Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-RM003B-EN-P - November 2020 9
Chapter 1
Migration Options
For each Ultra™3000 drive control feature, there is a suitable solution with
Kinetix® 5100 servo drives, Logix 5000™ controller platforms, and the
Studio 5000 Logix Designer® application.
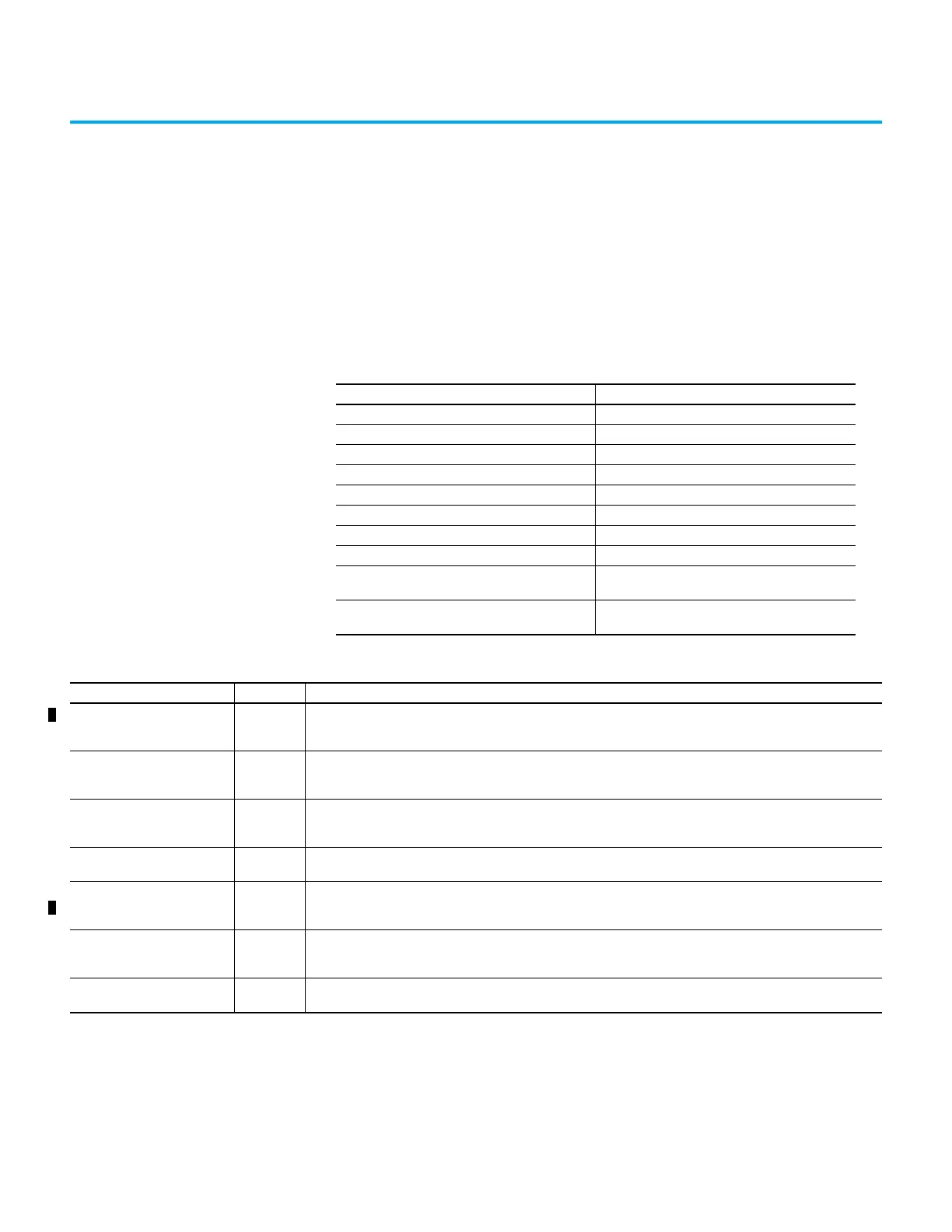
Table 1 - Ultra3000 Drive to Kinetix 5100 Drive Migration Options
Ultra3000 drive Operation Mode Equivalent Kinetix 5100 Drive Operation Mode
Analog Current T mode
Analog Velocity S mode
Analog Postion PT mode
Preset Current T or Tz mode
Preset Velocity S or Sz mode, or PR mode
Preset Position PR mode
Follower PT mode
Indexing PR mode
Host Command
Any mode with Explicit Messaging over EtherNet/IP™
network
DeviceNet
IO mode (with Logix Add-On Instructions) using the
EtherNet/IP network
Table 2 - Kinetix 5100 Drive Control Modes
Control Mode Short Name Description
Position mode (terminal block
input)
PT
This mode is sometimes referred to as Pulse Train. The servo drive receives the Position command and commands the
motor to the target position. The Position command is provided through the I/O terminal block and the signal type is
pulse.
Position mode (register input) PR
The servo drive receives the Position command and commands the motor to the target position. Position commands
comes from the program registers (99 in total). You can select the register number with binary-weighted DI signals or
through communication.
Speed mode S
The servo drive receives the Speed command and commands the motor to the target speed. The Speed command comes
from the internal registers (3 in total) or by analog voltage (-10V…+10V) that is provided through the terminal block. You
can select the command with binary-weighted DI signals.
Speed mode (no analog input) Sz
The servo drive receives the Speed command and commands the motor to the target speed. The Speed command comes
from the internal registers (4 in total, one is fixed at 0). You can select the command with binary-weighted DI signals.
Torque mode T
The servo drive receives the Torque command and commands the motor to the target torque. The Torque command
comes from the internal registers (3 in total) and by analog voltage (-10V…+10V) that is provided through the I/O terminal
block. You can select the command with binary-weighted DI signals.
Torque mode (no analog input) Tz
The servo drive receives the Torque command and commands the motor to the target torque. The Torque command
comes from the internal registers (4 in total, one is fixed at 0). You can select the command with binary-weighted DI
signals.
I/O mode IO
The servo drive receives commands from the Logix controller through the EtherNet/IP network connection. Commands
are issued through the Add-On_Profile (AOP) with Add-On Instruction (AOI) instructions in the Logix Designer application.

 Loading...
Loading...











