208
Promise Technology
Pegasus32 R4/R6/R8
The disk array’s data capacity is equal to the number of disk drive members multiplied by the smallest
drive’s capacity. For example, one 100 GB and three
120 GB drives form a 400 GB (4 x 100 GB) disk array instead of 460 GB.
If physical drives of different capacities are used, there is unused capacity on the larger drives.
RAID 0 logical drives on Pegasus consist of one or more physical drives.
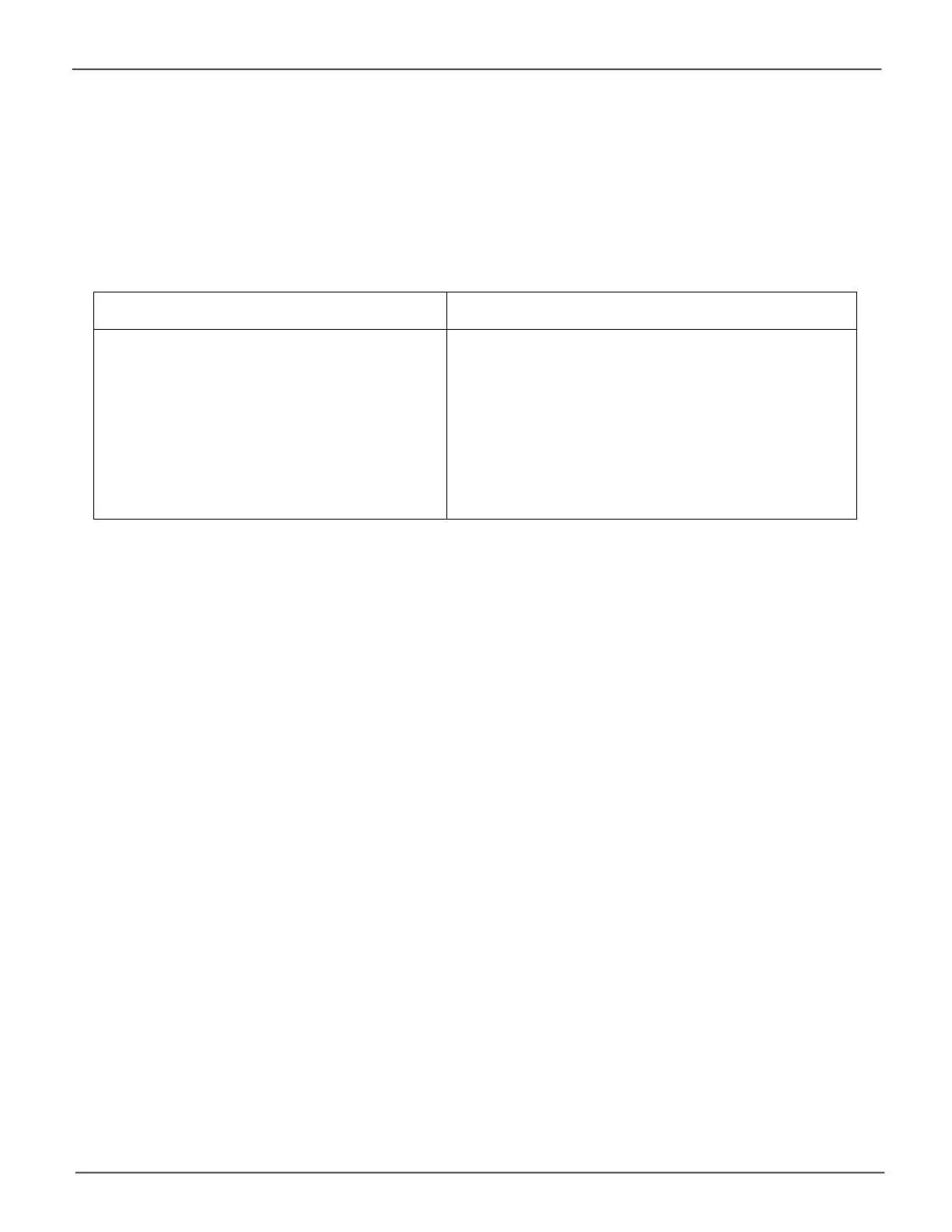
Advantages Disadvantages
• Implements a striped disk array, the data is
broken down into blocks and each block is
written to a separate disk drive
• I/O performance is greatly improved
by spreading the I/O load across many
channels and drives
• No parity calculation overhead is involved
• Not a true RAID because it is not fault-tolerant
• The failure of just one drive results in all data in an
disk array being lost
• Not suitable for mission-critical environments
RecommendedApplicationsforRAID0:
• Image Editing
• Pre-Press Applications
• Any application requiring high bandwidth

 Loading...
Loading...











