6–14 Entering and Evaluating Equations
File name 33s-E-Manual-1008-Publication(1st).doc Page : 386
Printed Date : 2003/10/8 Size : 13.7 x 21.2 cm
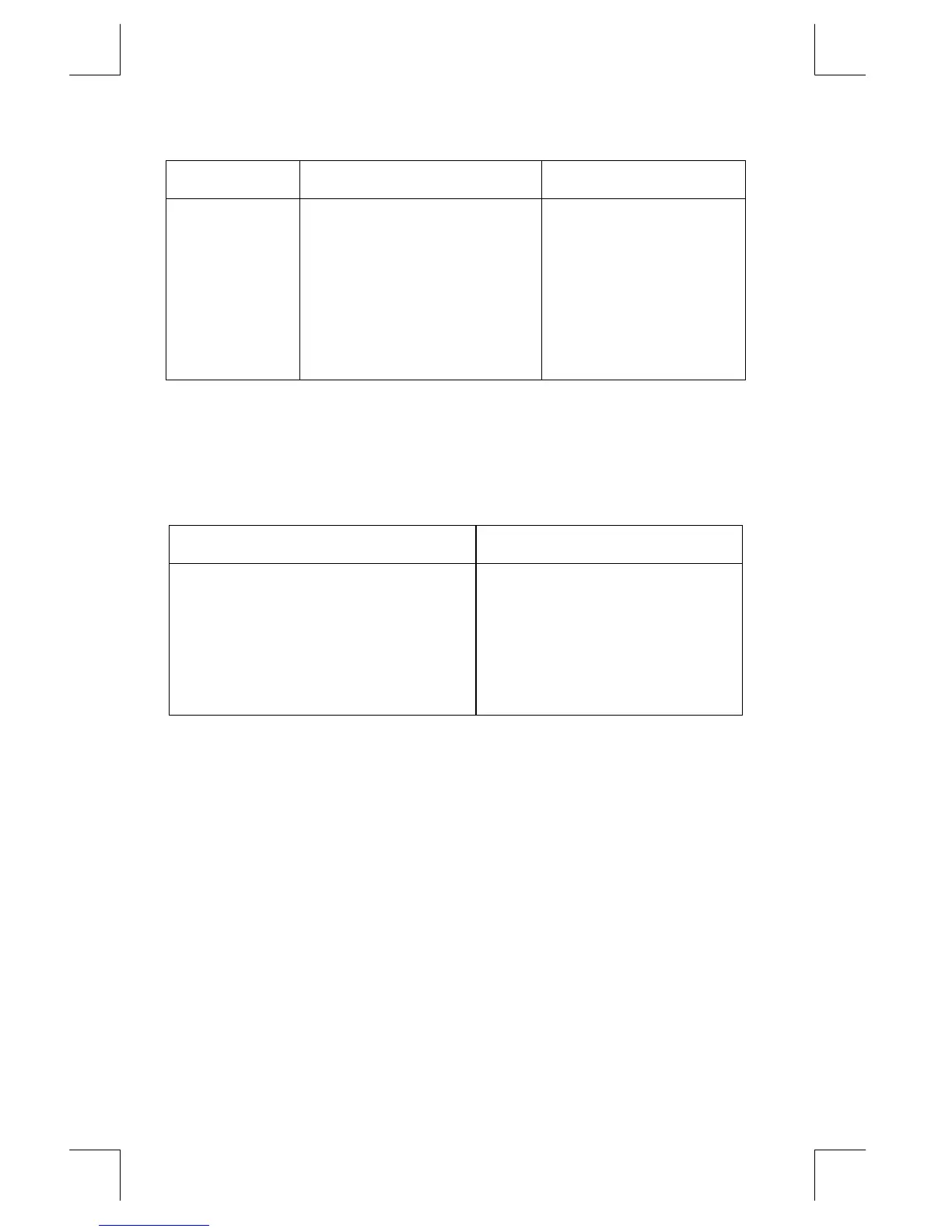
Order Operation Example
1 Functions and Parentheses
,
2 Unary Minus (
z
)
3 Power (
)
)
4 Multiply and Divide
,
5 Add and Subtract
,
6 Equality
So, for example, all operations inside parentheses are performed before
operations outside the parentheses.
Examples:
Equations Meaning
a
×
(b
3
) = c
(a
×
b)
3
= c
a + (b/c) = 12
(a + b) / c = 12
[%CHG ((t + 12), (a – 6)) ]
2
You can't use parentheses for implied multiplication. For example, the expression
p (1 – f) must be entered as
, with the "
" operator inserted between P
and the left parenthesis.

 Loading...
Loading...





