3. If the result S is > 500 mm, then recalculate S as follows:
S = 1,600 mm/s × T + 8 ×(d – 14 mm)
4. If the new value S is > 500 mm, then use the newly determined value as the mini‐
mum dis
tance.
5. If the new value S is ≤ 500 mm, then use 500 mm.
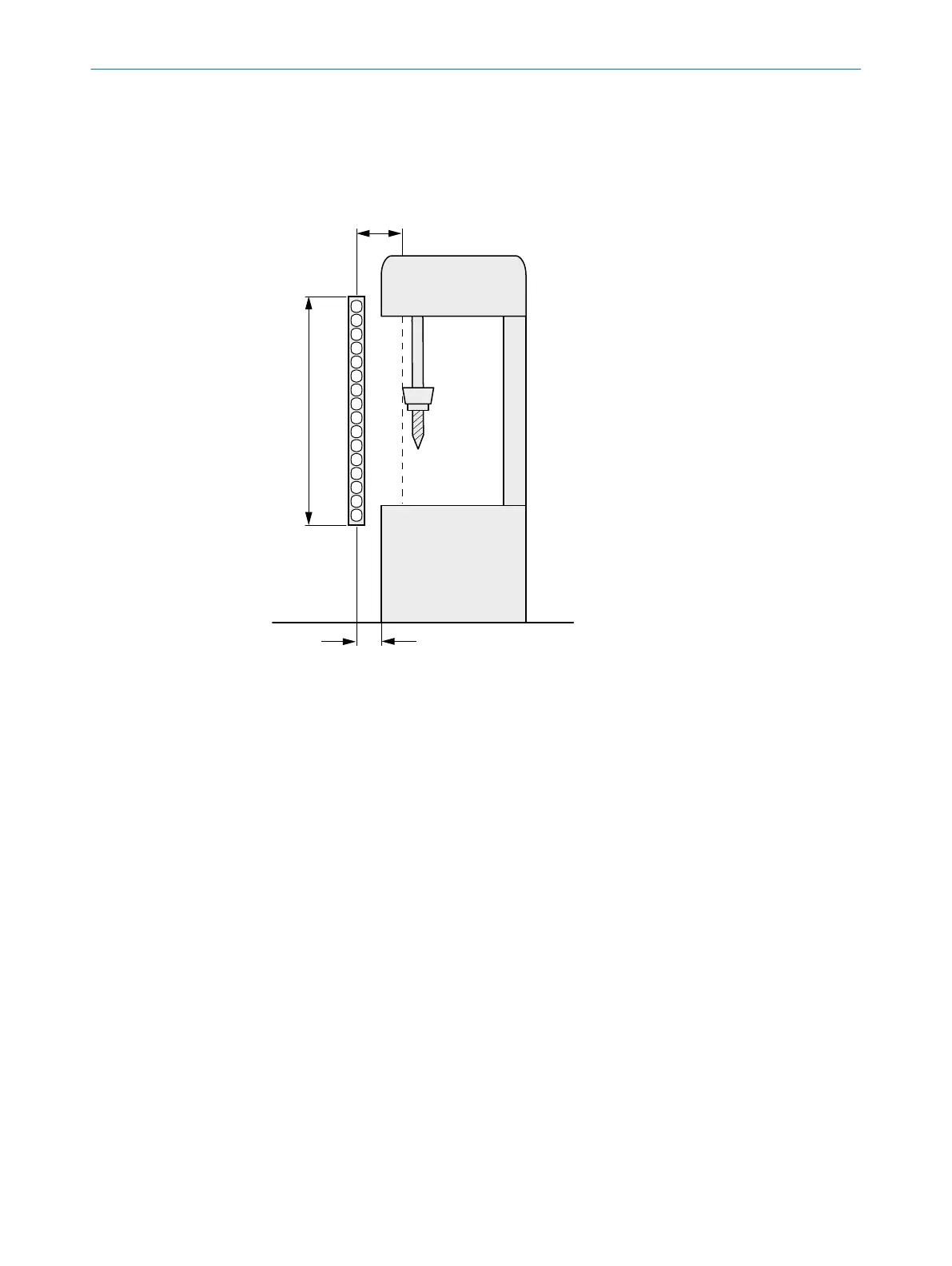
Figure 7: Minimum distance to hazardous point for orthogonal (right-angled) approach to protec‐
t
ive field
1
Minimum distance S
2
Protective field height
3
Hazardous point
4
Depending on the application and distance, persons must be prevented from standing
behind the protective device.
Example calculation
Mac
hine stopping time = 290 ms
Response time after interruption of the light path = 30 ms
Resolution of the safety light curtain = 14 mm
T = 290 ms + 30 ms = 320 ms = 0.32 s
S = 2,000 mm/s × 0.32 s + 8 × (14 mm – 14 mm) = 640 mm
S > 500 mm, therefore:
S = 1,600 mm/s × 0.32 s + 8 × (14 mm – 14 mm) = 512 mm
4.3.2.2 Taking reach over into account
If access to the hazardous area by reaching over a protective field cannot be prevented,
t
he height of the protective field and minimum distance of the ESPE must be deter‐
mined. This is done by comparing the calculated values based on the possible detec‐
tion of limbs or body parts with the values resulting from reaching over the protective
field. The greater value resulting from this comparison must be used.
4 P
ROJECT PLANNING
20
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | deTec4 Core 8014253/ZOH3/2017-08-04 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...