Block calls can be unconditional or conditional as follows:
Unconditional call
The "JU" statement belongs to the unconditional operations. It has no
effect on the RLO. The RLO is carried along with the jump to the new
block. Within the new block, it can be evaluated but no longer
combined logically.
The addressed block is processed regardless of the previous result of
logic operation (RLO - see Section 3.4).
Example: JU PB 100
Conditional call
The JC statement belongs to the conditional operations. The addressed
block is processed only if the previous RLO = 1. If the RLO = 0, the
jump is not executed.
Example: JC PB 100
Note
After the conditional jump operation is executed, the RLO is set
to "1" regardless of whether or not the jump to the block is
executed.
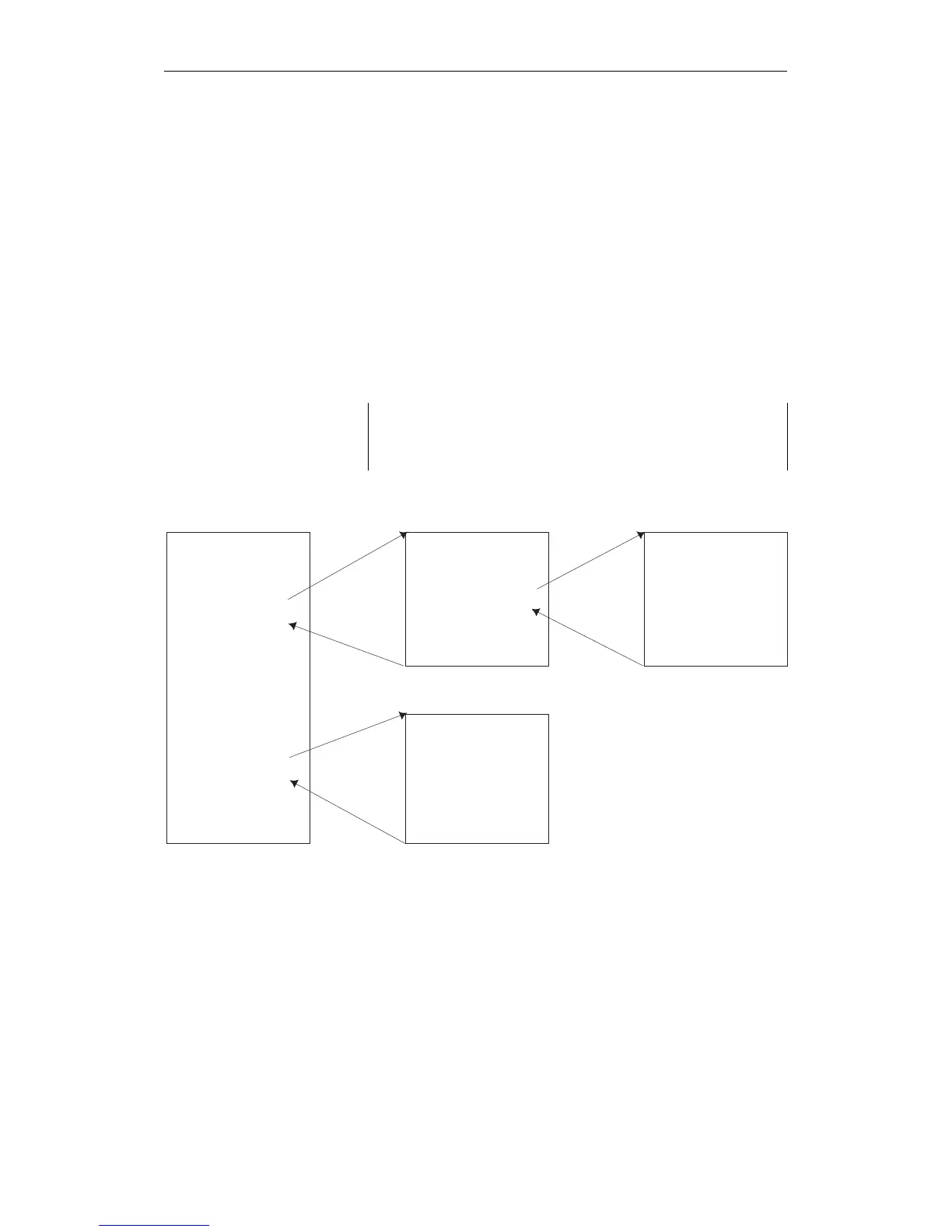
PB 1 PB 5 PB 10
PB 6
BE
BE
BE
BE
AA
O
I1.0 I2.0
I3.0
JU PB 5
OI5.3
AI1.5
JC PB 6
AI3.2
JC PB 10
OF1.5
Fig. 2-3 Block calls that enable processing of a program block
Program, Organization and Sequence Blocks
CPU 948 Programming Guide
C79000-G8576-C848-04
2 - 17
 Loading...
Loading...











