255
Appendix B
How to Use the Sequence Table Block
Introduction
A sequence table is a table containing multiple rules, each of which execute a specified action when the corre-
sponding condition is established. A sequence table is implemented as a function block with block model 302.
Up to 200 tables can be used. (Block addresses from 701 to 900 can be allocated.)
Note 1. Sequence tables can be used with the LCB05/05D only.
2. The maximum number of tables that can be used is 100 tables if the number of conditions/actions is
expanded from 32 to 64 in all sequence tables, because block addresses are allocated to the expand-
ed portion of the tables in order from block address 701. The maximum number of rules in a table can
also be expanded from 32 to 64. The maximum number of tables that can be used is 50 tables if both
the number of conditions/actions and the number of rules are expanded from 32 to 64 in all sequence
tables.
3. Up to 200 tables can be registered including main tables and reference tables. (LCB01/03/05 Ver. 3.0
or later).
Starting a Sequence Table
A sequence table can be executed with any of the following methods.
• Execute every cycle (always operating).
• Start with S1. (Starts when control switch S1 is ON and stops when S1 is OFF.)
• Start first cycle only. (Start just one time when the Loop Controller starts operation.)
• Do not start.
To specify one of the start conditions listed above, display the sequence table, select Sequence Table Exe-
cute Form from the Operation Menu, and specify the desired method.
Rules
• A single rule is composed of a condition generated by logically ANDing the ON/OFF status of two or more
input signals and an action that turns output signals ON/OFF when that the condition is met (ON) or goes
from not met to met (OFF → ON.)
Note It is also possible to just switch to a specified step without executing an action when the condition is met
or goes from not met to met. (See the following explanation.)
Sequence table ITEM Data Settings
006 Sequence table exe-
cute form
0: Every Cycle
1: Start by S1
2: Start Only First Cycle
3: Not Execute
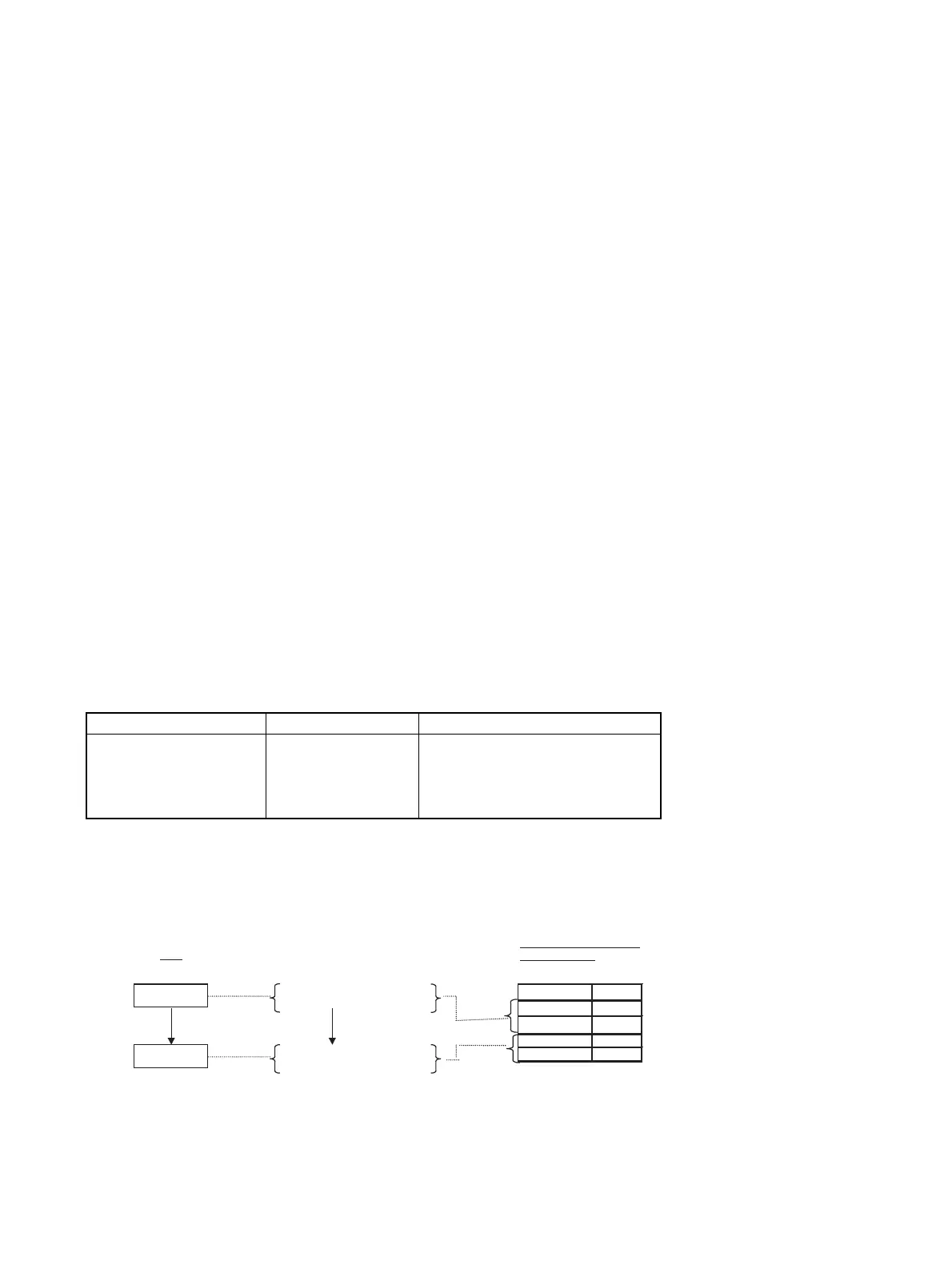
Example action
Action
Condition
Rule description in the
sequence table
Rule
Action
Condition
Turn ON output C and turn
OFF output D.
When input A is ON and input
B is OFF,
Signal Rule
Input A
Y
Input B
N
Output C
Y
Output D
N
 Loading...
Loading...











