BRP-Rotax
Operators Manual
If these gear ratios are still not sufficient, try the next shorter or next longer gear ratio.
NOTE
When using short gear ratios, it may happen that the response behavior of the en-
gine in 1
st
gear is aggressive and the vehicle handling becomes difficult. For a
good lap time, often a longer gear ratio is helpful to achieve reasonable perform-
ance behavior.
NOTE
To help with the choice of adequate gear ratios, the two charts below illustrate the
traditional gear ratios and the top speeds in [kmh] that can be reached in the re-
spective gear at an engine speed of 12.500 rpm.
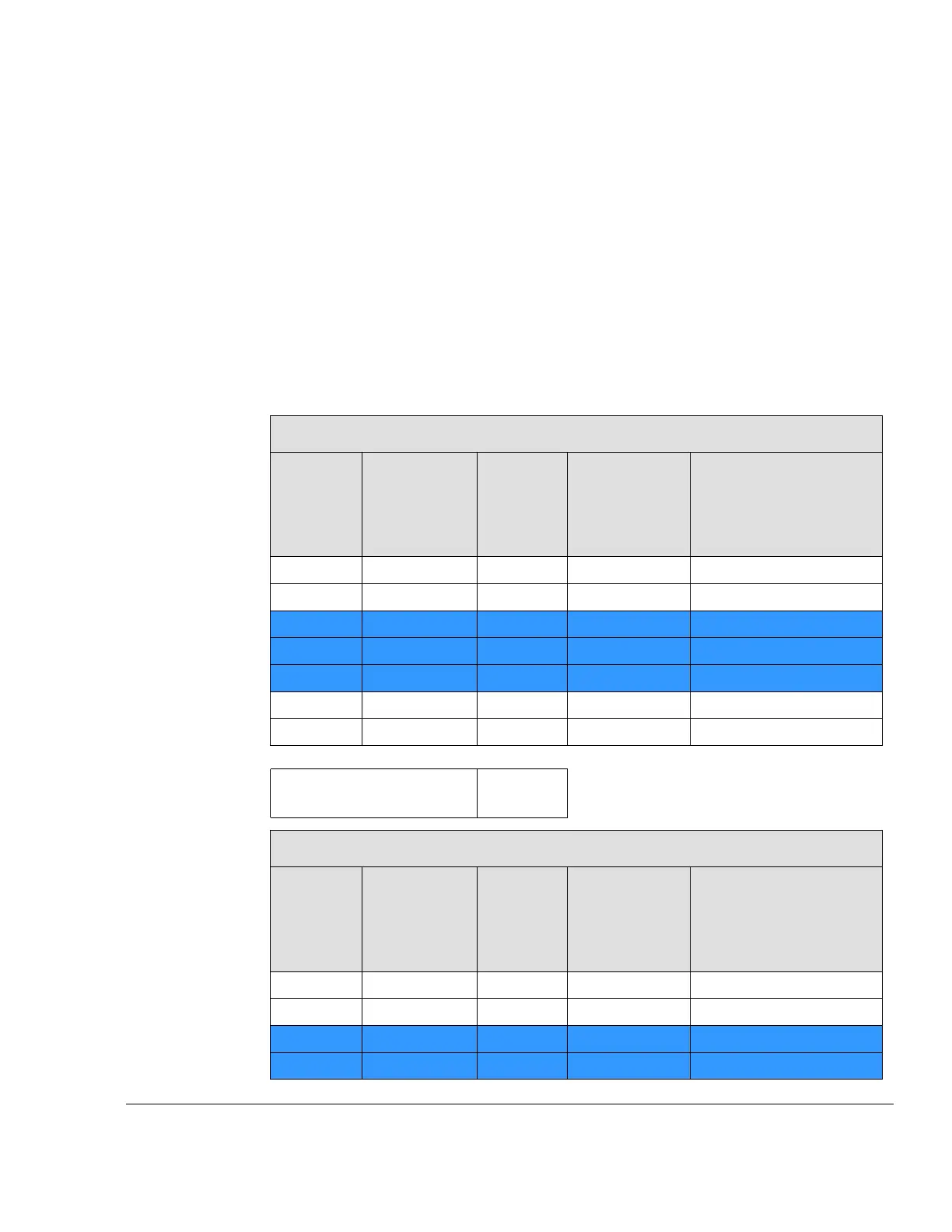
Gear ratio 1
st
gear
Number
of teeth of
primary
drive gear
Number of
teeth of
secondary
drive gear
Gear ratio
Traditional
gear ratio
(in sprocket
size)
Theoretical max. speed
(in km/h / mile/h) (at
12.500 rpm and wheel
diameter 870 mm /34.25
in.)
32 65 8.65 10 to 87
75 / 47
33 64 8.26 11 to 91
79 / 49
34 63 7.89 11 to 87
83 / 52
35 62
7.55
12 to 90
86 / 53
36 61 7.22 12 to 87 90 / 56
37 60 6.91 12 to 83 94 / 58
38 59 6.61 12 to 80
99 / 62
gear ratio of 1
st
gear
(cannot be changed)
4.26
Gear ratio 2
nd
gear
Number
of teeth of
primary
drive gear
Number of
teeth of
secondary
drive gear
Gear ratio
Traditional
gear ratio
(in sprocket
size)
Theoretical max. speed
(in km/h / mile/h) (at
12.500 rpm and wheel
diameter 870 mm /34.25
in.)
32 65 6.52 14 to 91 100 / 62
33 64 6.23 14 to 87
105 / 65
34 63 5.95 14 to 83
110 / 68
35 62 5.69 14 to 79
115 / 72
Effectivity: 125 MAX DD2 evo
3
Page 15
Edition: September 01 2019

 Loading...
Loading...