Figure 8: Representation of the accessibility of electro-sensitive protective device by reaching
o
ver. Left: Protective field that cannot be reached over. Right: Protective field that can be reached
over.
4.3.3 Minimum distance to reflective surfaces
Overview
T
he light beams from the sender may be deflected by reflective surfaces and dispersive
media. This may prevent an object from being detected.
Therefore, all reflective surfaces and objects (e.g. material bins, machine table, etc.)
must maintain a minimum distance (a) from the protective field. This minimum dis‐
tance (a) must be maintained on all sides of the protective field. This applies in horizon‐
tal, vertical and diagonal directions as well as at the end of the safety light curtain. The
same area must be free of dispersive media (e.g., dust, fog, or smoke).
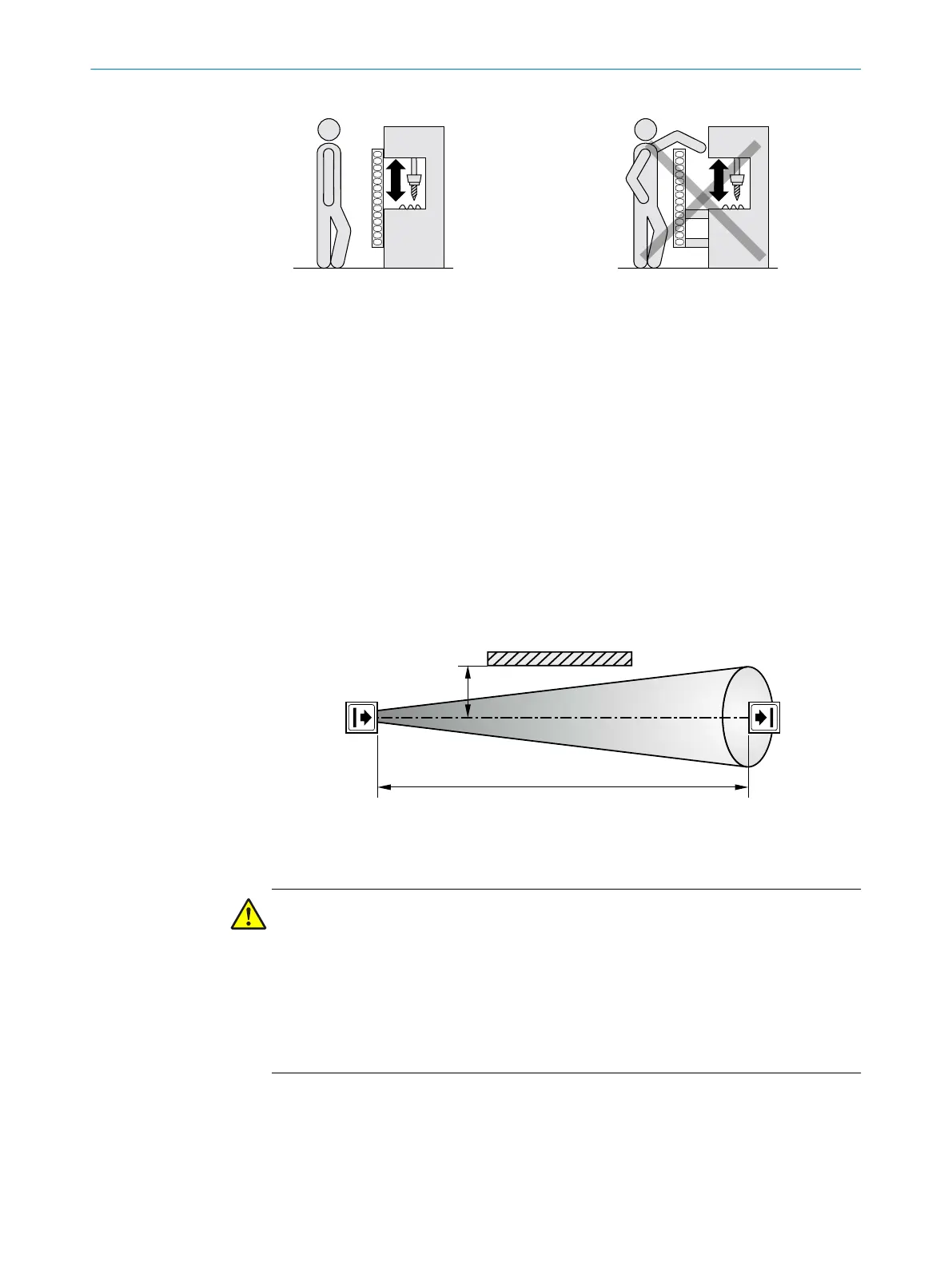
The minimum distance (a) depends on the distance (D) between sender and receiver
(protective field width).
Figure 9: Minimum distance from reflective surfaces
Important information
DANGER
H
azard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
Reflective surfaces and dispersive media can prevent persons or parts of the body to
be protected from being properly reflected and, therefore, remain undetected.
b
Make sure that all reflective surfaces and objects maintain a minimum distance
from the protective field.
b
Make sure that no dispersive media (e.g., dust, fog, or smoke) are within the calcu‐
lated minimum distance from the protective field.
Determining minimum distance to reflective surfaces
b
D
etermine the distance between sender and receiver D in meters (m).
b
Read the minimum distance a in millimeters (mm) in the graph or calculate it
based on the respective formula table 1:
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8014253/ZOH3/2017-08-04 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | deTec4 Core
21
Subject to change without notice

 Loading...
Loading...