191
Examples of Applied Control Types Section 5-2
5-2 Examples of Applied Control Types
This section shows examples of applied control types when controlling special
control targets.
As the function blocks of the Loop Controller can be combined as desired
(excluding restrictions on the number of function blocks according to function
block address), use this feature to build a control system suited to your partic-
ular control requirements.
The following table shows the relationship between example control types cor-
responding to special control targets and the purpose of the control.
Note “Special control targets” here refer to the following.
• Processes having a prolonged dead time
• Processes whose dynamic or static characteristics change
• Processes whose dynamic characteristics are not the “regular dead time
+ first-order lag”
• Processes whose non-linearity of dynamic or static characteristics are
large
• Processing involving a large number of variables and strong mutual inter-
action
However, design your system taking into consideration the possibility that the
control target cannot be completely controlled by this Loop Controller (take
into consideration that functions for observing the characteristics of the con-
trol target are required).
5-2-1 Cascade Control
In the following instances, input the MV of PID1 on the primary loop and the
Remote Set Point of PID2 on the secondary loop, and connect the PLC in
series. This configuration is referred to as “cascade control.”
• When there are two controllable processes, and the process to be con-
trolled is one of the processes (PV of primary loop)
• When the other (primary loop) can be controlled by controlling the other of
the two (secondary loop)
• When there is disturbance on the other process (secondary loop), or
when there is dead time until the effect of change on the other (secondary
loop) operated terminal appears in the PV of the other (primary loop)
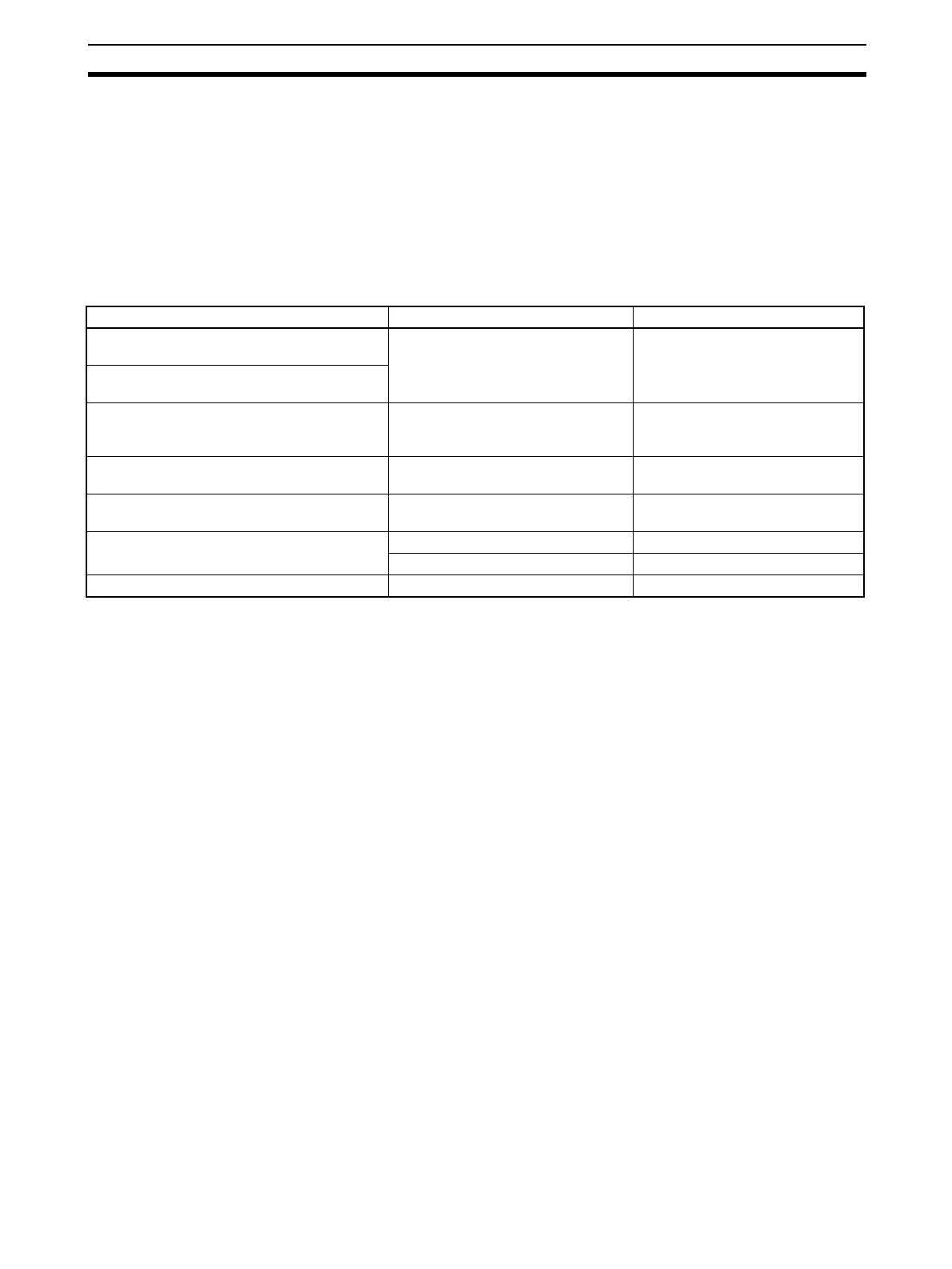
Control purpose Control type example Section
Suppression of disturbance (on secondary
loop)
Cascade control 5-2-1 Cascade Control
Adaptation to dead time from secondary
through to primary loop
Suppression of disturbance (on primary loop)
Suppression of disturbance (on primary and
secondary loops)
Feedforward control 5-2-2 Feedforward Control
Suppression of disturbance (on primary and
secondary loops)
Cascade + feedforward control 5-2-1 Cascade Control/5-2-2
Feedforward Control
Adaptation to mutual interaction between pro-
cesses
Non-interacting control (a type of
feedforward control)
5-2-2 Feedforward Control
Adaptation to dead time Sample PI control 5-2-3 Sample PI Control
Dead time compensation 5-2-4 Dead Time Compensation
Adaptation to changes in dead time Variable sample cycle control 5-2-4 Dead Time Compensation

 Loading...
Loading...











