© Microhard Systems Inc. Confidential 39
3.0 Mesh Configuration
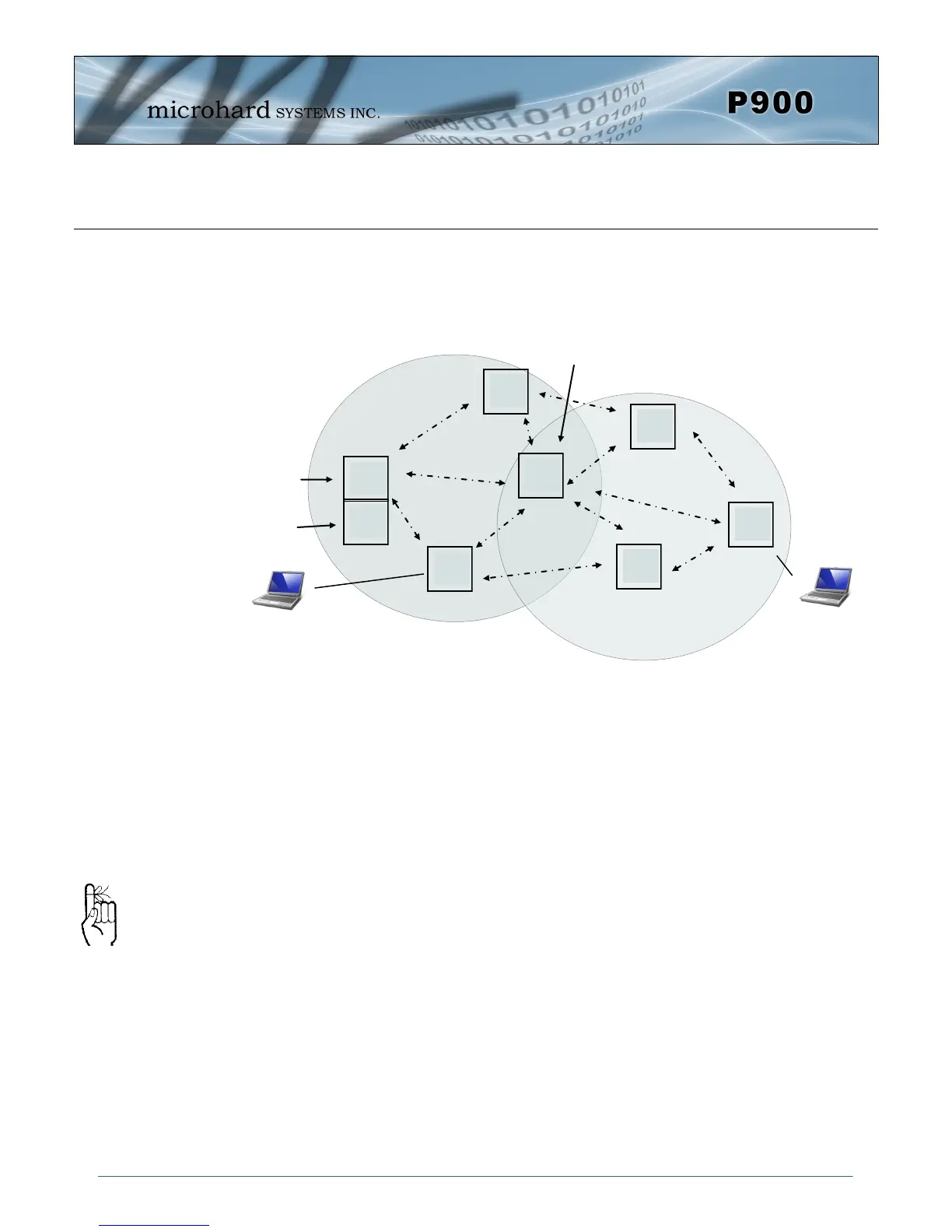
A remote (slave) is any unit that is not a coordinator. A remote is generally connected to an end device,
but it may also be deployed to provide redundant paths to reach other devices in the network. As with
any other device in the network, the remote can be used to provide routing services. Although all units
could be configured to provide routing services, it is not efficient to do so since there would be a great
deal of overhead consuming network bandwidth.
Units can be configured to perform the various roles discussed by setting register S101 as follows:
ATS101 = 2 - Remote (Slave)
ATS101 = 4 - Primary coordinator
ATS101 = 5 - Secondary coordinator
ATS101 = 6 - Standby Coordinator
The next section discusses the use of the factory default settings to set all required registers at once
based on the unit type or role in the network.
3.2.2 Configuration Using Factory Defaults
To aid in the configuration and deployment of the Pico series modules, the factory default settings can
be used as a known starting point for each unit type. Using the factory default commands sets all appli-
cable registers to factory recommended settings and allows initial connectivity between units. For some
networks, these commands may be all that is necessary to configure and deploy a Mesh Network.
AT&F1 - Mesh Primary Coordinator
AT&F2 - Mesh Remote
AT&F3 - Mesh Secondary Coordinator
The following screen shots will illustrate how the commands are used and also highlight the key regis-
ters that have been changed, or need to be changed for a successful deployment.
Rem
P.C.
Rem
Rem
S.C
Rem
Rem
Primary
Coordinator
Stand
by
Standby
Coordinator
Secondary
Coordinator
Each Mesh Network
must have a unique
network ID. This can
be changed using
register S104: Network
Address.
Drawing 3-5: Remote (Slave)
 Loading...
Loading...