How To Verify the Orifice Selection Appendix C: Valve Orifice Selection
54
How To Verify the Orifice Selection
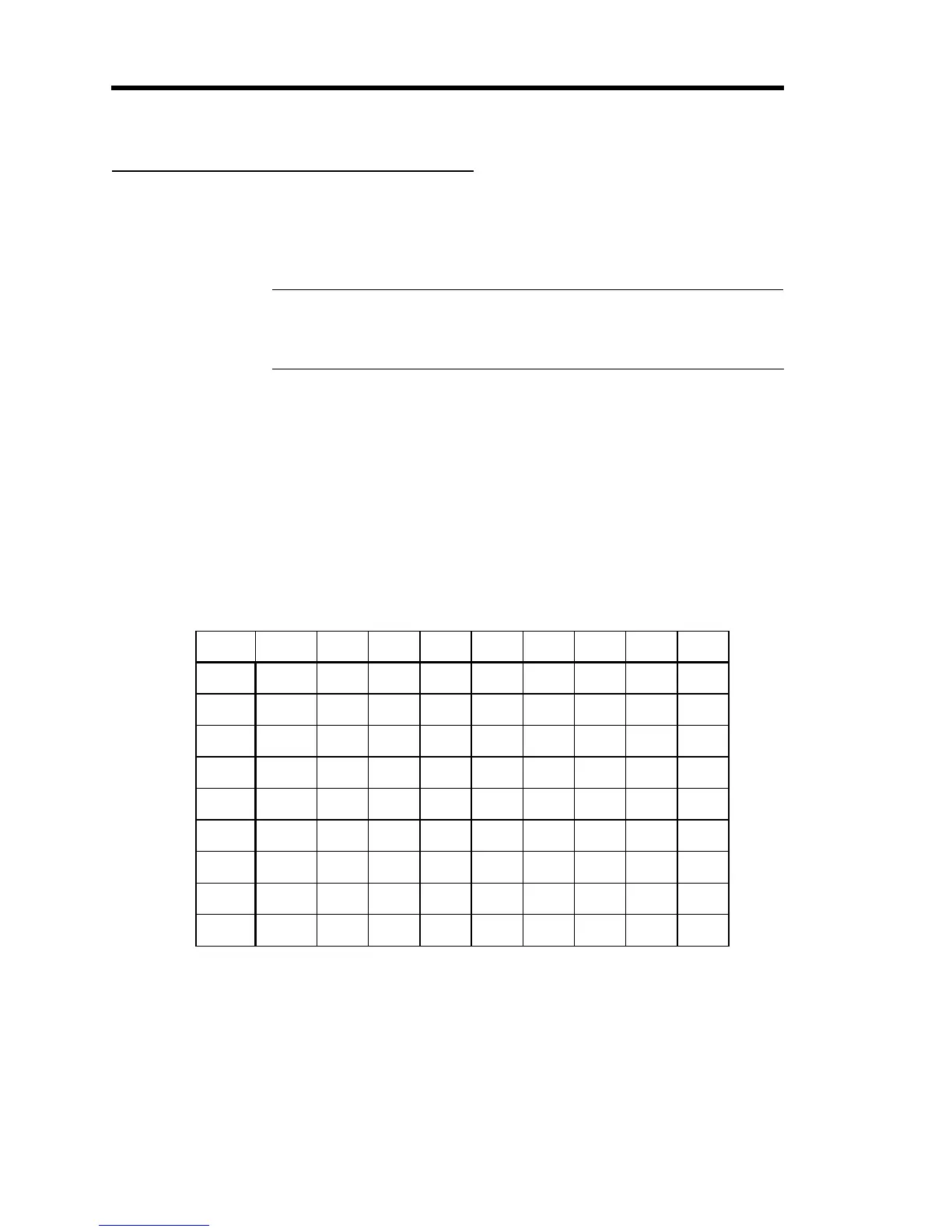
The correct orifice depends on three pieces of information: the upstream pressure, the
downstream pressure, and the flow rate. These instructions assume that you are using nitrogen
gas.
Note
The valves are not calibrated to match the valve orifice selection graph in
Figure 15, page 55. The graph displays
typical valve behavior.
1. Determine the pressure differential (delta P), by subtracting the outlet pressure from the
inlet pressure.
2. Use the inlet pressure and the pressure differential to determine the valve orifice index
number listed in Table 11.
For example, if your inlet pressure is 207 kPa and your outlet pressure is at atmosphere
(103 kPa), the pressure differential (delta P) is 103 kPa. Therefore, your valve orifice
index number would be 175.
Delta Pressure (kPa)
>345 345 207 103 55 28 14 6.9 3.4
689
585 585 480 355 265 190 135 95 65
345
⎯
295 295 240 185 130 95 65 50
207
⎯
⎯
175 175 140 100 75 50 40
Inlet
138
⎯
⎯ ⎯
115 110 80 60 40 30
Pressure 103
⎯
⎯ ⎯
90 90 70 50 35 25
(kPa)
69
⎯
⎯ ⎯ ⎯
60 55 40 30 20
34
⎯
⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
30 25 20 15
14
⎯
⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
10 10 9
6.9
⎯
⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
6 6
Table 11: Valve Orifice Index Number

 Loading...
Loading...