Kaoss Physics
61
Kaoss Physics
Overview
Kaoss Physics models a ball rolling on a surface. You can start the motion by dragging and releasing the on-screen
ball with your mouse or trackpad, or launch the ball automatically using a trigger source such as Gate + Damper. You
can also directly control the ball by dragging without releasing. e position of the ball produces several modulation
signals, which can be used to control any modulation destination:
• Kaoss X is the horizontal position of the ball: negative to the le of center, 0 in the middle, and positive to the right.
• Kaoss Y is the vertical position: negative below the center, 0 in the middle, and positive above the center.
• Kaoss Distance is the distance from the center, which is always positive.
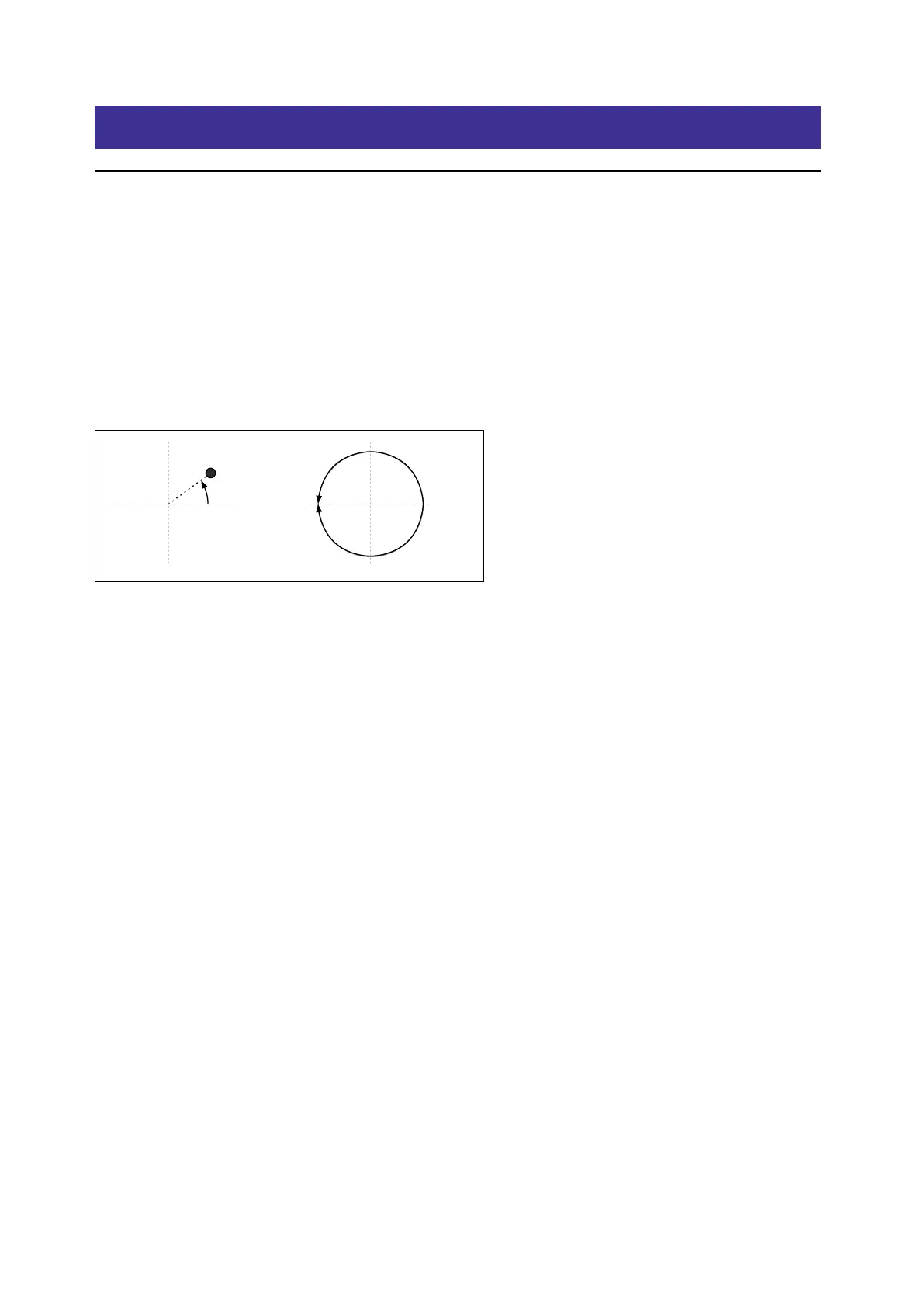
• Kaoss Angle is the current angle of the ball relative to the x axis. e value is always positive, regardless of whether it
is above or below the x axis.
Kaoss Angle
0.0
+1.0
Kaoss Angle
ere is a bump in the surface, going either down or up, like a hole or a hill. You can set the height or depth of the bump,
and choose one of several dierent shapes for its slopes. e surface has adjustable friction, so that the ball slows down
as it travels. ere are walls on the four sides of the surface, and when the ball hits a wall, it bounces o. Walls can slow
down the ball, as if they were padded, or accelerate the ball, like bumpers in a pinball machine. e walls can also be
removed entirely, so that the surface wraps around to the opposite edges like a vintage arcade game.
Note that most parameters, including Tilt, Friction, Time, Bump Height and Position, etc., are modulatable. You can
even modulate them from the Kaoss Physics outputs—for instance, try modulating Tilt X with Kaoss Y.
Using Kaoss Physics to create specic results
Kaoss Physics can be interesting in itself, but you can also use it to create specic modulation eects. For instance:
• Use a centered Bump with negative Height so that the modulation values always eventually return to 0
• Position a Bump with positive Height on a side or a corner, to push modulation values away from that zone
• Set up opposing edges (top and bottom, and/or le and right) so that one has positive Bounce and the other has
negative Bounce, with the result that the ball repeatedly speeds up and slows down
• Use Friction to slow down the ball over time, so that movement ends gradually and naturally
• Use the dierent forces—Tilt, Friction, Bump Height, and Bounce—to oppose and balance one another
Kaoss Physics automation
You can record Kaoss Physics gestures as automation data in your DAW.
e most important automation parameter is Touched (On/O). When you’re directly controlling the ball by dragging
it with the mouse/trackpad, Touched is On, and the absolute x and y position of the ball is recorded as automation data.
When you release the mouse button and “throw” the ball into the Kaoss Physics environment, Touched turns O. e
release position, direction, and velocity of the throw are recorded in high resolution as a set of automation parameters.
e absolute x and y positions of the ball, however, are not recorded. Instead, the automation data is processed by Kaoss
Physics as if you were playing live. Modulation of Kaoss Physics parameters, like Tilt and Time, can change the results
of the recorded gestures.
MIDI Control from the hardware modwave instrument
You can control Kaoss Physics from the x/y pad of a modwave keyboard running soware version 1.1.2 or later.
Make sure that the hardware modwave’s Kaoss Physics CC assignment, on the MIDI CC Assign page, match the

 Loading...
Loading...