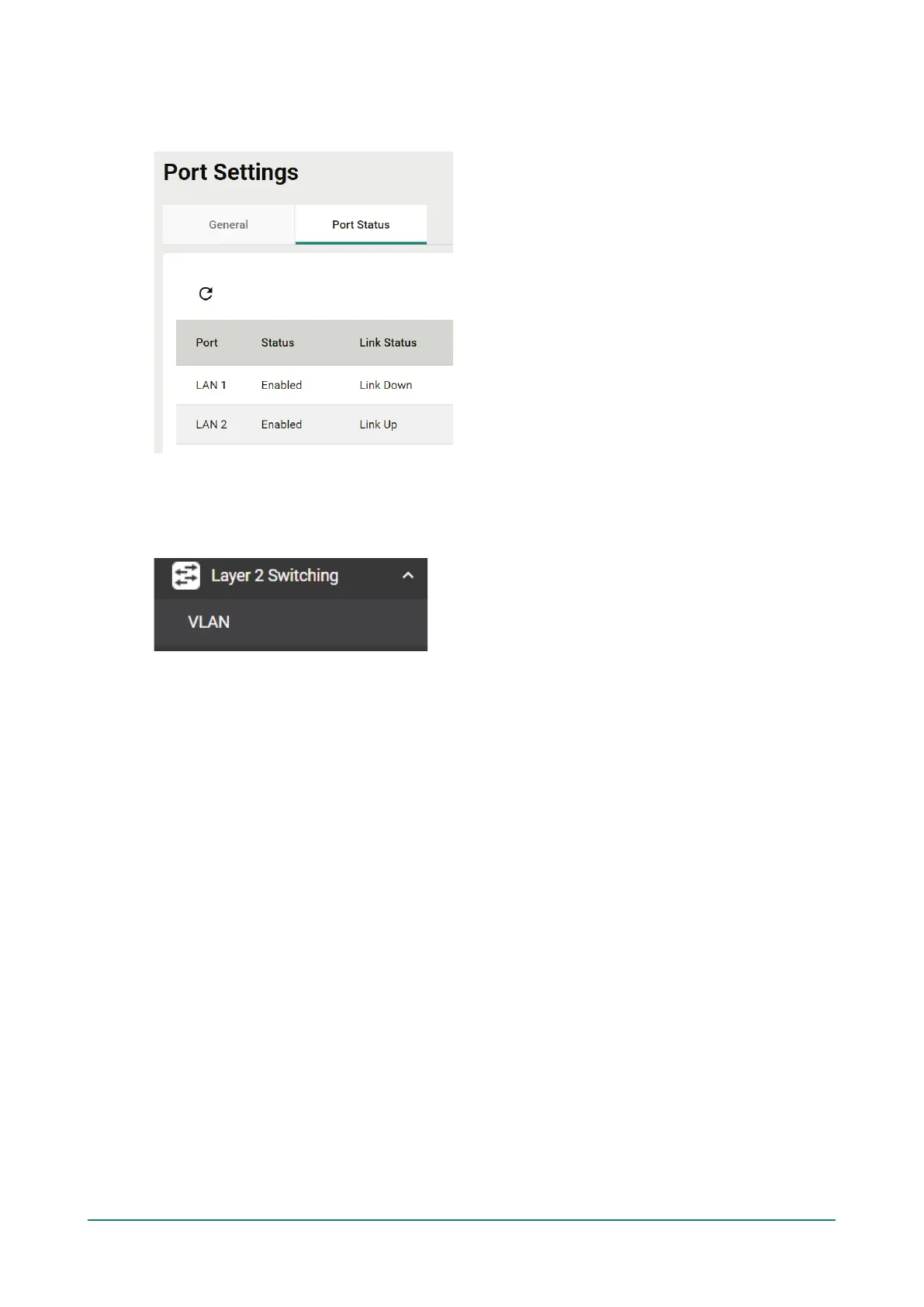
Status Check
Click the Port Status tab to check the current port and port link status.
Layer 2 Switching
This section describes how to configure the VLAN settings for the AWK.
VLAN
The Virtual LAN (VLAN) Concept
What is a VLAN?
A virtual LAN, commonly known as a VLAN, is a group of hosts with a common set of requirements that
communicate as if they were connected to the same broadcast domain, regardless of their physical location.
A VLAN has the same attributes as a physical LAN, but it allows for end stations to be grouped together
even if they are not located on the same network switch. Network reconfiguration can be done through
software instead of physically relocating devices.
VLANs now extend as far as the reach of the access point signal. Clients can be segmented into wireless
sub-networks via SSID and VLAN assignment. A Client can access the network by connecting to an AP
configured to support its assigned SSID/VLAN.
Benefits of VLANs
VLANs are used to conveniently, efficiently, and easily manage your network in the following ways:
• Manage additions, relocations, and changes from a single point of contact
• Define and monitor groups
• Reduce broadcast and multicast traffic to unnecessary destinations
• Improve network performance and reduce latency
• Increase security
• Secure network restricts members to resources on their own VLAN
• Clients roam without compromising security
 Loading...
Loading...