211
Technology BackgroundPegasus32 Product Manual
RecommendedApplicationsforRAID1E:
• Imaging applications
• Database servers
• Generalleserver
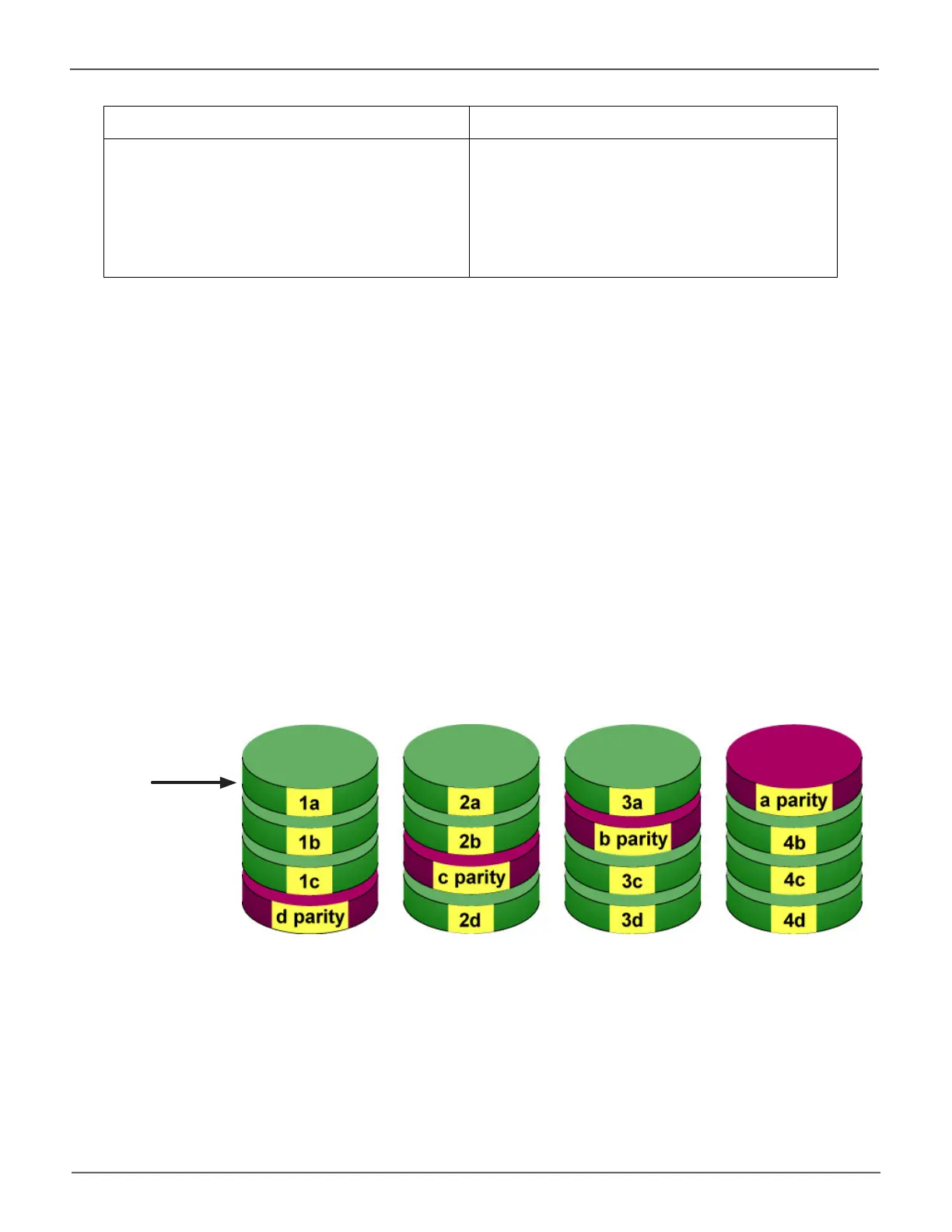
RAID 5 – Block and Parity Stripe
RAID 5 organizes block data and parity data across the physical drives. Generally, RAID Level 5 tends
to exhibit lower random write performance due to the heavy workload of parity recalculation for each
I/O.RAID5isgenerallyconsideredtobethemostversatileRAIDlevel.Itworkswellforle,database,
application and web servers.
RAID 5 stripes all drives with data and parity informaon
The capacity of a RAID 5 logical drive equals the smallest physical drive times the number of physical
drives, minus one. Hence, a RAID 5 logical drive with four 100 GB physical drives has a capacity of
300 GB. A RAID 5 logical drive with two 120 GB physical drives and one 100 GB physical drive has a
capacity of 200 GB. RAID 5 is generally considered to be the most versatile RAID level.
Advantages Disadvantages
• Implemented as a mirrored disk array whose
segments are RAID 0 disk arrays
• High I/O rates are achieved thanks to
multiple stripe segments
• Can use an odd number of disks
• Very high disk overhead – uses only 50% of
total capacity
Distributed Parity
Data
Blocks
Physical Drives

 Loading...
Loading...











