60
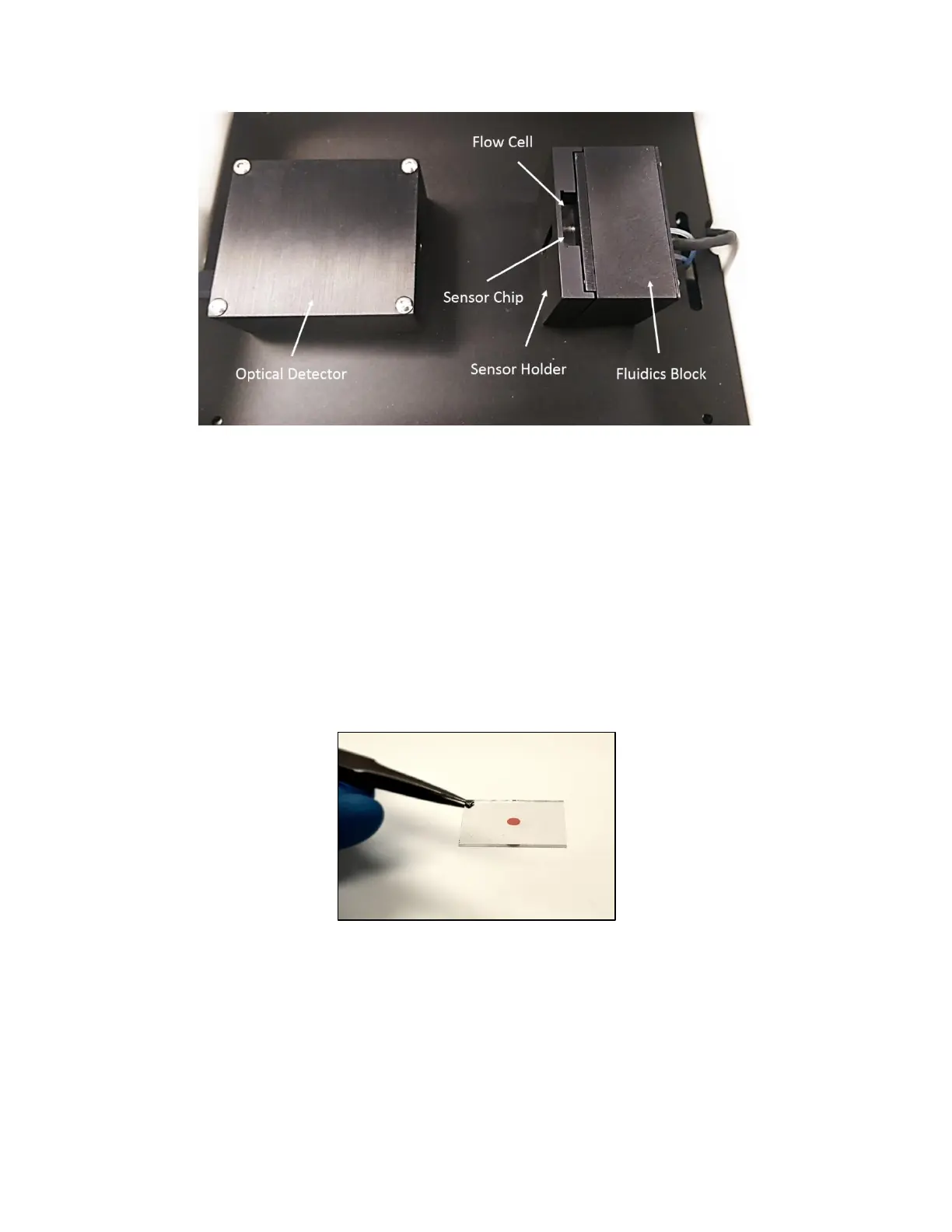
Figure 4.2 - OpenSPR™ instrument setup including optical, fluidic and Sensor Chip components
The Sensor Chips are made of a nanogold coating on glass substrates. An example of a Sensor
Chip is shown below in Figure 4.3. The red spot is the nanogold coating. The optical properties of
this spot are kept highly uniform by our proprietary manufacturing process. Without these Sensor
Chips, the OpenSPR™ system cannot be used. By themselves, these Sensor Chips are highly
sensitive refractive index sensors applicable to any sensing applicable imaginable. For typical SPR
biosensing experiments, the surfaces must be given specific functionality by immobilizing one of
the binding partners (the ligand) onto the surface. There are a number of ways to do this, and
Nicoya Lifescience Inc provides a variety of pre-prepared surface chemistries to ensure consistent
and high quality ligand immobilization. See OpenSPR Kinetics Handbook for more details on the
Sensor Chips.
Figure 4.3 - Sensor Chip with nanogold (red spot)
The optical system is a transmission based spectroscopy setup. It consists of a white light LED and
a high sensitivity spectrometer (the Optical Detector) which measures the absorbance of light
across the visible spectrum (400-700nm). The LED is located in the Fludics block [Figure 4.4]. The
light from the LED illuminates the Sensor Chip, and the spectrometer measures the absorbance
of the nanogold coating. The localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect of the nanogold
coating results in a large absorbance peak near 550nm, which the OpenSPR™ software tracks
 Loading...
Loading...