip alarm log
Each trip event is saved with the following information:
- Trip cause
- Phase concerned by the fault (only for long time delay, short time delay and
instantaneous causes)
- Fault current value (only long time delay, short time delay, instantaneous and
ground causes)
- User time
- Machine time
 Loading...
Loading...