© Microhard Systems Inc. Confidential 66
4.0 Point to Point Configuration
4.2.5 Hop Patterns
Frequency Hopping modems hop from frequency to frequency to allow for multiple networks to share
the same frequency spectrum. The pattern at which the modems hop is known as the hopping pattern.
In the Pico Series modems the hop pattern is pseudo-randomly generated using a complex combination
of the Network ID (S104), Register S106 (or S206), and S180 (or S181), which define which channels
are to be included in the calculation. This ensures that no two networks have the same hopping pattern,
which would cause interference and collisions.
Register S106: The primary Hop Pattern selects the hop pattern to use between a Master or Repeater
to communicate with its associated units. The value set in this register should be the same for each unit
that is to communicate with the specific Master or Repeater. A slave will automatically discover the hop
patterns of its Master/Repeater based on its S118 setting. Setting S106 to match its Master/Repeater
may shorten the discovery process.
S106 = 0 - Primary Hopping Pattern
Register S206: The Secondary Hop Pattern selects a orthogonal, or different, hop pattern with non-
overlapping channels used by repeaters to communication with its’ associated units.
S206 = 1 - Secondary Hopping Pattern
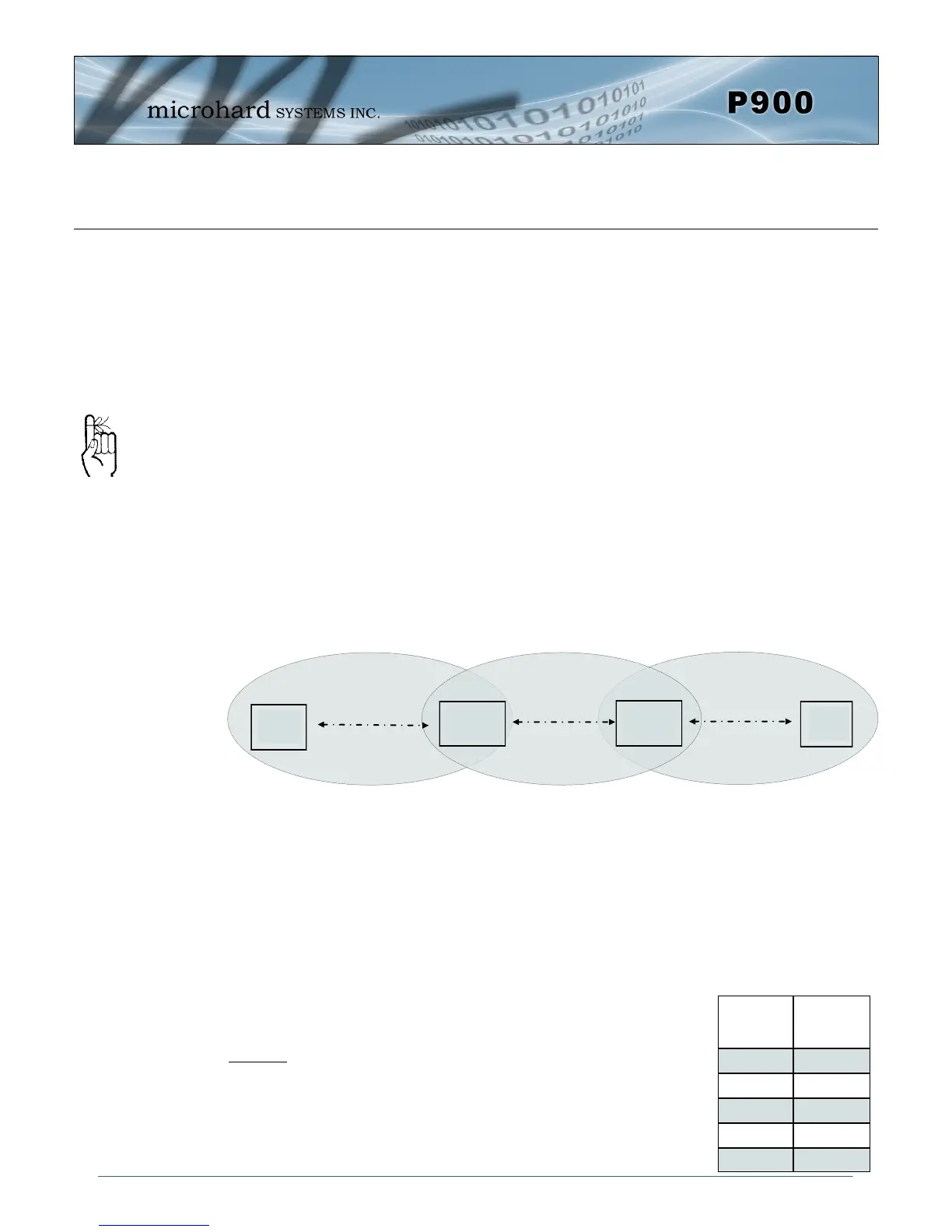
The following illustration should help to describe how to provision the hop patterns in systems with re-
peaters.
Link Rate
(bps)
Channel
Bandwidth
(kHz)
57600 100
115200 200
172800 250
230400 280
276480 350
FCC requires that FHSS systems hop on 50 different channels within the 900 MHz ISM Band. The
maximum time spent on any one channel must not exceed 400ms.
To calculate the center frequency represented by each channel only the starting frequency and the size
of each channel (Channel Bandwidth) need to be known. For the 900 MHz ISM
Band, the starting frequency is 902.4 MHz, and the Channel Bandwidth is dependent on the current link
rate.
Freq channel n = 902.4+ ((n-1) x BW) MHz.
Example: Channel 75 @ 172 kbps = 902.4 +((75-1) x 0.250) MHz
902.4 + (74 x 0.250) MHz
902.4 + 18.5 MHz
920.9 MHz
Slave
Master
Repeater
Primary Hop
Pattern
Secondary
Hop Pattern
Slave
Repeater
Primary Hop
Pattern
S106 =0 S106 = 0
S206 = 1
S106 = 1
S206 = 2
S106 =2
Drawing 4-5: Hop Pattern (PP)
Not every hop pattern is
generated orthogonally
to others, use AT&H26
command for more
information.
 Loading...
Loading...