© Microhard Systems Inc. Confidential 35
3.0 Mesh Configuration
3.2 Mesh Network
In a Mesh Network Topology, radios can communicate with each other directly or, if required, through
another mesh node. In traditional Point to Multipoint (PMP) and Point to Point (PP or PTP) network to-
pologies a Master is used to not only keep the network synchronized in frequency and time
(synchronization), but all data is also routed through the Master. Using Mesh, data can be sent directly
between devices without the need to route all data through a single unit, which, when offline, brings
down the entire network.
In situations where a direct path is not available between source and destination units, routing can be
enabled to find and provide route information to ensure that data is delivered to the required destination.
A Mesh network can be designed in such a way that redundant paths are available for data transfer,
unknown routes can be auto discovered, and the best path is used to reach the intended destination. If
a path or route changes due to a unit going offline, or moving such as in a mobile application, the net-
work can heal itself by finding a new path to the destination. All this is done without data being routed
through a single point as seen in traditional PMP and P2P networks. Routing features can be enabled
on any unit, coordinators or remotes. Enabling routing on multiple units provides the greatest redun-
dancy, eliminating the risk of any single point of failure.
Any frequency hopping network, even a Mesh Network requires that at least one unit be tasked with the
job (primary coordinator) of making sure all units in the network are hopping at the same time, on the
same frequency. This is accomplished by sending out synchronization data for all units to hear. If the
network grows, or additional coverage is required, additional units can also be tasked with the job of
synchronization (secondary coordinators).
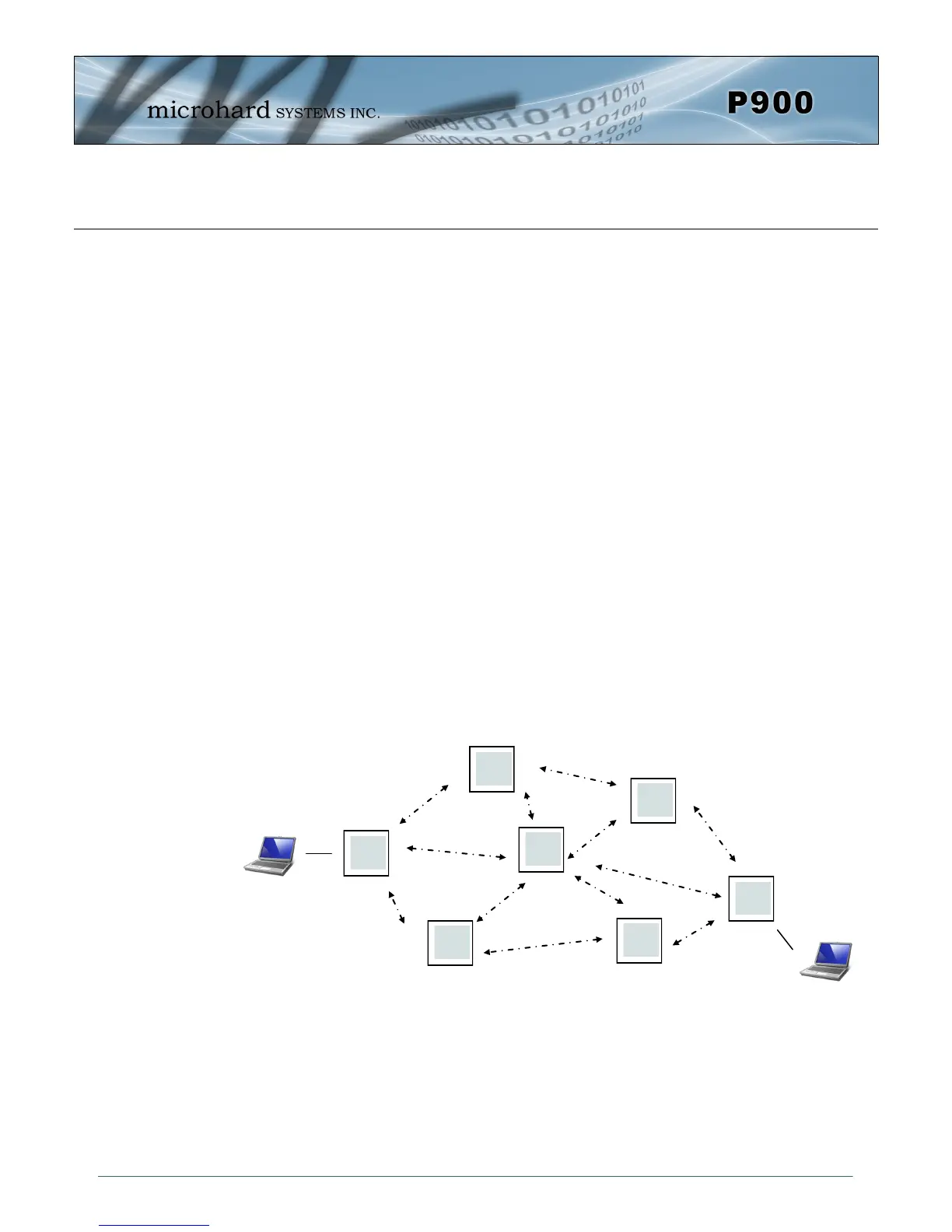
As seen in the illustration below, there are many paths that data could take to each any destination in a
Mesh network. Mesh Networking generally results in achieving extensive network redundancy. Mesh is
enabled by setting register S133 to 2 or 3 (for Mesh with Roaming) (ATS133=2 or ATS133=3, Network
Type).
Mesh
Mesh
Mesh
Mesh
Mesh
Mesh
Mesh
Drawing 3-1: Mesh Network Topology
 Loading...
Loading...