IEC 61158 Data Highway
Publication PUB089-005-00_0618 25 of 116
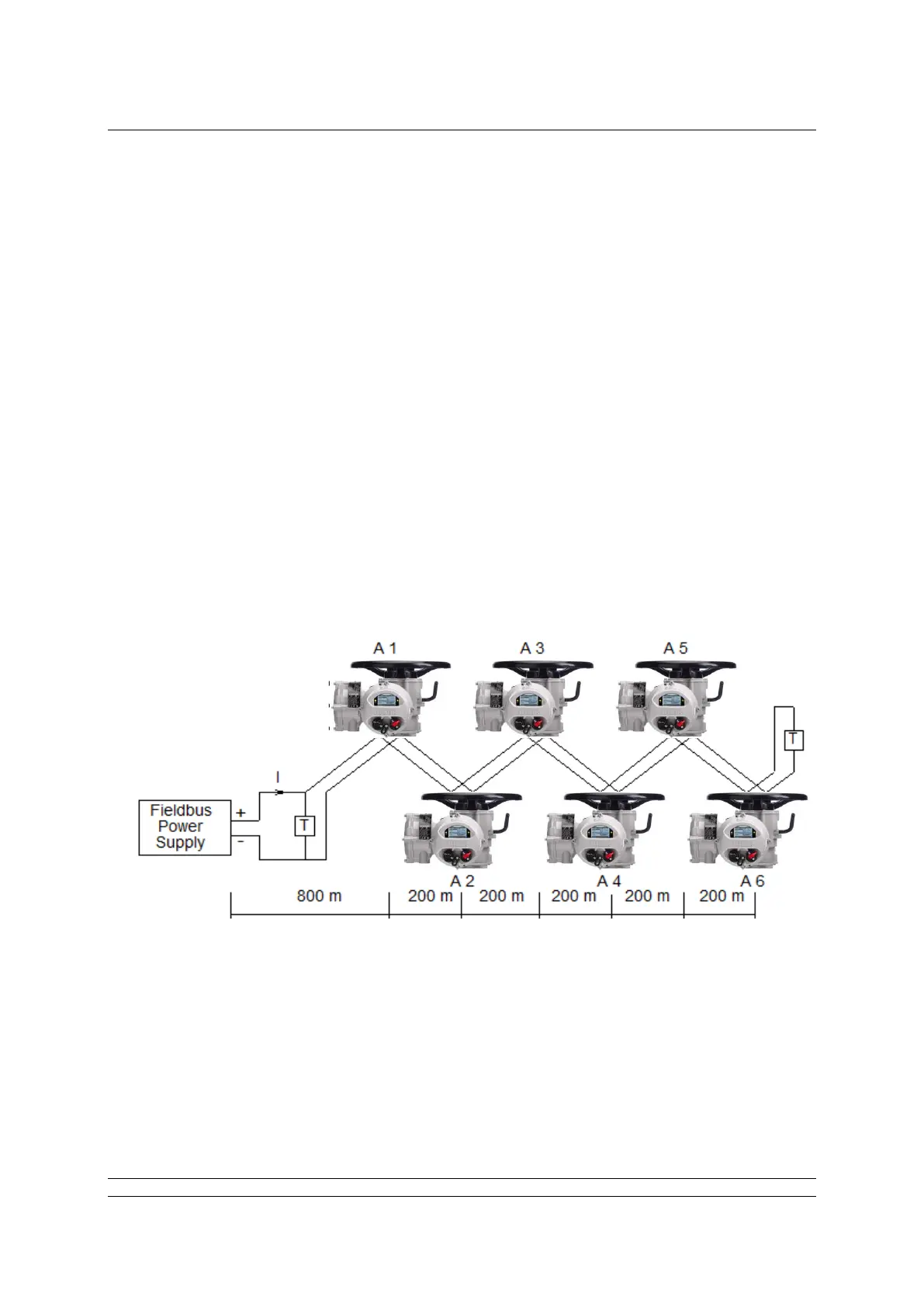
Example of voltage drop calculation:
Assume the cable is Type A (24 Ohm per km per conductor), the resistance of each 1000 metre pair
is 24 x 2 = 48 Ohms per km.
The current drawn by each node A1 to A6 is 20 mA.
Voltage drop Power supply to A1 = current x resistance
= (6 x 0.020) x (0.8 x 48) = 4.6 volts
Voltage drop A1 to A2 = (5 x 0.020) x (0.2 x 48) = 0.96 volts
Voltage drop A2 to A3 = (4 x 0.020) x (0.2 x 48) = 0.768 volts
Voltage drop A3 to A4 = (3 x 0.020) x (0.2 x 48) = 0.576volts
Voltage drop A4 to A5 = (2 x 0.020) x (0.2 x 48) = 0.384volts
Voltage drop A5 to A6 = (1 x 0.020) x (0.2 x 48) = 0.192volts
Total system volt drop = 4.6 + 0.96 + 0.768 + 0.576 + 0.384 + 0.192 = 7.48 volts
If the power supply is a 24 V unit, then the voltage at actuator A6 will be (24 – 7.48) = 16.52 volts
which is within the specified limits.
Whilst we have shown the power supply at one end of the segment, they can be fitted to the middle of
the network. This would reduce the voltage drop.
 Loading...
Loading...