36
Figure 9 GTS
For example, in Figure 10, Switch B performs traffic policing on packets from Switch A and drops
packets exceeding the limit. To avoid packet loss, you can perform GTS on the outgoing interface of
Switch A so that packets exceeding the limit are cached in Switch A. Once resources are released,
GTS takes out the cached packets and sends them out.
Figure 10 GTS application
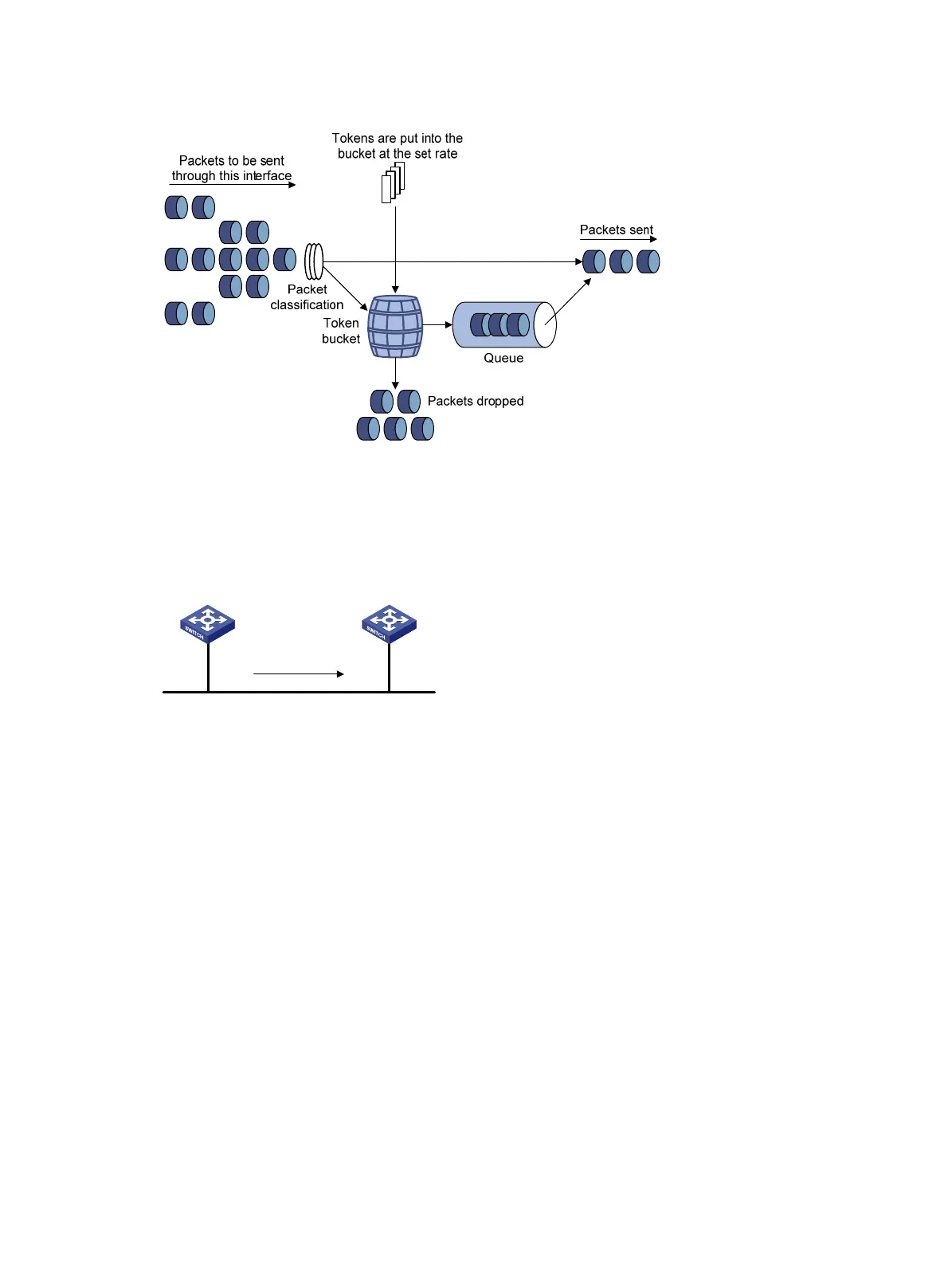
Rate limit
Rate limit controls the rate of inbound and outbound traffic. The outbound traffic is taken for example.
The rate limit of a physical interface specifies the maximum rate for sending or receiving packets
(including critical packets).
Rate limit also uses token buckets for traffic control. When rate limit is configured on an interface, a
token bucket handles all packets to be sent through the interface for rate limiting. If enough tokens
are in the token bucket, packets can be forwarded. Otherwise, packets are put into QoS queues for
congestion management. In this way, the traffic passing the physical interface is controlled.
Device A
Device B
Physical link

 Loading...
Loading...



















